International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013)
65
Performance Analysis of One stage and Two stage Parallel
Interference Cancellation for Optical Code Division Multiple
Access System
Vandana Nath
1, Sandeep Dogra
21 Assistat Professor., ECE Deptt, USICT, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Dwarka, New Delhi, INDIA 2
M.tech student, DWC Deptt, USICT, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Dwarka, New Delhi, INDIA
Abstract— Code division multiple access (CDMA) is a powerful multiplexing scheme which is very suited to the optical domain with its broad spectrum. Optical code division multiple access (OCDMA) technique allows multiple users to share the same transmission media by assigning different codes and is a very promising technique for the broadband communication. OCDMA networks can provide all customers with upstream data rates of Gigabits/seconds with inherent flexibility. In the optical domain, the traditional method to recover the data at the receiving end of an optical CDMA system is to use an optical correlator followed by a photo detector and a decision device. However as the number of simultaneous users increases the capacity of the system is limited by Multiple Access Interference (MAI) and various detection noises. There are many reception techniques like decorrelation receiver, Minimum Mean Square error, Interference Cancellation etc. which are very efficient for multiuser detection in Radio frequency (RF) communication .Their success in RF domain has inspired usage in OCDMA. Interference Cancellation techniques are any technique or combination of techniques that allow an existing receiver to operate with higher levels of co-channel interference. This paper presents the effect of MAI, using parallel interference cancellation (PIC) techniques for incoherent OCDMA which is non-linear multiuser detector. One stage and two stage PIC, have been simulated for various data rates and fiber lengths. Simulated results show that two stage PIC shows better performance than Direct detection technique and one stage PIC.
Keywords—BER, CDMA, DD, MAI, OCDMA, PIC
I. INTRODUCTION
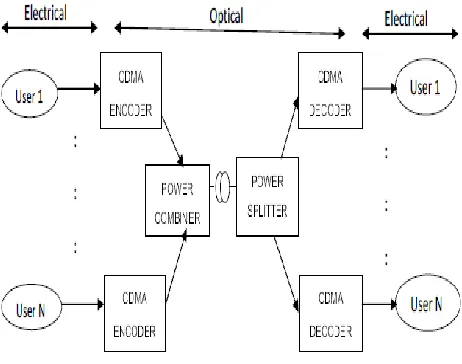
CDMA exploits the coding technique in which every user is allocated the entire spectrum for the full time and different users are distinguished by different spreading codes. CDMA offers various benefits like efficient bandwidth utilization, asynchronous access and secure communication, which has led to its implementation in optical domain termed as optical CDMA (OCDMA) communication systems [1]. The basic schematic diagram of OCDMA system is given in Figure 1.
[image:1.612.328.559.349.531.2]OCDMA systems uses two basic detection schemes namely, coherent which uses bipolar code and incoherent which uses unipolar codes. In incoherent systems, codes are quasi orthogonal and their performance can be significantly reduced by MAI as the number of users increases [2]. Several methods have been investigated in the literature aiming at lowering the effect of MAI [1] [3].
Figure 1: A Basic Block Diagram of OCDMA system
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013)
66
Linear multiuser detectors ignore part of the structure of transmit signals as they allow any continuous value for the estimate of the transmit signal whereas Non-linear MUD exploits the fact that the transmit signal can only contain members of a finite transmit alphabet. Non-linear MUD based receivers are MLSE, interference cancellation, decision feedback receivers and turbo receivers.
II. DIRECT DETECTION TECHNIQUE
[image:2.612.49.284.380.592.2]Direct Detection (DD) technique retains only those components of the optical spectrum which are desired, remaining undesirable components are removed by filtering[5]. This technique is applicable only to those codes, in which the spectral chips are not overlapped with other spectral chips of the other channel, i.e. a minimum of one clean chip in every code sequence. A block diagram of Direct Detection technique is shown in Figure 2. Figure shows that same frequency component being directly detected at the receiver side and hence its circuitry is very simple and less costly.
Figure 2: A Block Diagram of Direct Detection Technique[5].
III. PARALLEL INTERFERENCE CANCELLATION TECHNIQUE
Parallel interference cancellation (PIC) is a multiuser detection technique where a desired user’s decision statistic is formed by subtracting an estimate of the multiple-access interference from the original observation of the desired user [6].
In a structure with parallel interference cancellation (PIC); all undesired users are detected at the same time using the conventional receiving systems. The PIC receiver as shown in Figure 3 [4] [7] has the principle of the reproduction interference from undesired users, to remove it from the total received signal.
Steps of Single stage PIC Technique:
1) Firstly, data signals of undesired users are decoded using basic direct detection technique for OCDMA system, let mi (k) be the estimated bits of undesired user #k.
2) Second step is to again encode the all undesired user data with their corresponding ZCC code, this step is similar to respreading in RF domain.
3) In the third step, the interference term mi(t) which is actually the sum of the reconstructed signals, is then subtracted from the received signal r (t).
c(t) = r(t) - ∑ z(k) (1) Where z(k) is corresponding Walsh Hadamard code.
[image:2.612.326.568.400.651.2]4) The last step is the detection of the desired user data # 1 from the signal "cleaned" from the interference i.e c(t).
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013)
67
[image:3.612.317.572.213.559.2]Two Stage Parallel Interference Cancellation Technique Two stage PIC second stage uses the first stage’s tentative decision outputs to generate new multiple-access interference estimates and subtracts these interference estimates from the original observation to produce new tentative decision outputs with presumably lower multiple-access interference [6]. Second stage of two stage PIC is shown in the Figure 4.
Figure 4: Block Diagram of 2nd Stage of Two stage Parallel
Interference Cancellation Technique.
IV. SIMULATIONS
[image:3.612.52.288.239.469.2]Firstly the CDMA is simulated using DD, PIC one stage and PIC two stage detection techniques for which simulation parameters are given in the Table-I.
Table I
simulation parameters used for DD, PIC one stage and PIC two stage for CDMA System.
Parameters Values
No. of simultaneous active Users 10
Code length and Number of symbols 10 and 1000 respectively.
SNR 1-11 dB
[image:3.612.46.289.602.693.2]Secondly, DD, PIC one stage and PIC two stage techniques are then simulated and compared for OCDMA System by varying data rates and fiber distance using parameter as described in Table-II.
Table II
simulation parameters used for DD, PIC one stage and PIC two stage for OCDMA system.
Parameters Value
Optical Source specification
Continuous wavelength source 1549.7 nm - 1550 nm
Continuous wavelength source power
10 dBm
Optical fiber
Type of optical fiber The ITU-T G.652 standard single
mode optical fiber.
Optical Filter specifications
FBG cut off wavelength λ0 1549.7 nm
FBG cut off wavelength λ1 1549.8 nm
FBG cut off wavelength λ2 1549.9 nm
FBG cut off wavelength λ3 1550 nm
PIN Photo detector specifications
Dark Current 1nA
Other parameters
Bandwidth .1nm
V. SIMULATION RESULTS
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013)
[image:4.612.320.567.116.338.2]68
Figure 5: BER vs. SNR for CDMA System.
These three techniques are employed in multiuser detection of OCDMA system. Performance evaluation of DD, PIC one stage and PIC two is done by comparing BER under two circumstances ,firstly by varying Bit Rate from 2-10 Gbps and secondly by varying Fiber length from 1 to 50 km respectively. Figure 6 shows variation of BER by varying bit rates, for these three detection technique. Figure 6 shows that BER increases as the bit rate is increased but two stage PIC has very low BER in the range of 2Gbps to 4 Gbps. Similarly BER also increases with increasing fiber distance as shown in Figure 7, but by using two stage PIC receivers BER rate can be reduced.
[image:4.612.51.292.123.302.2]Figure 6: Comparison of BER vs. Bit Rate for various Detection Schemes for OCDMA system.
Figure 7: Comparison of BER vs. Fiber Length for various Detection Schemes for OCDMA system.
VI. CONCLUSION
Proposed paper presented two stage Parallel interference cancellation techniques for OCDMA to detect signal in multiuser environment and compared its performance with one stage PIC and DD. Although one stage PIC shows better performance than conventional detection method but by using two stage PIC, MAI is reduced further. Two stage PIC has lesser Bit error rate even if data rate or fiber distance is increased. However as the number of stages increases hardware complexity increases, so there is a tradeoff between number of stages to decrease MAI and hardware complexity. Future work will be centered on decreasing MAI further while maintaining hardware complexity to minimum.
REFERENCES
[1] J. A. Salehi, ―Code division multiple-user techniques in optical fiber
networks—Parts I and II,‖ IEEE Trans. Communication., vol. 37, pp. 824–842, Aug. 1989.
[2] Hussein Seleem, Abdelouahab Bentrcia, and Habib Fathallah, "A
Projected Parallel Interference Cancellation for Asynchronous Upstream OCDMA-PON ", IEEE Communications Letters, Vol. 16(11): 1721-1724, November 2012.
[3] Brandt-Pearce, M., Aazhang, B. " Multiuser detection for optical code division multiple access systems ",Communications, IEEE Transactions on (Volume:42 , Issue: 234 ) Page(s): 1801 - 1810.
[4] Wireless Communications (Wiley - IEEE), Molisch, Andreas F.
Wireless communications / Andreas F. Molisch. – 2nd edition.
Wireless communication systems–Textbooks. I. Title.
TK5103.2.M65 2011. 1.00E-60 1.00E-54 1.00E-48 1.00E-42 1.00E-36 1.00E-30 1.00E-24 1.00E-18 1.00E-12 1.00E-06 1.00E+00
2 4 6 8 10
B
E
R
Bit Rate (Gbps)
DD PIC 1st Stage PIC 2nd Stage 1.00E-25 1.00E-23 1.00E-21 1.00E-19 1.00E-17 1.00E-15 1.00E-13 1.00E-11 1.00E-09 1.00E-07 1.00E-05 1.00E-03 1.00E-01
1 10 20 30 40 50
B
E
R
Fiber Length (Km)
DD
PIC 1st Stage
[image:4.612.50.288.456.653.2]International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459,ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013)
69
[5] Vandana Nath, Nakul Jain, Sandeep Dogra, ―Effect Of Fiber
Distance On Various SAC-OCDMA Detection Techniques On Ocdma", IJRET March 2013, Volume: 2 Issue: 3 pp: 290 – 293, March 2013.
[6] D. Richard Brown, Mehul Motani, Venugopal V. Veeravalli,H.
Vincent Poor, and C. Richard Johnson, "On the Performance of Linear Parallel Interference Cancellation" ,IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 47, NO. 5, JULY 2001, Page(s): 1957 - 1970.
[7] N. Elfadel, E. Idriss, A. Mohammed, A.A. Aziz and N.M. Saad
![Figure 2: A Block Diagram of Direct Detection Technique[5].](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/8728392.886082/2.612.49.284.380.592/figure-block-diagram-direct-detection-technique.webp)

