Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection induces non apoptotic cell death of human dendritic cells
Full text
Figure


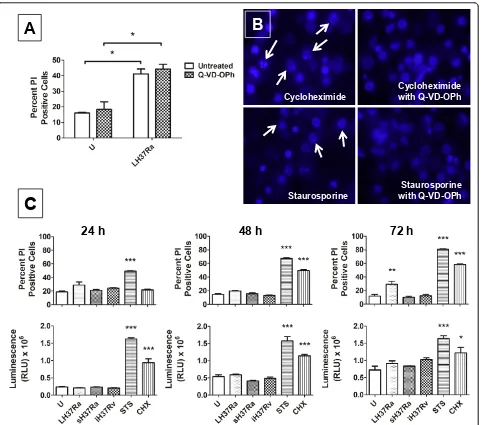
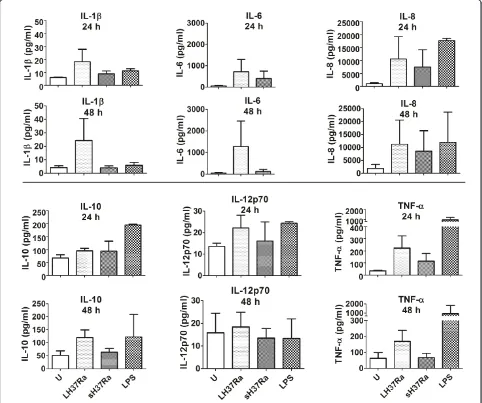
Related documents
Results: the present study reveals a significant deficiency of Vit D in group III ( late DPN) compared to early DPN (group II) and its negative correlation with
Purpose: To identify potential risk factors of lymph node metastasis and to verify the prognostic significance of the lymph node ratio (LNR) and the total number of lymph
The shallow parts of the entire interfaces are located near the south and southwestern outcrops while the deep parts are laid at the central, eastern and northeastern city.. It
COPYRIGHT © UNIVERSAL MULTIDISCIPLINARY RESEARCH INSTITUTE PVT LTD Evolution in Real Time.. Randy Wayne, Laboratory of Natural Philosophy, Section of Plant Biology, School
Figure 6.6 Adsorbed fluorescent magnetic label on each MR sensor chip under different glucose
once-daily treatment with olodaterol 5 and 10 μ g delivered via Respimat SMI (Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.) compared to placebo and formoterol 12 μ g twice daily
These findings highlight three mechanisms that strongly influence relationship management in virtual R&D teams: leadership, work organization and coordination mechanisms,
suitably record local field potentials generated by a small population of cells (e.g. a bundle of axons) within the field of observation. Multi-site multi-unit
