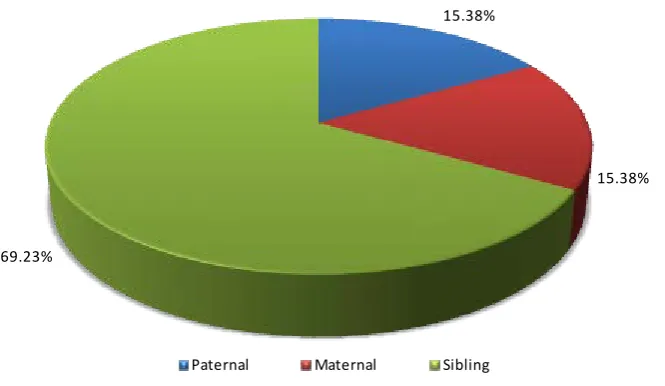
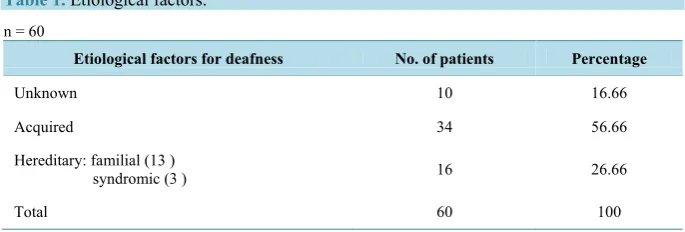
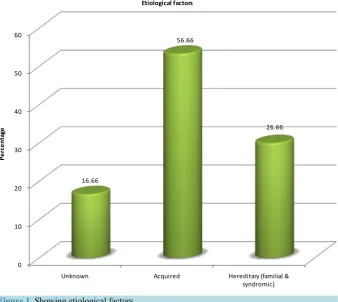
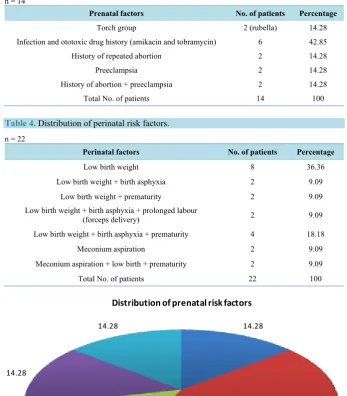
Etiology Profile of the Patients Implanted in the Cochlear Implant Program
Full text
Figure
Related documents
Results: Six themes were identi fi ed as most relevant to the PNH treatment experience from the concept elicitation interviews: disease symptoms (n=8/8); treatment frequency
The lack of protection observed in mice treated with B cells directly isolated from arthritogenic splenocytes fol- lowed by CII/anti-CD40 in vitro stimulation (Fig. 4 g) suggest
Using key-homomorphic constrained PRFs as constructed in this paper, in Section 5 we construct a scheme for outsourced storage that supports proxy re-encryption and fine-grained
Nevertheless, the two types of sponges showed completely opposite water wettability (Figure 8); hydrophobic for vhGS and hydrophilic for vhEGCG-GS. Hydrophilicity of amino
Layout of the ACE Isotopes facility, showing the cyclotron vault (middle), production vaults (left and right) and the expanded Telelift target transport system. Each production
The cut-off values of PSAD, percentage of positive cores, percentage of positive cores from the dominant side, and maximum percentage of cancer extent in each positive core were set
AHS: anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome; ADR: adverse drug reac- tion; AEDS: antiepileptic drugs; LP: lumber puncture; EBV: Epstein Barr virus; CMV: cytomegalovirus; HSV:
Patients with RH were more likely to be men, and to have higher waist circumference, increased blood levels of HbA1c, triglycerides, and serum creatinine, lower blood levels of