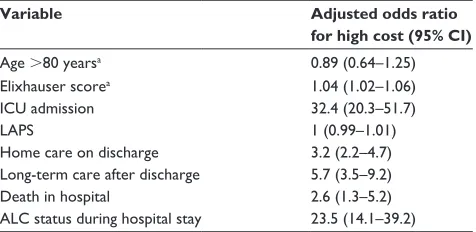
Factors contributing to high-cost hospital care for patients with COPD
Full text
Figure


Related documents
The impact of progressive gear geometry on the braking distance both in variable operating condi- tions and variable loading is analyzed.. The tests were conducted for the gear
This study aimed to explore the knowledge and atti- tude toward HIV/AIDS as well as identify associated factors with good knowledge in residents living in three Vietnamese
Seasonal variation in travel times to health facilities Spatial access to health services generally decreases dur- ing the wet season for all modes of transport and to all
The purpose of this study was to define the duration of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) before organ failure (DSOF) and determine the value of DSOF as a prognostic
Questionnaires on health outcomes and quality of life were mailed to pa- tients with childhood-onset ulcerative colitis who had undergone proctocolectomy with ileoanal anastomosis in
Three subscales of the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale were examined as ultrabrief alternatives: the anxiety subscale (3 items; Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale-3),
For bicyclists ⱖ 16 years of age, there were only slight changes in the average number of deaths per year and the mortality rate per 100 000 person-years, and the time series
3,6,10,22–24 Larger feedings in the current study triggered greater release of gastrin and moti- lin, but maturation of motor patterns and feeding outcomes were similar in the 2