Modeling the internalisation of external costs of transport
Full text
Figure
Related documents
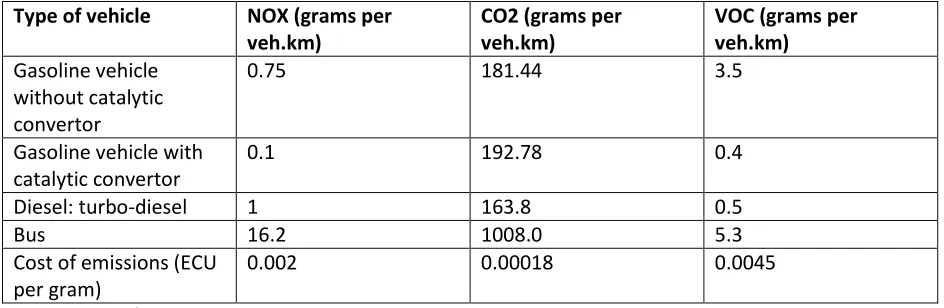
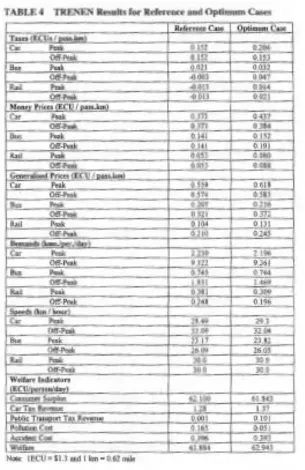
The objective of this paper is to develop a methodology to evaluate the social costs including internal and external costs of traffic roads, where the internal costs contains
In unitary terms, the total unit cost of freight transport - calculated as the sum of external costs generated by road and rail and divided by total tonnes transported - in South
The external costs of rail-only transport are always lower than the external costs of road transport (on an identical distance). When considering a PPH distance of 50 km, the
With this in mind, the 5th Florence Intermodal Forum on the Internalisation of the External Costs of Transport brought together representatives from all transport modes, as well
In the road transport sector external accident costs are the most important category, followed by air pollution, noise, and global warming. (Eds.): Environmental External Costs
Another way to illustrate the order of magnitude of the externalities in road transport is to recalculate them in terms of costs per litre of fuel. It should be stressed that this
However, Figure 11 confirms that not only marginal but also average external costs from total emissions generated for the production of fossil energy vectors
The research findings showed that there is no significant difference in the share of external costs of con- tainer transport and transport of other types of cargo in