Effect of Strain Rate and Temperature on Tensile Properties of Bi Based Lead Free Solder
Full text
Figure
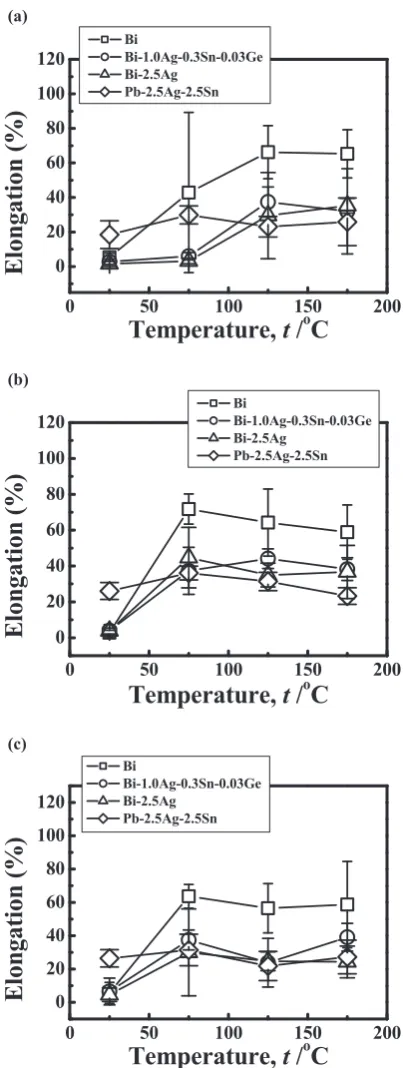
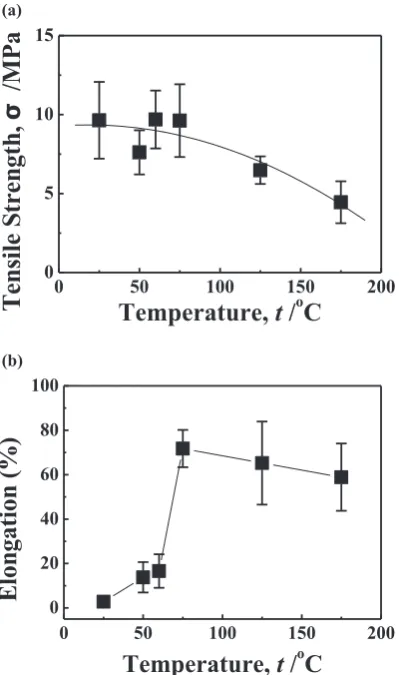
Related documents
The work reported here has investigated the suitability of a number of these techniques to study cracking in lead-free solder joints, and hence their used in assessing joint
The aim of this work was to create and apply a recycled bismuth-tin (Bi-Sn) solder in novel machinable lead-free brass. The Bi-Sn al- loys were obtained from a recycled solder used
Sn-0.7Cu and Sn-0.7Cu-xGe solder alloys were prepared to investigate the influence of trace Ge on liquid Sn-0.7Cu lead-free solder at high temperature. The spreadability and
The crack generation energy U1 and the crack progress energy U2 of eutectic Sn–37 mass%Pb solder ball and Sn–36 mass%Pb– 2 mass%Ag one were surveyed by the shear test.. Both balls
The Tensile test was conducted at room temperature (25°C ) for all solder composition to investigate the effects of Bi added on the mechanical properties of solder, yield
Three types of inexpensive Pb-free solder joints, namely Zn-based and Bi-based solders, and a CuSn alloy were studied for application to the high-temperature operation of wide
The mechanical properties of the bulk Sn-Bi-Sb solders were higher as the amount of antimony increases, making compressive strength augment from 65 MPa to 100 MPa when 6 wt% Sb
Conclusions In the present work, tensile behaviors under different tensile strain rates at room temperature of two typical nickel-based superalloys GH3044 and GH4033 were