HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage
1.3.0 Data Migration Guide
Abstract
This guide provides information about using HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage software to migrate data from an EMC Storage system to an HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
HP Part Number: QL226-98141 Published: May 2015
© Copyright 2014, 2015 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Acknowledgements
Microsoft® and Windows® are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies. Oracle RAC is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Contents
1 Overview of HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage...6
Types of Data Migration...6
Understanding Which Data is Migrated...6
EMC Storage to HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage Migration Process...7
2 Migration Process Checklists...8
Online Migration...8
Prerequisite Component Installation...8
Premigration...8
Migration...8
Post-Migration...9
Minimally Disruptive Migration...9
Prerequisite Component Installation...9
Premigration...10
Migration...11
Post-Migration...11
Offline Migration...12
Prerequisite Component Installation...12
Premigration...12
Migration...13
Post-Migration...13
3 Installation and Setup for Data Migration...14
Configuration Rules for HP 3PAR Online Import Support...14
Installing EMC SMI-S Provider...14
Configuring EMC SMI-S Provider...15
Installing the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility...16
Migrations Supported by HP 3PAR Online Import Utility...24
Migrations Supported for EMC VNX, CLARiiON CX4, and VMAX...24
Migrations Supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility for EMC VMAX Only...27
4 Preparing for Data Migration...29
Data Migration Considerations...29
General Considerations...29
System Requirements...30
Planning for Migration...30
Network and Fabric Zoning Requirements...31
Reconfiguring the Host Multipath Solution...32
Working with Consistency Groups...32
5 Premigration Steps...34
Zoning the Source EMC Storage to the Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System...34
Identifying the Source and Destination Storage Systems...35
Prerequisites...35
Required Information...36
Adding the Source Storage System...36
Adding the Destination Storage System...36
Preparing the Host for Data Migration...37
Creating the Data Migration Task...39
Required Information...40
Issuing the createmigration Command...40
6 Performing Data Migration for Red Hat Linux and Oracle RAC...42
Online Data Migration with Removal of EMC PowerPath...42 Contents 3
Online Data Migration with Native device-mapper Multipath...49
7 Performing Minimally Disruptive Migration Using a Windows Host...54
Creating the Data Migration Task...54
Updating Host Multipath Software and Unzoning from the Source EMC Storage System...54
Starting the Data Migration from Source EMC Storage System to Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System...57
Bringing the Windows Host Back Online...58
8 Performing Minimally Disruptive Migration Using a Linux Host...60
Creating the Data Migration Task...60
Updating Host Multipath Software and Unzoning from Source EMC Storage System...60
Starting the Data Migration from Source EMC Storage System to Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System...62
Bringing the Linux Host Back Online...63
9 Performing Minimally Disruptive Migration Using a Hyper-V Host...65
Creating the Data Migration Task...65
Updating Host Multipath Software and Unzoning from the Source EMC Storage System...66
Starting the Data Migration from Source EMC Storage System to Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System...67
Bringing the Hyper-V Host Back Online...69
10 Performing Offline Data Migration...70
Creating the Data Migration Task...70
Zoning the Host to the Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System...70
Shutting Down the Host...70
Removing the Host from the Storage Group...71
Starting the Data Migration from Source EMC Storage System to Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System...71
Performing Post-Migration Tasks Specifically for Offline Migration...72
11 Performing Common Migration and Post-migration Tasks...73
Viewing Migration Status...73
Viewing all Migrations...73
Viewing Migrations for a Selected Source Storage System...73
Viewing a Selected Migration...73
Viewing Selected Migration Progress by Volume...73
Aborting a Migration...73
Performing Subsequent Migrations...73
Removing a Storage System from EMC SMI-S Provider...73
12 Troubleshooting...75
HP 3PAR Online Import Utility Error Messages...75
Troubleshooting Resources...76
Understanding the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility Data Migration Process...76
HP 3PAR Online Import Utility Server Logs and Output...77
Increase the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility Server Logging Level...78
EMC SMI-S Provider Server Logs and Output...79
Increasing the EMC SMI-S Provider Server Logging Level...79
Troubleshooting Communication Between the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility Server and EMC SMI-S Provider...79
TestSmiProvider Login and Command Examples with Output...80
Troubleshooting Issues...84
Cannot Add a Source EMC Storage system...84
Cannot Create a Migration...84
Cannot Log into the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility...85
Migration Includes Unexpected LUNs and Hosts...85 4 Contents
Masking View Required for Offline Migration of LUN with No Host...85
HP 3PAR Online Import Utility Does Not Distinguish between Source Arrays When Managing the Same Host...85
The HP 3PAR Online Import Utility Does Not Open in Windows 7...85
Trailing Spaces in IP Address Return Login Error...86
The adddestination Command Returns Error OIUERRDST0004...86
The createmigration Command Fails for Migrated LUNs in a Storage Group with No Host...86
The createmigration Command Fails for LUN Name or Host Name Containing Special Characters...87
The createmigration Command Returns Error OIUERRAPP0000 or OIURSLAPP0000...87
The createmigration Command Returns Error OIUERRDB1006...87
The createmigration Returns Error OIUERRPREP1014...87
The createmigration Command Returns Error OIUERRCS1002...88
The createmigration Command with -srcvolmap Returns Error OIUERRAPP0000...88
The showmigration Command Returns Error OIUERRDST0008...89
The startmigration Command Fails with Host Name That Exceeds 31 Characters...89
The startmigration Command Returns Error OIUERRMS10006...89
13 Appendices...90
Appendix A: HP 3PAR Online Import Utility CLI Commands...90
adddestination...90
addsource...90
createmigration...92
help...95
installcertificate...95
removedestination...96
removemigration...97
removesource...97
showconnection...97
showdestination...98
showmigration...99
showmigrationdetails...100
showpersona...101
showsource...103
startmigration...103
Appendix B: Identifying and Deleting Source Array LUN Paths...105
Appendix C: Rolling Back to the Original Source Array...106
Appendix D: Clearing a Persistent SCSI Reservation with HP 3PAR OS 3.2.1 MU3 or Later...109
Appendix E: Clearing a Persistent SCSI Reservation from EMC Storage Arrays with HP 3PAR OS 3.2.1 MU2 or Earlier...110
Removing a Persistent SCSI Reservation from an EMC CX4 or VNX Device...110
Removing a Persistent SCSI Reservation from an EMC VMAX Device...111
14 Support and Other Resources...114
Contacting HP...114
HP 3PAR documentation...114
Typographic conventions...117
HP 3PAR branding information...117
15 Documentation feedback...118
Glossary...119
Index...120
1 Overview of HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage
HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage manages the migration of data from a source EMC Storage system to a destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. Using HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage, you can migrate EMC volumes and host configuration information to a destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system without changing host configurations or interrupting data access. The terms storage system and array are used interchangeably throughout this guide, and may refer to either the EMC Storage system or the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. The source in the migration is the EMC VMAX, VNX, or CX4 Storage system, and the destination is the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage coordinates the movement of data from the source to the destination while servicing I/O requests from the hosts. During the data migration, host I/O is serviced from the host EMC Storage system through the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. The host/volume presentation implemented on the EMC Storage is maintained on the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
For additional information about supported EMC Storage systems, see the HP 3PAR Online Import support matrix on HP SPOCK:
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock)
Types of Data Migration
HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage supports three types of data migration procedures. The appropriate type of data migration depends on the objects being migrated and the migration type. • Online—Migration type used when migrating a host or a volume presented to a host. During
online migration, all presentation relationships between hosts and volumes being migrated are maintained. Host I/O to the data is not disrupted during an online migration.
• Minimally disruptive migration (MDM)—Migration type used when migrating a host or a volume presented to a host. Host I/O is interrupted only during the time it takes to reconfigure the host.
• Offline—Migration type used when migrating one or more unpresented volumes. During offline migration, only the selected volumes are migrated. No hosts are migrated in this situation.
Understanding Which Data is Migrated
Data can be migrated by selecting a host or a volume on the source EMC Storage system. In addition to the host or volume explicitly selected for an online migration or for migration, other objects will be included in the migration using implicit selection. The migration process identifies the relationship between hosts and presented volumes and selects all additional objects to completely migrate the hosts. Consequently, the objects that will be migrated are the combination of the explicit and the implicit selection and may lead to the migration of a large amount of volumes.
Selecting a single host results in migration of the following: • The host as well as any volumes presented to it
• Any other hosts to which those volumes are presented • Any volumes presented to those other hosts
The maximum number of volumes that can be migrated with MDM or an online migration is 255. For an offline migration, the maximum number of volumes that can be migrated is 25. If you have more offline volumes to migrate, rerun the migration steps for the additional volumes.
IMPORTANT: The implicit selection of objects for migration occurs automatically and cannot be modified. If the number of objects selected for migration exceeds 255 for MDM and 25 for offline migration, the migration will be not be submitted and will return a failed status.
The migration process selects objects to migrate using the following rules:
• Hosts—When selecting a single host or group of hosts with volume presentations, all the volumes presented to the host(s) are migrated. In addition, any presentations the source volumes have to other hosts will include those hosts and all of their presented volumes in the migration. • Presented volumes—When selecting a volume or group of volumes with host presentations,
the selected volumes and the hosts to which they are presented are migrated. In addition, any presentations the source hosts have with other volumes will be included in the migration. • Unpresented volumes—Only the selected unpresented volumes are migrated. The offline
migration type is the only type available for unpresented volume migration.
NOTE: For more information about supported and unsupported configurations and about the implicit selection of objects for migration, see“Migrations Supported by HP 3PAR Online Import Utility” (page 24).
EMC Storage to HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage Migration Process
The process to migrate EMC Storage volumes to an HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system consists of three parts:
• Premigration—Work done to define the source and destination storage system for a migration definition. This work is not repeated when migrating a second host or additional volumes between the same source and the destination system after the first migration.
• Migration—Creating and executing the migration. The migration work can include the process of unzoning the host from the source storage system, zoning the host to the destination storage system, and removing the migration definition after the migration is complete. This work is repeated for every migration.
• Post-migration—Work done to clean up the configuration after migration is completed.
2 Migration Process Checklists
Follow the steps in this chapter to perform online migration, MDM, or offline migration.
Online Migration
Prerequisite Component Installation
Table 1 Prerequisite component installation—Online
See: Step
Number
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock) Check the HP SPOCK website to confirm proper
configuration. 1
See also“Configuration Rules for HP 3PAR Online Import Support” (page 14)
“Installing EMC SMI-S Provider” (page 14)
Install EMC SMI-S Provider. 2
“Installing the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility” (page 16)
Install the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility. 3
Premigration
Table 2 Premigration checklist—online
See: Step
Number
“Zoning the Source EMC Storage to the Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 34)
Zone the EMC Storage system and the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system as peers.
1
“Adding the Source Storage System” (page 36)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, add a source storage system with theaddsource command.
2
“Adding the Destination Storage System” (page 36)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, add a destination storage system with the
adddestinationcommand). 3
Validate connections by using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utilityshowconnection command.
Migration
If EMC PowerPath is installed, it must be uninstalled, and the native OS multipath software must be used to configure multipathing; see the third column in theTable 3 (page 8)for details about each step. If EMC PowerPath is not installed, see the column on the right for details.
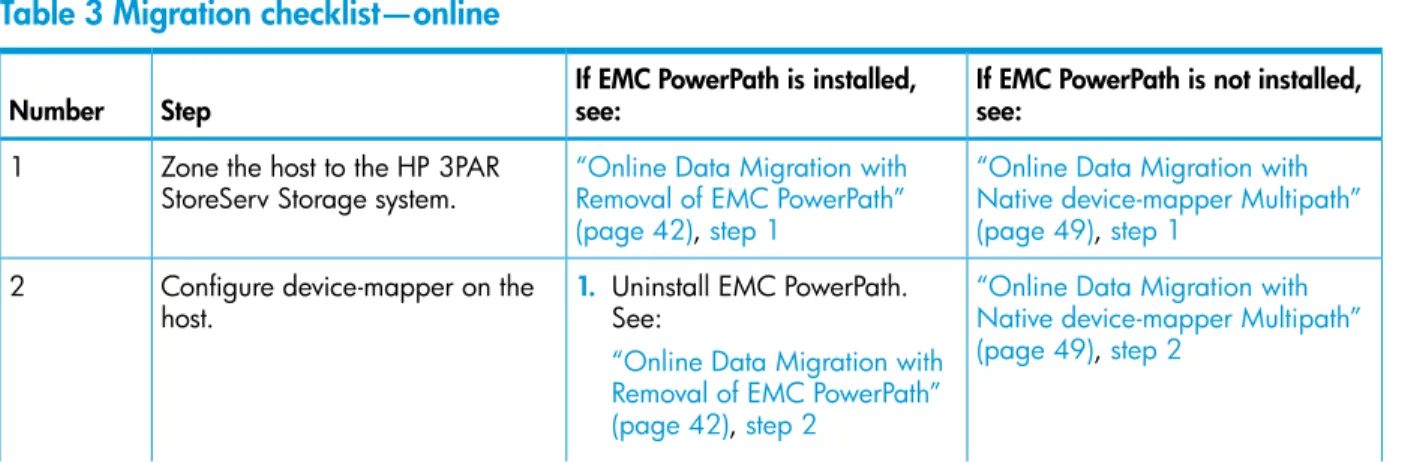
Table 3 Migration checklist—online
If EMC PowerPath is not installed, see:
If EMC PowerPath is installed, see:
Step Number
“Online Data Migration with Native device-mapper Multipath” (page 49),step 1
“Online Data Migration with Removal of EMC PowerPath” (page 42),step 1
Zone the host to the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. 1
“Online Data Migration with Native device-mapper Multipath” (page 49),step 2
Configure device-mapper on the host.
2 1. Uninstall EMC PowerPath.
See:
“Online Data Migration with Removal of EMC PowerPath” (page 42),step 2
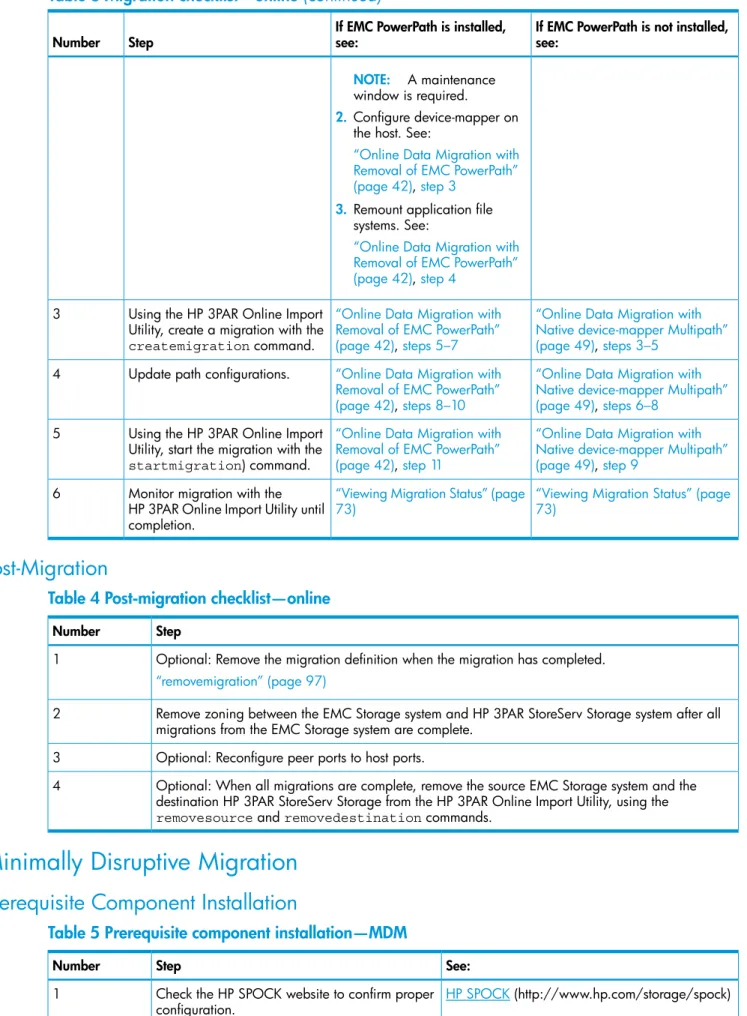
Table 3 Migration checklist—online(continued)
If EMC PowerPath is not installed, see:
If EMC PowerPath is installed, see:
Step Number
NOTE: A maintenance window is required.
2. Configure device-mapper on the host. See:
“Online Data Migration with Removal of EMC PowerPath” (page 42),step 3
3. Remount application file systems. See:
“Online Data Migration with Removal of EMC PowerPath” (page 42),step 4
“Online Data Migration with Native device-mapper Multipath” (page 49),steps 3–5
“Online Data Migration with Removal of EMC PowerPath” (page 42),steps 5–7
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, create a migration with the createmigrationcommand. 3
“Online Data Migration with Native device-mapper Multipath” (page 49),steps 6–8
“Online Data Migration with Removal of EMC PowerPath” (page 42),steps 8–10
Update path configurations. 4
“Online Data Migration with Native device-mapper Multipath” (page 49),step 9
“Online Data Migration with Removal of EMC PowerPath” (page 42),step 11
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, start the migration with the startmigration) command. 5
“Viewing Migration Status” (page 73)
“Viewing Migration Status” (page 73)
Monitor migration with the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility until completion.
6
Post-Migration
Table 4 Post-migration checklist—online Step
Number
Optional: Remove the migration definition when the migration has completed. 1
“removemigration” (page 97)
Remove zoning between the EMC Storage system and HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system after all migrations from the EMC Storage system are complete.
2
Optional: Reconfigure peer ports to host ports. 3
Optional: When all migrations are complete, remove the source EMC Storage system and the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage from the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, using the removesourceandremovedestinationcommands.
4
Minimally Disruptive Migration
Prerequisite Component Installation
Table 5 Prerequisite component installation—MDM
See: Step
Number
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock) Check the HP SPOCK website to confirm proper
configuration. 1
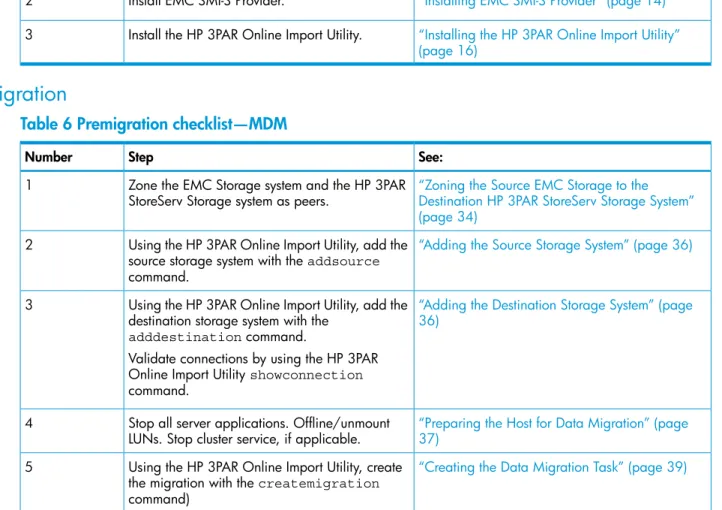
Table 5 Prerequisite component installation—MDM(continued)
See: Step
Number
See also“Configuration Rules for HP 3PAR Online Import Support” (page 14)
“Installing EMC SMI-S Provider” (page 14)
Install EMC SMI-S Provider. 2
“Installing the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility” (page 16)
Install the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility. 3
Premigration
Table 6 Premigration checklist—MDM
See: Step
Number
“Zoning the Source EMC Storage to the Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 34)
Zone the EMC Storage system and the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system as peers.
1
“Adding the Source Storage System” (page 36)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, add the source storage system with theaddsource command.
2
“Adding the Destination Storage System” (page 36)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, add the destination storage system with the
adddestinationcommand. 3
Validate connections by using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utilityshowconnection command.
“Preparing the Host for Data Migration” (page 37)
Stop all server applications. Offline/unmount LUNs. Stop cluster service, if applicable. 4
“Creating the Data Migration Task” (page 39)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, create the migration with thecreatemigration command)
5
Migration
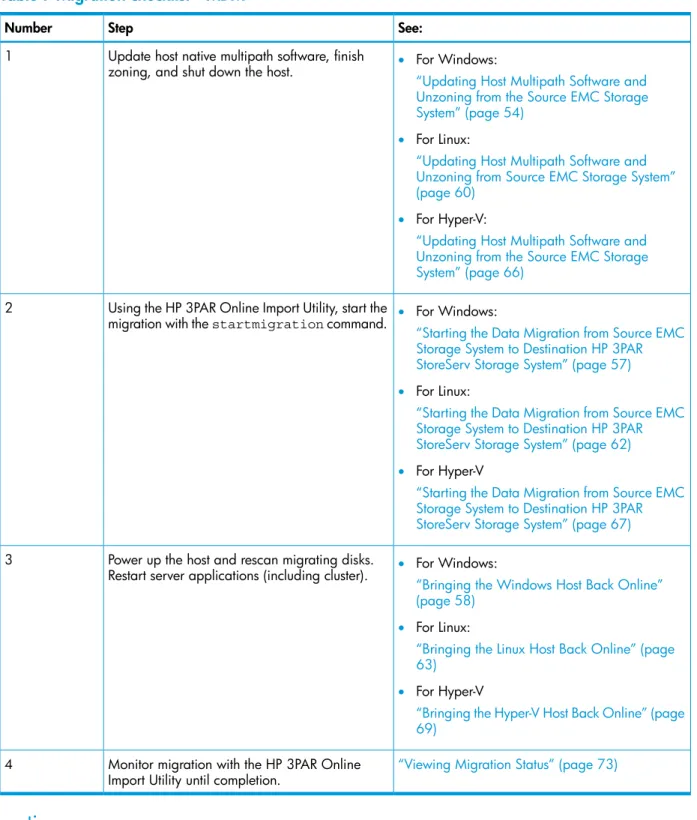
Table 7 Migration checklist—MDM
See: Step
Number
Update host native multipath software, finish zoning, and shut down the host.
1 • For Windows:
“Updating Host Multipath Software and Unzoning from the Source EMC Storage System” (page 54)
• For Linux:
“Updating Host Multipath Software and Unzoning from Source EMC Storage System” (page 60)
• For Hyper-V:
“Updating Host Multipath Software and Unzoning from the Source EMC Storage System” (page 66)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, start the migration with thestartmigrationcommand.
2 • For Windows:
“Starting the Data Migration from Source EMC Storage System to Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 57) • For Linux:
“Starting the Data Migration from Source EMC Storage System to Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 62) • For Hyper-V
“Starting the Data Migration from Source EMC Storage System to Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 67)
Power up the host and rescan migrating disks. Restart server applications (including cluster).
3 • For Windows:
“Bringing the Windows Host Back Online” (page 58)
• For Linux:
“Bringing the Linux Host Back Online” (page 63)
• For Hyper-V
“Bringing the Hyper-V Host Back Online” (page 69)
“Viewing Migration Status” (page 73)
Monitor migration with the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility until completion.
4
Post-Migration
Table 8 Post-migration checklist—MDM Step
Number
Optional: Remove the migration definition when the migration has completed. 1
See“removemigration” (page 97).
Remove zoning between the EMC Storage system and HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system after all migrations from the EMC Storage system are complete.
2
Table 8 Post-migration checklist—MDM(continued)
Step Number
Optional: Reconfigure peer ports to host ports. 3
Optional: When all migrations are complete, remove the source EMC Storage system and the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage from the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, using the removesourceandremovedestinationcommands.
4
Offline Migration
Prerequisite Component Installation
Table 9 Prerequisite component installation—offline
See: Step
Number
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock) Check the HP SPOCK website to confirm proper
configuration. 1
See also“Configuration Rules for HP 3PAR Online Import Support” (page 14)
“Installing EMC SMI-S Provider” (page 14)
Install EMC SMI-S Provider. 2
“Installing the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility” (page 16)
Install the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility. 3
Premigration
Table 10 Premigration checklist—offline
See: Step
Number
“Zoning the Source EMC Storage to the Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 34)
Zone the EMC Storage system and the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system as peers.
1
“Preparing the Host for Data Migration” (page 37)
Stop all server applications; offline/unmount LUNs.
2
“Identifying the Source and Destination Storage Systems” (page 35)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, add the source storage system with theaddsource command).
3
“Identifying the Source and Destination Storage Systems” (page 35)
Add destination storage system (HP 3PAR Online Import Utility:adddestinationcommand). 4
Validate connections by using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utilityshowconnection command.
“Creating the Data Migration Task” (page 70)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, create the migration with thecreatemigration command).
5
“Zoning the Host to the Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 70)
Zone the host and the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system and shut down the host.
6
Migration
Table 11 Migration checklist—offline
See: Step
Number
“Starting the Data Migration from Source EMC Storage System to Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 71)
Using the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, start the migration with thestartmigrationcommand. 1
“Viewing Migration Status” (page 73)
Monitor migration with the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility until completion.
2
Post-Migration
Table 12 Post-migration checklist—offline
See: Step
Number
“Performing Post-Migration Tasks Specifically for Offline Migration” (page 72),step 1
Unzone the source EMC Storage system from the host.
1
“Performing Post-Migration Tasks Specifically for Offline Migration” (page 72),step 2
Restart the host. 2
“Performing Post-Migration Tasks Specifically for Offline Migration” (page 72),step 3
Remove the EMC PowerPath multipath software, if present, and configure native multipath software.
3
“Performing Post-Migration Tasks Specifically for Offline Migration” (page 72),step 4
Export the imported LUNs from the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system to the host. 4
“removemigration” (page 97)
Optional: Remove the migration definition when the migration has completed.
5
“removesource” (page 97)
Optional: When all migrations are complete, remove the source EMC Storage system and the 6
“removedestination” (page 96)
destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage from the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, using the removesourceandremovedestination commands.
3 Installation and Setup for Data Migration
This chapter describes requirements for data migration using the HP Online Import Utility.
Configuration Rules for HP 3PAR Online Import Support
For detailed information about ensuring that the source EMC Storage system and the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system are configured properly for data migration, see the HP SPOCK website:
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock)
The HP SPOCK website lists the supported system environment, including:
• The supported source EMC Storage systems and their associated firmware levels.
• The supported destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage systems and their associated HP 3PAR OS levels.
• The supported host operating systems.
• The supported HBAs and the associated BIOS/firmware/driver versions to allow HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage and EMC Storage coexistence.
• The supported configuration environments for installing HP 3PAR Online Import.
Installing EMC SMI-S Provider
The HP 3PAR Online Import Utility manages the source EMC Storage system through the EMC SMI-S Provider software. The EMC SMI-S Provider is a component of EMC Solutions Enabler and requires underlying EMC Solutions Enabler code to function. However, installation of the base EMC Solutions Enabler software does not include the EMC SMI-S Provider component. Installation of the EMC SMI-S Provider includes only the necessary underlying EMC Solutions Enabler code, not a full installation of EMC Solutions Enabler.
IMPORTANT: It is technically possible to install the EMC SMI-S Provider on a machine where EMC Solutions Enabler is already installed, but be aware that the EMC SMI-S Provider installation uninstalls any existing EMC Solutions Enabler software and reinstalls only the subset of EMC Solutions Enabler that comes with the EMC SMI-S Provider.
The connection between an EMC VMAX and the EMC SMI-S Provider runs over Fibre Channel. The connection between an EMC VNX or CLARiiON CX4 EMC and the EMC SMI-S Provider runs over Ethernet.
For VMAX, a VMAX gatekeeper device must be presented to the SMI-S server.
The EMC Solutions Enabler and the EMC SMI-S Provider are provided by EMC as separately installable products, available on the following website:
https://support.emc.com/
NOTE: This link will take you outside the Hewlett-Packard website. HP does not control and is not responsible for information outside hp.com.
The HP 3PAR Online Import Utility supports installation of the EMC SMI-S Provider only on Windows. See product release notes for full installation details:
SMI Provider Release Notes(https://developer-content.emc.com/developer/devcenters/storage/ snia/smi-s/downloads/SMI_Provider_RN.pdf)
NOTE: This link will take you outside the Hewlett-Packard website. HP does not control and is not responsible for information outside hp.com.
To install the EMC SMI-S Provider software, follow these steps:
1. Download EMC SMI-S Provider 4.6.2.9 Installer from EMC. An EMC login account is required. To download the program, go to the following website:
EMC(https://support.emc.com/downloads/5587_SMI-S-Provider)
NOTE: This link will take you outside the Hewlett-Packard website. HP does not control and is not responsible for information outside hp.com.
2. Launch these76226installer. TheEMC Solutions Enablerwelcome page appears, prompting you to install Solutions Enabler with SMI-S version V4.6.2.9.
3. ClickNextto begin the installation process.
4. TheDestination Folderdialog box opens and prompts you to select an install directory for Solutions Enabler and EMC SMI-S Provider. It is recommended that you choose the default directory.
5. ClickNextto continue. TheProvider List dialog box opens.
6. SelectArray Provider.
7. ClickNextto continue. TheReady to Install Programdialog box opens.
8. ClickInstallto begin installing files to your selected folder. This may take several minutes.
9. When the Installation WizardCompleteddialog box opens, clickFinishto complete the setup.
Configuring EMC SMI-S Provider
The EMC SMI-S Provider must be configured to allow remote software to connect to the EMC Storage system.
1. Open a Windows command prompt on the server where the EMC SMI-S Provider software was installed.
2. Change the directory to the location of the EMC SMI-S Provider installation. The default is:
C:\Program Files\EMC\ECIM\ECOM\bin
3. Start thetestsmiprovider program.
4. Accept all default settings when prompted.
5. Attach the storage system to the EMC SMI-S Provider.
NOTE: If both an EMC VMAX and an EMC CLARiiON or VNX storage system are being migrated, both of the following steps must be performed.
a. For VMAX storage systems, any VMAX storage arrays connected to the EMC SMI-S Provider server will be automatically detected, provided that:
• SMI-S and VMAX have a Fibre Channel connection and are zoned. • A gatekeeper LUN is presented to the SMI-S server.
If the VMAX does not show up, run thediscocommand to rescan for arrays. Proceed tostep 6, unless you want to add an EMC CLARiiON or VNX storage system.
b. To attach an EMC CLARiiON or VNX storage system to SMI-S Provider, use theaddsys
command:
(localhost:5988) ? addsys
Add System {y|n} [n]: y
ArrayType (1=Clar, 2=Symm) [1]:
One or more IP address or Hostname or Array ID
Elements for Addresses
IP address or hostname or array id 0 (blank to quit): <IP address of SPA>
IP address or hostname or array id 1 (blank to quit): <IP address of SPB>
IP address or hostname or array id 2 (blank to quit):
Address types corresponding to addresses specified above.
(1=URL, 2=IP/Nodename, 3=array ID)
Address Type (0) [default=2]:
Address Type (1) [default=2]:
User: <Global Administrator>
global administrator user for CX4 array
Password [null]: <password>
++++EMCAddSystem++++
OUTPUT : 0
Output codes are shown in the following table: Success
0
Not Supported 1
Unknown 2
Timeout 3
Failed 4
Invalid Parameter 5
Job Queued 4096
Size Not Supported 4097
6. Use the dvcommand to verify that the storage system is discovered.
NOTE:
If your EMC SMI-S Provider has client IP filtering enabled, you need to add the IP address of the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility server to the trusted IP address list.
To add an HP 3PAR Online Import Utility server to the EMC SMI-S Provider trusted IP address list:
1. Log into SMI-S ECOM administration page using one of the SMI-S user and password configured:
• https://<SMI-S IP address>:5989/ECOMConfig • http://<SMI-S IP address>:5988/ECOMConfig
2. Select theClient IP Filteringlink on the ECOM Administration page.
3. Add the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility server IP address in theTrusted client’s IPfield on the Client IP Filtering page and clickExecuteto complete.
Installing the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility
The HP 3PAR Online Import Utility can be obtained from the HP Software Depot using the following link:
HP Software Depot
(https://h20392.www2.hp.com/portal/swdepot/displayProductsList.do?category=3PAR)
NOTE: If you are upgrading from an earlier version of the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility to a later version, you must uninstall the earlier version before upgrading to the latest version.
See the HP SPOCK website for supported target environments for the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility server:
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock)
The HP 3PAR Online Import Utility software consists of two installable applications: the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility client and the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility server.
If one component has already been installed on a given system, and you want to add the second component on the same system, first run the installer to remove the component already installed, and then rerun the installer to install both components at once.
These steps describe the process for installing the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility. The default directories and options are shown below:
• Default installation directory:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Hewlett-Packard\hp3paroiu
• Default log file name :
C:\Program Files (x86)\Hewlett-Packard\hp3paroiu\OIUTools\ tomcat\32-bit\apache-tomcat-7.0.37\logs\hpoiu.log
• Default port numbers: Service port: 2370
◦
◦
Shutdown port: 23711. Double-click the installer package image icon to begin the installation process.
The HP 3PAR Online Import Utility splash screen appears with the InstallShield Wizard.
2. When the Welcome screen appears, click Next.
3. Accept the end user license agreement and clickNext.
TheCustom Setupdialog box appears.
4. To choose the default setup (installation of the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility server and client on this machine), clickNext.
Otherwise, select the component that you want to omit from this installation. Use this option if you want to install the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility server and client on separate machines,
and then clickNext to continue.
5. ClickYesif you have a CA signed certificate, or clickNoto generate a certificate from the installer.
NOTE: After the certificate installation dialog box is passed, the installer checks whether the default ports are already in use on this machine. If they are, another dialog box will be displayed, prompting you to specify available ports to use for this installation. This is not a common occurrence.
If there was a conflict with the default port numbers and different port numbers were supplied to the installation process, the following steps must be taken after installation is complete to properly use the new ports:
a. EditOIUCli.bat, located at:
<Install location>\Hewlett-Packard\hp3paroiu\CLI
b. If port 2396 was chosen as the alternative to 2370, make the change in the OIUCli.bat file, as shown in the following example:
Example 1 Editing the service port in theOIUCli.batfile
java -jar ..\CLI\oiucli-1.0.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar %* -port
2396
6. ClickInstall.
7. Monitor the progress of the installation. When complete, clickNext.
8. Tomcat services will begin installation. When complete, clickNext.
IMPORTANT: The installer does not support doing a close, cancel, or kill action during the Tomcat Installation. If the installation of Tomcat is interrupted, the software installation is not fully cancelled and is left in an indeterminate state. Do not click theCancelbutton or close the window by clicking the X in the upper-right corner.
9. Select theShow the Windows Installer logcheck box, and then clickFinish.
10. After you click theFinish button, the log appears in a separate window. Save the log in a location of your choice.
11. The HP 3PAR Online Import Utility shortcut is installed on your desktop.
12. After successful installation, verify that the following groups have been created:HP Storage Migration Adminsgroup has been created.
• HP Storage Migration Admins
• HP Storage Migration Users
13. Add theAdministratoraccount or another account with administrator privileges as a member ofHP Storage Migration Adminsgroup. This is the USERNAME that will be used in starting the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
14. To start the utility, double-click theHP 3PAR Online Import Utilitydesktop icon, and provide local credentials as stated in the note below.
NOTE: If the client and server components have been installed on the same machine, you can use the keyword LOCALHOST to connect to the local server. Otherwise, use the IP address or the DNS hostname of the machine where the server is located.
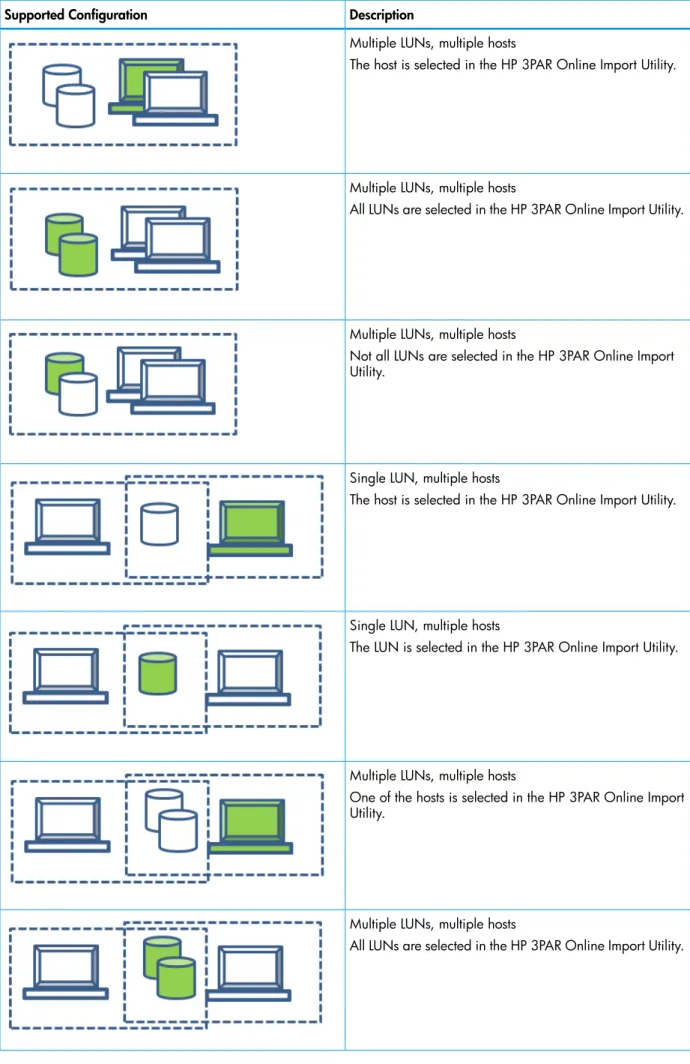
Migrations Supported by HP 3PAR Online Import Utility
For migration types supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility for EMC VNX, CLARiiON CX4, and VMAX, see Table 14 (page 24)
For migration types supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility for EMC VMAX only, see
Table 15 (page 28)
SeeTable 13 (page 24)for a legend for the migration-type tables.
Table 13 Legend for the migration support tables
LUN
Host
Storage group
Item selected by user input on the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility
Migrations Supported for EMC VNX, CLARiiON CX4, and VMAX
Migrations supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility for are shown in Table 14 (page 24).
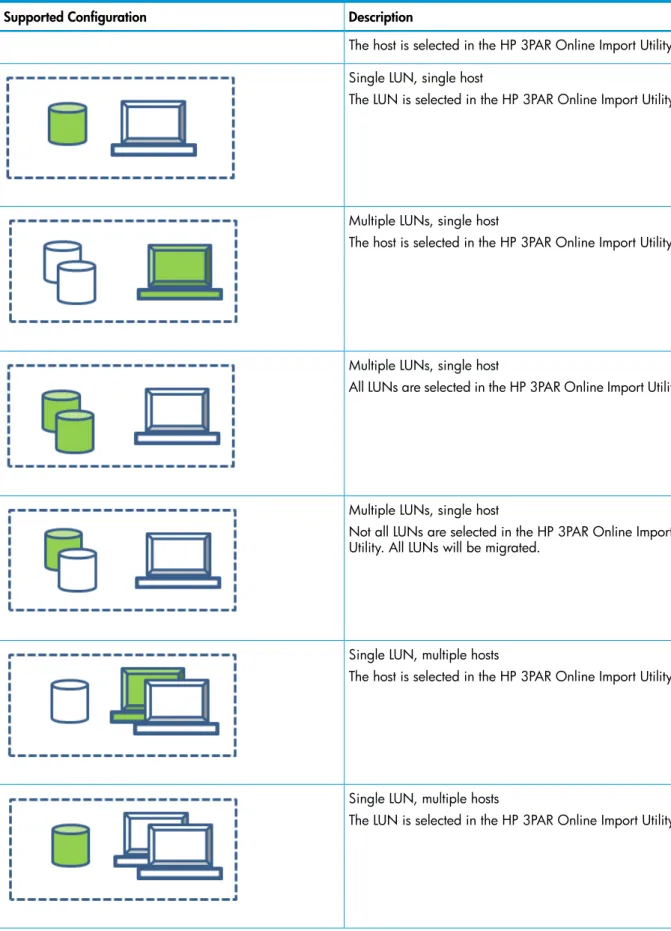
Table 14 Migration supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility Description
Supported Configuration
Single LUN, single host
Table 14 Migration supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility(continued)
Description Supported Configuration
The host is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Single LUN, single host
The LUN is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, single host
The host is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, single host
All LUNs are selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, single host
Not all LUNs are selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility. All LUNs will be migrated.
Single LUN, multiple hosts
The host is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Single LUN, multiple hosts
The LUN is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Table 14 Migration supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility(continued)
Description Supported Configuration
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
The host is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
All LUNs are selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
Not all LUNs are selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Single LUN, multiple hosts
The host is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Single LUN, multiple hosts
The LUN is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
One of the hosts is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
All LUNs are selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
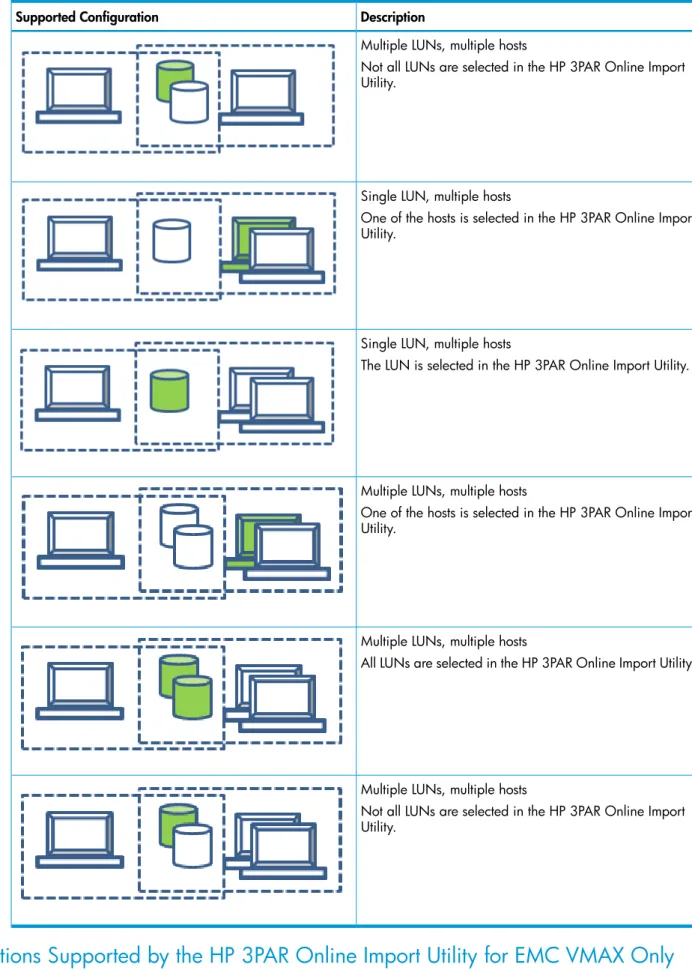
Table 14 Migration supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility(continued)
Description Supported Configuration
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
Not all LUNs are selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Single LUN, multiple hosts
One of the hosts is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Single LUN, multiple hosts
The LUN is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
One of the hosts is selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
All LUNs are selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Multiple LUNs, multiple hosts
Not all LUNs are selected in the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Migrations Supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility for EMC VMAX Only
IMPORTANT: The migrations shown here are supported only for VMAX.NOTE: These configurations are not supported for EMC VNX or CLARiiON CX4:
• Thecreatemigrationcommand checks for these configurations and blocks migrations of
unsupported configuration.
• In most cases, unsupported configurations are those in which multiple LUNs that span multiple storage groups are to be added to the migration (either explicitly or implicitly).
• It is an error when the added storage groups do not contain exactly the same LUNs.
Table 15 Migration supported by the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility for VMAX only Description
Configurations Supported by VMAX Only
A LUN in multiple storage groups is selected, and the groups are not identical.
A LUN in a single storage group is selected, but it is grouped with a shared LUN, and the shared LUN’s storage groups are not identical.
A host is selected, but it is grouped with a shared LUN, and the shared LUN’s storage groups are not identical.
LUNs are selected spanning multiple groups, and the storage groups are not identical.
LUNs are selected spanning multiple storage groups, and the storage groups are not identical.
4 Preparing for Data Migration
Use the information in this chapter to ensure all necessary tasks are performed and considerations are understood before beginning a migration.
Data Migration Considerations
Before migrating data using 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage, be aware of the following general considerations, system requirements, and other tasks associated with planning, host configuration, and network and zoning requirements.
General Considerations
• LUNs and hosts can be implicitly added to the migration, even if they are not specified by the input.
• Only volumes presented to Fibre Channel hosts can be migrated. Volumes presented to iSCSI or FCoE hosts cannot be migrated.
• All LUNs present in a source group are migrated, even if only one was selected. All hosts present in a host group are migrated. When a host is selected for migration, all LUNs presented to that host are migrated to the same CPG.
• When a cluster is being migrated, all the hosts in the cluster must be migrated at once. • HP 3PAR host persona/host OS: EMC Storage arrays do not implement specific OS settings
when registering host initiators on the EMC Storage array. During migration, online import cannot determine the host OS when migrating the hosts to the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage. All hosts that are being created on the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage during EMC migration are set by default to host persona 2. Change the HP 3PAR host persona/host OS to the appropriate setting before enabling access to the HP 3PAR array.
• LUNs identified for migration should not be part of any current replication or backup jobs. • The LUN limit for offline migrations is 25. The maximum number of volumes that can be
migrated with MDM or online migration is 255.
• Acreatemigrationcommand cannot simultaneously contain a host and a LUN for migration.
• Only onecreatemigration is allowed at a time because 3PAR Peer Ports can be in only one EMC Storage storage group at a time.
• When a volume on the source EMC Storage system is migrated, a SCSI-3 reservation is issued to prevent any unwanted management changes to the volume during the migration. With HP 3PAR OS 3.2.1 MU2 and earlier, the SCSI-3 reservation remains on the volume after the migration. With HP 3PAR OS 3.2.1 MU3 and later, the SCSI reservation is removed upon successful migration. For information about removing a SCSI reservation following an unsuccessful migration, see:
◦
“Appendix D: Clearing a Persistent SCSI Reservation with HP 3PAR OS 3.2.1 MU3 or Later” (page 109)◦
“Appendix E: Clearing a Persistent SCSI Reservation from EMC Storage Arrays with HP 3PAR OS 3.2.1 MU2 or Earlier” (page 110)• Only one EMC Storage system at a time can be attached as a source to the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• EMC volumes cannot be migrated if they are less than 256 MB, the minimum volume size on the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage systems. The HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage is 256 MB
boundary-based. A volume, even one that is not a multiple of 256 MB, can still be migrated, provided that the volume is not smaller than 256 MB.
• EMC volumes cannot be migrated if they are larger than 16 TB, the maximum volume size on the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• Snapshots become standalone objects on the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. For more information, see the appropriate HP 3PAR implementation guide. Implementation guides are available at the following website:
HP Storage Information Library(http://www.hp.com/go/storage/docs)
System Requirements
NOTE: For detailed information about ensuring the source EMC Storage system and the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system are configured properly for data migration, see the HP SPOCK website:
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock)
Before migrating data from an EMC Storage system to an HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system using HP 3PAR Online Import for EMC Storage, the system environment must meet the following
requirements:
• Source EMC Storage system must be running a supported firmware level. See the HP SPOCK website for supported firmware versions:
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock)
• The destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system must have a valid HP 3PAR Online Import or HP 3PAR Peer Motion license installed.
• The destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system must be at a supported HP 3PAR OS level. See HP SPOCK:
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock)
Planning for Migration
Advanced planning ensures that you achieve the desired results when migrating data. • It is a recommended best practice to make a backup of your host/data before starting a
migration.
• A maintenance window is required for the removal of EMC PowerPath, if present.
• Identify which volumes and/or hosts will be migrated. If you do not want to migrate all the volumes presented to a host, you must unpresent the volumes that you do not want migrated. Otherwise, all the volumes will be implicitly included in the migration.
• When you migrate TPVVs from the EMC Storage system, only those volumes can be migrated where the TPVV pool size is greater than or equal to the total size of the volumes selected for migration.
NOTE: Volume size is the actual size, not merely the space used by the TPVV.
• Determine whether you will be using thin, full, or dedupe provisioning on the destination storage system. This decision impacts the amount of capacity needed on the destination storage system.
NOTE: For HP 3PAR Online Import, TDVVs are supported on a destination with HP 3PAR OS 3.2.1 MU2 or later.
• Because there is some impact on performance, you may want to schedule migrations during off-peak hours, if possible. Hosts with a lighter load/less data should be migrated first. • If you are using any LUNs larger than 2 TB, then before performing a migration, set the system
option mode on the EMC Storage array to enable the 16 byte commands for LUNs larger than 2 TB. Setting this system option mode does not change the behavior on the host side, so it can be set at any time before migration. See EMC documentation for more information. • When selecting objects for migration, be aware of any overlap or sharing of volumes between
hosts. In this situation, selecting a host or a volume in any set results in every volume and every host in all sets being implicitly selected for migration due to the overlap. For additional information, see“Migrations Supported by HP 3PAR Online Import Utility” (page 24). • For VMAX only: Gatekeeper LUNs are widely used for communication between host and
VMAX array or for array operations such as backups. Gatekeeper LUNs are typically smaller than 256 MB, and are therefore too small to be migrated. If gatekeeper LUNs have been presented to hosts explicitly in the masking view that corresponds to a migration, they cause the migration to fail.
Gatekeeper LUNs (or any small LUNs) must be removed from masking views being migrated. Identify which functions on the host are relying on the gatekeeper and ensure that they are properly shut down. In the case of operations such as automated backup, plan to perform the operation after the migration.
Network and Fabric Zoning Requirements
Data migration requires zoning operations to create paths between the source and destination storage systems and any hosts involved in the migration. The data paths used are shown in
Figure 1 (page 31). A blue line indicates a peer link between the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage and the EMC Storage system. A red line indicates a data link.
Figure 1 Data migration zoning
• Two unique paths must be zoned between the source and destination storage systems. To create two paths, two controller ports on the source EMC Storage system must be connected
to two peer ports on the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. See “Zoning the Source EMC Storage to the Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System” (page 34). • Paths between the host and the source EMC Storage system are unzoned before the data
migration starts. The timing for this depends on the operating system of the host and the migration type.
• During data migration, paths must be zoned between the host and destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. The time at which these paths are created is determined by the operating system of the host and the migration type.
Reconfiguring the Host Multipath Solution
Data migration may involve reconfiguring the host multipath solution from an EMC multipath solution to one supported by an HP 3PAR Storage system. For the supported multipath solutions for HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage systems, see HP SPOCK:
HP SPOCK(http://www.hp.com/storage/spock)
After the migration preparation phase is complete, the host must be reconfigured to use the multipath software for the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
For MDM, the host must be shut down for the zoning changes and multipath reconfiguration. While the host is down, data transfer is started, after which the host is brought back online. This process ensures that the host is never multipathing between the source EMC Storage system and the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. Even if the native multipath software is already configured, it is necessary to restart the host after unzoning the source EMC Storage system from the host.
IMPORTANT: If you unzone the host from the EMC Storage system but do not reconfigure the host multipathing software, the host/cluster will experience an outage, because it will not be able to communicate with the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
Working with Consistency Groups
The optional HP 3PAR Consistency Group feature allows you create and consistently migrate dependent volumes of applications. I/O that is issued to volumes that are members of a consistency group is mirrored to the source array until all members are completely migrated to the destination array, keeping the source volumes in a consistent state.
NOTE:
• Consistency groups are supported on the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system running HP 3PAR OS version 3.2.1 or later on supported platforms.
• A consistency group can be created for “all volumes” of a host or a “subset of volumes” of a host. The HP 3PAR Consistency Group feature can be used for host-based migration.
A consistency group can be created for “all volumes” of a host or a “subset of volumes” of a host. The HP 3PAR Consistency Group feature can be used for host-based migration.
• For consistent imports, HP recommends that you limit the number of volumes in a consistency group to 20.
• To avoid long switch-over times at the end of imports, HP recommends that you limit the total size of volumes in a set to 40 TB.
Creating a Consistency Group
Consistency groups are defined in thecreatemigrationcommand. The following parameters
are available to create consistency groups:
• cgvolmap: Defines the consistency groups and their member volumes.
• allvolumesincg: All volumes (including implicit volumes) will be migrated consistently.
Example 2 Volume-based migration with specified volumes in consistency groups
# createmigration -sourceuid AF0002AC001BA1 -srcvolmap "[{vol1, thin, testcpg},{vol2, thin, testcpg},{vol3,
thin, testcpg}]" -destcpg testcpg -destprov testcpg -cgvolmap{“values":{"cg1": ["vol1","vol2]}} —migtype online -persona “RHEL_5_6”
Three volumes (vol1,vol2andvol3) are chosen for migration. A consistency group named
cg1will be created, containingvol1andvol2. When astartmigrationcommand is issued, I/O to bothvol1andvol2will be mirrored to both the source storage array and the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage until bothvol1andvol2import tasks are complete. After bothvol1and
vol2import tasks are complete, I/O for both volumes will cut over to the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage.
Example 3 Volume-based migration with all volumes in a consistency group
# createmigration -sourceuid AE0002AC001BA2 -srcvolmap "[{vol1, thin, testcpg},{vol2, thin, testcpg},{vol3,
thin, testcpg}]" -allvolumesincg -destcpg testcpg -destprov testcpg —migtype online -persona “RHEL_5_6”
All volumes (including implicit volumes) will be placed in a single consistency group. When a
startmigrationcommand is issued, I/O to all volumes will be mirrored to both the source storage array and the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage until all import tasks complete. After all import tasks are complete, I/O for all volumes will cut over to the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage.
Example 4 Host-based migration with specified volumes in consistency groups
# createmigration -sourceuid 8F0002AC001BA4 -srchost "hostname" -migtype online -destcpg testcpg -destprov thin
-cgvolmap{“values":{"cg1":["vol1","vol2","vol3"],"cg2":["vol4","vol5","vol6"]}} —migtype online -persona “RHEL_5_6”
All volumes (including implicit volumes) presented to the host are chosen for migration. Two consistency groups will be created:
• cg1, containingvol1,vol2, andvol3
• cg2, containingvol4,vol5, andvol6
Any other volume that was defined explicitly in thecreatemigrationcommand, or that was added implicitly, will be migrated, but not as a part of a consistency group. When a
startmigrationcommand is issued, I/O for volumes in bothcg1andcg2will be mirrored to both the source storage array and the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage until allcg1orcg2import tasks are complete. Aftercg1orcg2import tasks are complete, I/O to the respective consistency group volumes will cut over to the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage.
Example 5 Host-based migration with all volumes in a consistency group
# createmigration -sourceuid 8F0002AC001BA3 -srchost "hostname" -migtype online -destcpg cpg1 -allvolumesincg
—migtype online -persona “RHEL_5_6”
NOTE: HP recommends that only allvolumesincgbe used with Oracle RAC.
All volumes (including implicit volumes) presented to the host will be placed in a single consistency group. When a startmigrationcommand is issued, I/O to all volumes will be mirrored to both the source storage array and the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage until all import tasks are complete. After all import tasks complete, I/O for all volumes will cut over to the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage. Working with Consistency Groups 33
5 Premigration Steps
Perform these steps to prepare for migration.
Zoning the Source EMC Storage to the Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ
Storage System
The correct zoning must be present between the source EMC Storage system and destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system at every stage of the migration operation. The following zoning rules apply:
• There must be two unique paths between the source and destination storage systems. To create two paths, the two controller host ports on the source EMC Storage system must be zoned to two peer ports on the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. The peer ports on the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system must be on adjacent nodes: 0/1, 2/3, 4/5, or 6/7.
• Zone the source and destination systems together and make sure they are visible to each other before zoning hosts to the destination system.
• Do not unzone the source and destination systems from each other until the data migration is complete.
To create the zoning:
1. On the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system, configure two free ports as peer ports using adjacent nodes: 0/1, 2/3, 4/5, or 6/7.
a. Set the port connection type topoint.
b. Set the port connection mode topeer.
Example 6 HP 3PAR CLIcontrolportcommand
# controlport offline n:s:p
# controlport config peer -ct point n:s:p # controlport rst n:s:p
2. Create two zones between the source EMC Storage system and the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system, ensuring that one EMC host port is in the same zone with one HP 3PAR peer port.
NOTE: The WWN of a host port changes when it is set to become a peer port. Use the new WWN of the peer port in the zoning.
Each zone should contain only two ports: one from each storage system. Adjacent HP 3PAR peer nodes should be zoned to separate EMC controllers in a one-to-one mapping. For example, zone the peer port on node 0 on the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system to controller
A on the EMC Storage system, and zone the peer port on node 1 on the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system to controller B on the EMC Storage system.
3. Verify that the EMC Storage system can detect both ports on the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
Ensure that the peer port WWNs appear in the discovered port list. • To check peer port connections using VMAX, follow these steps:
a. Issue the following command:
#symaccess -sid <vmax id> list logins
b. Check theIdentifierlisted for each HP 3PAR peer port and make sure they are logged in (Yes).
C:\Users\Administrator>symaccess -sid 1212 list logins
Symmetrix ID : 000194901212
Director Identification : FA-7E Director Port : 0
User-generated Logged On Identifier Type Node Name Port Name FCID In Fabric ---- --- ---
---20210202ac005f91 Fibre ---20210202ac005f91 ---20210202ac005f91 020400 Yes Yes
Director Identification : FA-8E Director Port : 0
User-generated Logged On Identifier Type Node Name Port Name FCID In Fabric ---- --- --- ---21210202ac005f91 Fibre ---21210202ac005f91 ---21210202ac005f91 020200 Yes Yes
Alternatively, verify that the EMC Storage system is shown as a connected device on both peer ports of the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• To check peer port connections from the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage, issue the
showtargetcommand with the-rescanoption, and then issue theshowtarget
command.
In this example,Node_WWNis the WWN of the source array # showtarget -rescan
#
# showtarget
Port ----Node_WWN---- ----Port_WWN---- ---Description---1:2:2 50000972C012F110 50000972C012F11C reported_as_scsi_target 0:2:2 50000972C012F110 50000972C012F118 reported_as_scsi_target
Identifying the Source and Destination Storage Systems
This section provides information on how to identify and add the source and destination storage systems for migration. Before beginning, prerequisites must be met and information about the source and destination systems must be gathered.
Prerequisites
• EMC SMI-S Provider is installed and operational.
• The source EMC Storage system must be registered in the EMC SMI-S Provider application. • The source EMC Storage system has one or more storage groups configured with the hosts
and volumes to be migrated.
• The HP 3PAR Online Import Utility is installed and operational with access to the SMI-S Provider server managing the source EMC Storage system and the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• The source EMC Storage system and destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system are zoned to each another.
Required Information
EMC Storage source system:
• IP address of the EMC SMI-S Provider server that is managing the source EMC Storage system from which the volumes are being migrated and the WWN of the source EMC Storage system being managed by the EMC SMI-S Provider.
• User name and password for the EMC SMI-S Provider. • Port to access the EMC SMI-S Provider.
Secure port default 5989.
◦
◦
Non-secure port default 5988.Destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system
• IP address of the destination HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• User name and password for the HP 3PAR management application with Super user permission.
Adding the Source Storage System
To identify the source storage system, follow these steps:
1. From the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, issue theaddsource command.
NOTE: Use local user credentials to log into the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility.
Example 7addsourcecommand
# addsource -type VNX -mgmtip XX.XX.XX.XX -user admin -password adminpw —uid xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
# SUCCESS: Added source storage system
whereXX.XX.XX.XXis the IP address of the EMC SMI-S Provider server, and
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxis the WWN of the EMC Storage system.
2. Issue theshowsourcecommand to verify the source storage system information.
Example 8showsourcecommand
# showsource –type VNX
NAME TYPE UNIQUE_ID FIRMWARE MANAGEMENT_SERVER OPERATIONAL_STATE CLARiiON+APM00125345014 VNX 50067890BEE0177F 05.32.000.5.201 XX.XX.XX.XX Good
Adding the Destination Storage System
To add the destination storage system, follow these steps:
1. From the HP 3PAR Online Import Utility, issue theadddestinationcommand.
Example 9adddestinationcommand
# adddestination –mgmtip XX.XX.XX.XX –user 3paradm –password 2Password # SUCCESS: Added destination storage system
whereXX.XX.XX.XXis the HP 3PAR management port IP address.
If a certificate validation error occurs on theadddestinationcommand (see
Example 10 “Certificate validation error”), first run the installcertificatecommand (seeExample 11 “Installcertificatecommand”), then run theadddestination
command again.
Example 10 Certificate validation error
# adddestination -mgmtip xx.x.xx.xx -user 3paradm -password ******* -port 5783
# ERROR: OIUERRDST0010 Unable to validate certificate. C:\\InFormMC\security\HP-3PAR-MC-TrustStore
Example 11Installcertificatecommand
# installcertificate –mgmtip xx.xx.xx.xx
TParCertifacteVO [issuedTo=HP 3PAR HP_3PAR 7400 1645897, commonName=null, issuedByOrganization=null, issuedToOrganization=null, serialNo=null, issedBy=HP 3PAR HP_3PAR 7400 1645897,
fingerprint=89:E5:D0:13:6F:D1:07:80:70:76:5C:FE:5B:65:E5:54:C0:18:21:2F, signatureAlgo=SHA1withRSA, version=v1,validFrom=08/14/2014, validTo=08/11/2024. issuedOn=null, expiresOn=null, validDateRange=true] Do you accept the certificate? Y/YES Y
# SUCCESS: Installed certificate successfully.
2. Issue theshowdestination command to verify the destination storage system information.
Example 12showdestinationcommand
# showdestination
NAME TYPE UNIQUE_ID FIRMWARE MANAGEMENT_SERVER OPERATIONAL_STATE PEER_PORTS
3par_7200_DCB_01 3PAR 2FF70002AC005F91 3.2.1 (MU3)
XX.XX.XX.XX Normal 2021-0202-AC00-5F91(0:2:1) 2121-0202-AC00-5F91(1:2:1)
Preparing the Host for Data Migration
NOTE: This section does not apply to online migration. To prepare for a successful migration:
• Stop all applications on the host that may be accessing the LUNs to be migrated. This also includes any replication and backup applications on the LUNs.
• Set the LUNs to be migrated to an offline/unmounted state.
NOTE: Modify the startup scripts for all applications and services that are using the migrating LUNs to prevent them from starting at the next reboot. They should remain disabled until after the migration has started and documentation instructs you to bring your host back online.
For Hyper-V running on Windows Server 2008 R2, follow these steps to prepare the host for migration:
1. Stop all applications currently running on the virtual machine.
2. Shut down the virtual machines using Failover Cluster Manager.
Preparing Windows Clusters for Migration
When a Windows cluster is migrated, the cluster must first be disabled so that any SCSI reservations in use are released. For active/passive cluster running Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server Preparing the Host for Data Migration 37
2008 R2 , this can be achieved by stopping all applications running on the cluster, then stopping the cluster service on all nodes.
When a Windows Server 2012 active/passive cluster is migrated, maintenance mode must be set on the cluster disks to clear SCSI reservations on the disks. Because the quorum disk cannot be set in the maintenance mode, it must be set to the offline mode to clear its SCSI reservations. Then, the cluster service must be stopped on all nodes.
For Hyper-V running on Windows Server 2008 R2, follow these steps to stop the cluster:
1. Set the quorum disk toOffline, CSV disksinMaintenancemode.
2. Using the Failover Cluster Manager, selectShutdown Cluster.
3. Clear the cluster reservation, if present, by following the appropriate Microsoft documentation about Hyper-V clusters.
For Windows Server 2003 or Windows Server 2003 R2, stop the cluster service on each cluster node.
For more information, see Microsoft documentation on how to start/stop the cluster services.
Preparing Veritas Clusters for Migration
NOTE: Only EMC VMAX arrays are supported with Veritas clusters at this time. On Veritas clusters, stop the clusters by issuing the following command:
# /opt/VRTSvcs/bin/hastop -all
Then verify cluster status by issuing the following command: # /opt/VRTSvcs/bin/hastatus
When the clusters are down, messages like the following will appear: attempting to connect....
VCS ERROR V-16-1-10600 Cannot connect to VCS engine attempting to connect....not available; will retry
To verify that a reservation is clear after stopping a cluster, follow these steps:
1. Issue the following command to get a list of all LUNs used in the cluster:
Example 13 Listing LUNs in a cluster
# vxdisk list
DEVICE TYPE DISK GROUP STATUS
cciss/c0d0 auto:none - - online invalid emc0_00fe auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm emc0_00ff auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm emc0_0100 auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm emc0_0101 auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm emc0_0102 auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm emc0_0103 auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm emc0_0104 auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm emc0_0105 auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm emc0_0106 auto:cdsdisk - - online thinrclm
2. Create atmpfilein the /rootdirectory with all the LUNs. the tmpfilewill be similar to
the following example:
Example 14tmpfilewith LUNs /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_00fe /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_00ff /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0100 /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0101 /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0102 /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0103 /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0104 /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0105 /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0106
3. Issue the following command to verify that the reservation keys are clear:
Example 15 Verifying that reservation keys are clear
# vxfenadm -s all -f tmpfile
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_00fe Total Number Of Keys: 0
No keys...
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0100 Total Number Of Keys: 0
No keys...
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_00ff Total Number Of Keys: 0
No keys...
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0101 Total Number Of Keys: 0
No keys...
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0102 Total Number Of Keys: 0
No keys...
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0106 Total Number Of Keys: 0
No keys...
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0105 Total Number Of Keys: 0
No keys...
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0103 Total Number Of Keys: 0
No keys...
Device Name: /dev/vx/rdmp/emc0_0104 Total Number Of Keys: 0
4. If the reservation keys are not clear, issue the following commands on any one cluster node to clear them:
# vxfenadm -a -k 111111 -f tmpfile # vxfenadm -c -k 111111 -f tmpfile
The reservation keys are clear when each device in thetmpfileindicatesNo keys.
Creating the Data Migration Task
The data migration task performs the following actions in the preparation required for data migration: