'A Better Way to Measure Choices' Discrete Choice Experiment and Conjoint Analysis Studies in Nephrology: A Literature Review
Full text
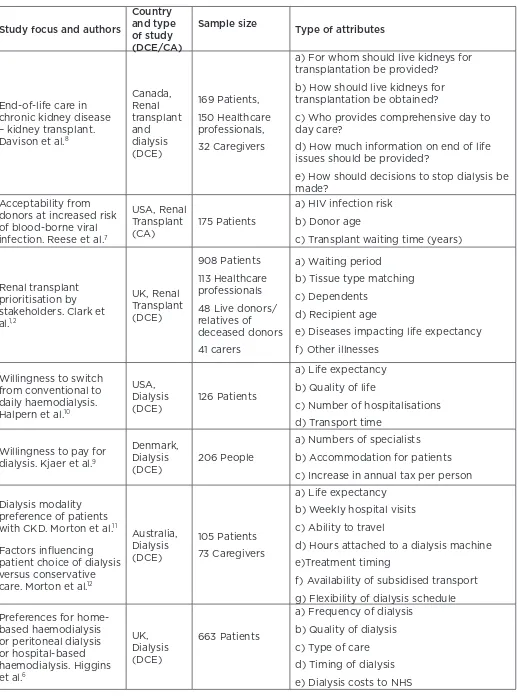
Figure


Related documents
"Therefore, from this point, because the attitude of the representatives of the Party of Labor of Albania, was opposing the views of the delegation of the Communist Party of
Current Practice Regarding the Enteral Feeding of High-Risk Newborns With Umbilical Catheters In Situ..
This study was conducted to evaluate the pharmacoki- netics (PKs), safety, and tolerability of 120 mg fimasartan and 20 mg rosuvastatin when coadministered or administered alone as
These findings were felt to be consistent with a proximal, axonal left ulnar neuropathy rather than a lower trunk plexopathy since the medial antebrachial cutaneous sensory,
Using this model, we find that credit rationing can amplify the effects of small idiosyncratic shocks to a firm, potentially even causing the firm to exit the market.. If a firm
As discussed by Wu & Murray (2003) for HD 80606b, a hypothetical additional body HAT-P-7c in the HAT-P-7 system could destroy the Kozai migration process (Innanen et al. 1997),
Our patients’ CSF abnormalities included elevated opening pressures, a n average peak protein level of 103 mg percent, and a n average CSF pleocytosis of 121 leukocytes
We hypothesized that at 3 months, post-intervention families in the FACE intervention study would be signifi- cantly more likely to: 1) complete an advance