A Fast Explicit FETD Method Based on Compressed Sensing
Full text
Figure
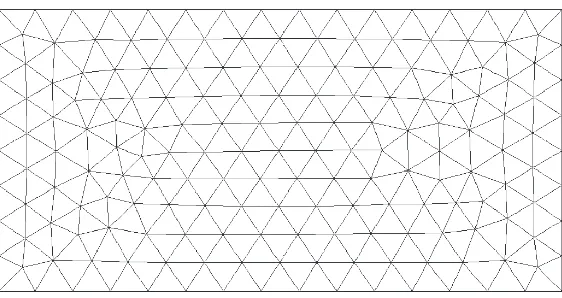

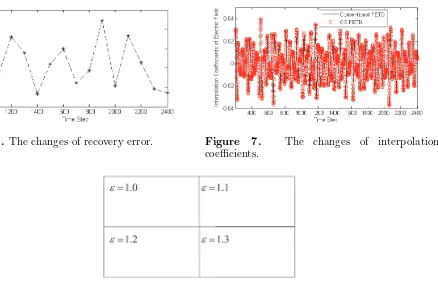
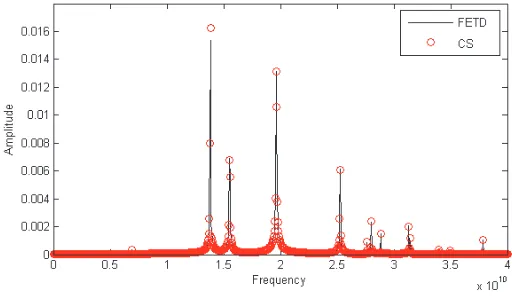
Related documents
The Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) method is an application of the finite difference method, commonly used in solving differential equations, to solve
Li, “A penalty finite element method based on the Euler implicit/explicit scheme for the time-dependent Navier-Stokes equations,” Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics,
The method is fully explicit similarly to classical so- called DGTD (Discontinuous Galerkin Time-Domain) methods that have been extensively studied during the last 15 years for
INDEX TERMS Backward Euler method, error estimates, Maxwell’s equations, time domain finite element methods, simulation, symplectic method,
Wang and Han [37] used the finite element space discretization for non-Fourier heat conduction and solved the obtained differential equations in time with
In the last few decades, the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method has been widely used to solve the Maxwell’s Equations in the time domain [1, 2], where the
A mesh connects the nodes discretising the domain where the governing equations are solved using a stabilised version of the Finite Element Method (FEM). This can be done because
On Stabilized Finite Element methods for Linear Systems of Convection- Diffusion-Reaction Equations, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 199: 61-82. Comparison