4 Methoxyanilinium 2 carboxy 4,5 dichlorobenzoate
Full text
Figure

Related documents
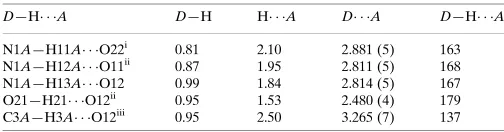
Intramolecular C—H O hydrogen bonds generate S (6) ring motifs in both the cation and the anion.. In the crystal, N—H O, N—H N and C—H O hydrogen bonds are also
Two oxide O atoms occupy the axial positions. In the crystal, mol- ecules form centrosymmetric dimers through hydrogen bonding between ethanol O—H donors and phenolate O-
The molecular structure features an intramolecular N—H O interaction. In the crystal, N— H O hydrogen bonds involving carboxyl O-atom acceptors generate a chain extending
In the crystal, cation–anion hydrogen-bonding interactions involving pyrim- idine–carboxy N + —H O and amine–carboxy N—H O pairs give a cyclic R 2 2 (8) motif while
Each imine H atom is intramolecularly in contact with the adjacent carboxyl O atom, forming an S (6) motif, while all the carboxylic acid H atoms are hydrogen bonded to O atoms of
An O atom of the nitrate anion links the acidic H atoms of the cation via N—H O hydrogen bonding.. In addition, neigh- bouring cations are connected by intermolecular N—H
In the crystal structure, the protonated N atom of the pyridine ring and the 2-amino group of the cation are hydrogen bonded to the carboxylate O atoms of the anion via.. a pair of N—H
In the molecule, the pyran ring adopts an envelope conformation with the O atom at the flap position. Weak intermolecular C—H O hydrogen bonding is present in the