Original Article Microvasculature femoral head cartilage and subchondral bone in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
Full text
Figure
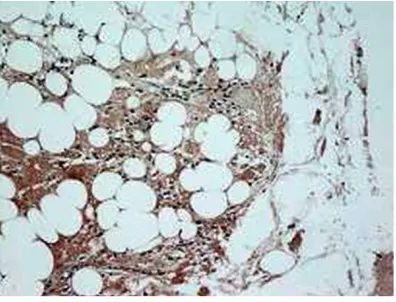
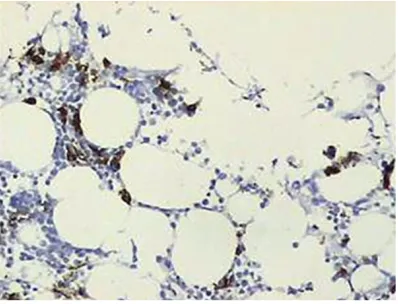
Related documents
Our aim was to evaluate the bone quality of the femoral head in the area recommended for the screw insertion based on trabecular bone micro- structure in vivo.. Patients
MMP , matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP , tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases; alcohol- induced ONFH, alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head; BMSC, bone marrow
Abstract: Autologous implantation of bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) has achieved promising clinical effica- cy for the treatment of early-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral
Abstract: The study aims to compare the clinical efficacy of core decompression (CD) and bone marrow mesenchy - mal stem cells (BMMSC) on the patients with osteonecrosis of the
In summary, PHILOS combined with allogeneic femoral head bone grafting has the advanta- ges of fast fracture healing, shorter hospital stays, and less postoperative complications
Comparison of CRC patients with bone metastases using a median split for maximal transrenal DNA quantity detected within a six-month period.. Comparison of CRC patients without
Abstract Aim of the work: The aim of this work was to assess the bone mineral density (BMD) in Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) patients and to investigate its relation with clinical
3, expression of the P4HA2, SPP1 and CRTAC1 proteins in the superficial zone, middle zone, and deep zone of cartilage from patients with NFH was sig- nificantly higher than in