In vivo hypoglycemic activity and acute oral toxicity of ethanolic and aqueous leaves extract of Momordicacharantia Linn(Cucurbitaceae) from Benin
Full text
Figure
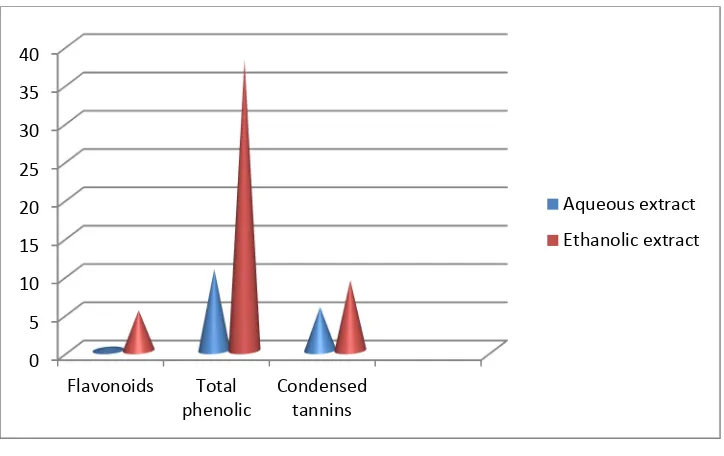

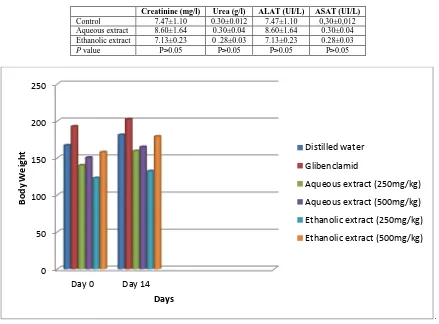

Related documents
In 1941, Philip Levine and co- workers#{176} astutely surmised that the disease resulted from immunization of the mother against a blood group factor of her infant and the
Methods: As the generalizability of results from RCT ’ s is questionable we designed a longitudinal, prospective non-interventional study (DACCORD) of two years duration plus two
These included intended purposes of the mission statement, standards for faculty staff, requirements for clinical training by students, program budgetary autonomy and transparency,
(2016) based upon an analysis of China’s Pulp & Paper Industry (CPPI), provides estimates of each of the following: carbon emissions from energy consumption,
The pattern of clustering of the A β deposits was also similar in control and AD cases, i.e., the deposits were aggregated into clusters that were regularly distributed
It shows that over - representation is carefully managed by the NZ state in four ways: (i) a perpetual representation of Māori as the offenders; (ii) the selective endorsement
In the present wor k we have firstly determinate the yield of the essential oils of 15 Eucalyptus species implanted in the Sahel of Tunisia “ Sidi Ismail Arboretum”, secondly, we
the fixed sample value). One sees that accruing additional patients while the initial patients are followed results in a greater expected sample size, but shorter expected and
