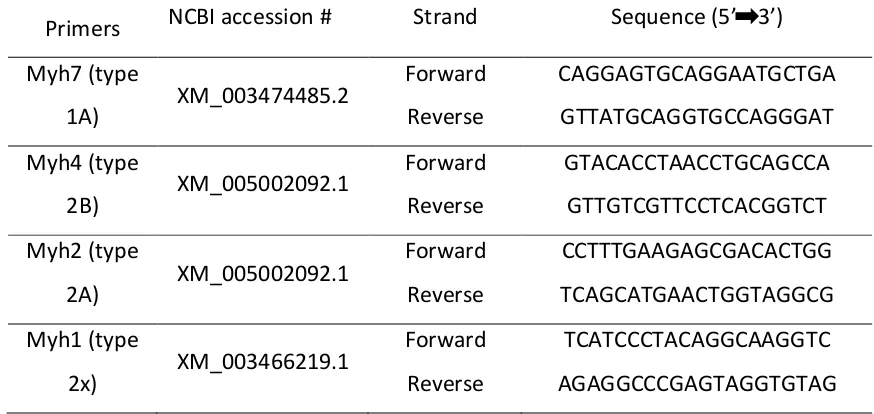
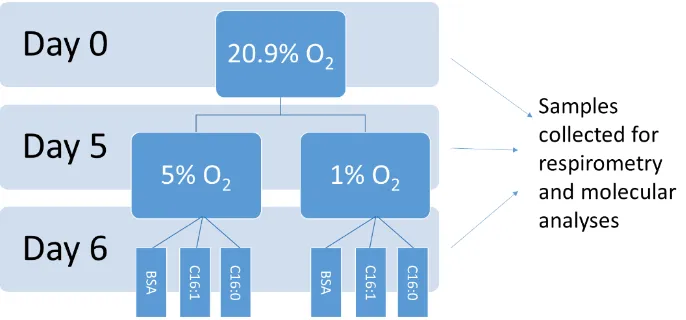
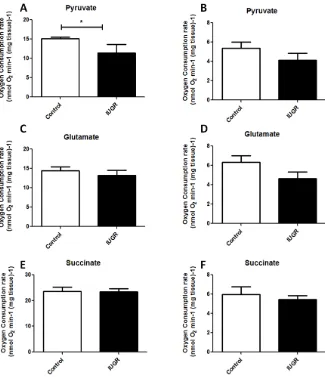
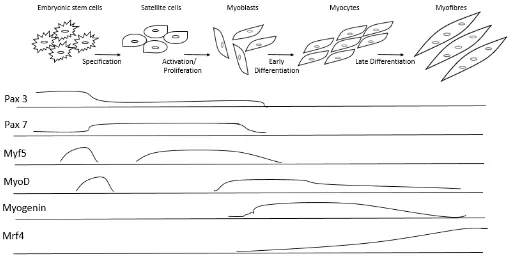
Low Birth Weight and Post-Natal Diet Induced Alterations in Skeletal Muscle Oxygen Consumption and Fiber Type Composition
Full text
Figure


Outline
Related documents
The figure shows the average execution time of the microbiology query group over 24 hours without autonomic management and with actions taken by the reactive, deliberative
The main purpose of this study is to determine whether the TAM (Technology Acceptance Model) could be extended to include external variables including computer self-efficacy,
Only when the organisation and the counselling service have proved themselves to be trustworthy is the inclusion of conditions for mandatory referral likely to be acceptable
Adverse events that may occur with any intra-articular injection include arthralgia, joint swelling, joint effusion, injection site pain, and arthritis.. Precautions
We sought to test the hypothesis that among children without a history of aspirin sensitivity, the use of ibuprofen suspension for fever control increases the risk of acute
Only the pullback in the main branch was available for the current analysis. The analyzed bifurcation lesions were classified into the proximal or distal bifurcation group based on
First, when it comes to the narrative, Compliance Standards’ research shows that the overwhelming majority of large enterprises put data security at the top of their agenda, not
Publically available data used in this study can be found as deposited in the following data sets; DNAse I hypersensitivity data from GM12878: NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus