The Role of Foxo3 in Leydig Cells
Full text
Figure
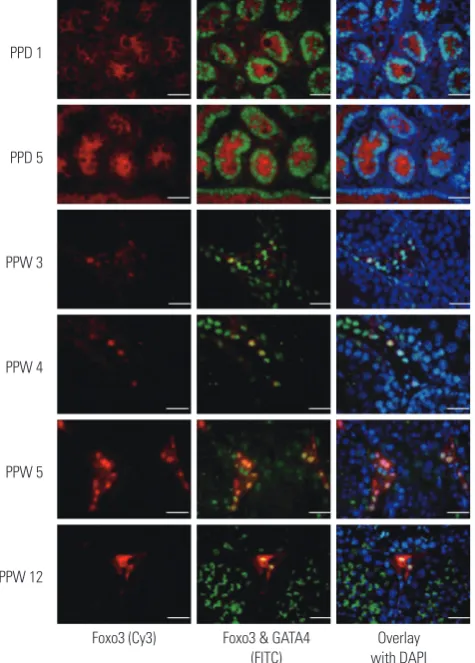
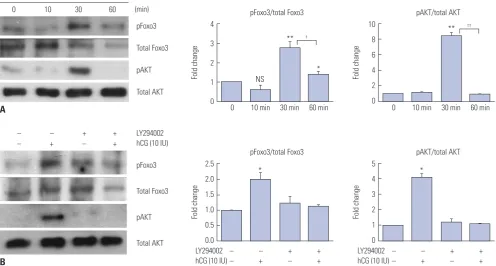

Related documents
Furthermore, group with EPO injection after release ligation of vas deferens showed no significant difference in spermatogonia, Sertoli cells and Leydig cells compared
The im- munostaining of the AR testis is localized at somatic (Sertoli, Leydig and peritubular myoid cells) and germ cells in D’Man
Tumors formed from ovarian cells (e.g., granulosa cells and theca cells) are often hyperestrogenic, whereas those comprising testicular cell types (e.g., Sertoli and Leydig cells)
Recently, we have reported in testicular biopsies from men with Sertoli Cell Only Syndrome (SCO) or Hypospermatogenesis (H) with Leydig cell hyperplasia (LCH) an increase in
To identify the main signaling pathway underlying FOXO3-induced apoptosis in T-ALL cells, we generated CEM/FOXO3 cells overexpressing either anti-apoptotic members of the
This development of Leydig cells can be mimicked in vitro by the induction of stem Leydig cells into the Leydig cell lineage on the surface of the semin- iferous tubules after 21
The somatic epithelial cells in ovary (A , B , D) and Sertoli cells in testicular (E) smears have abundant cytoplasm and pale stained nuclei whereas the stem cells are spherical
The testicular damage related to the MTX-induced oxidative stress occurs directly in the spermatogenic cells and Sertoli cells, and leads to dysfunction of Leydig cells and