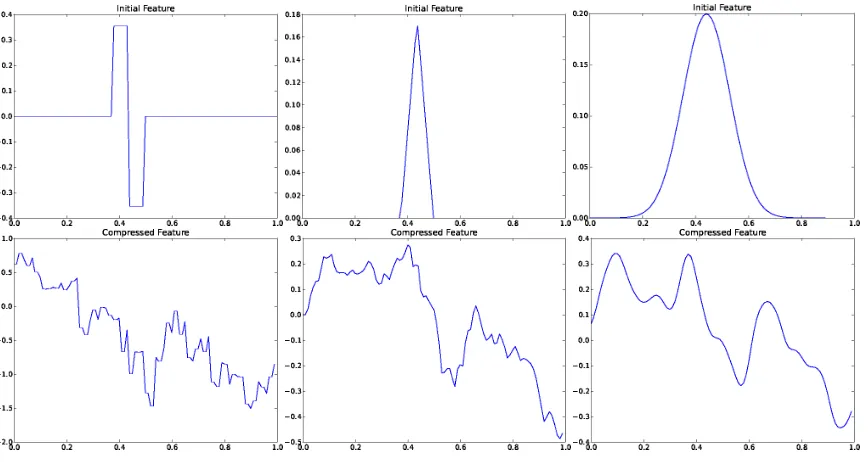
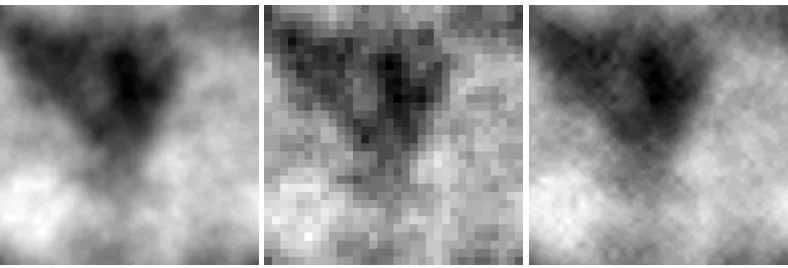
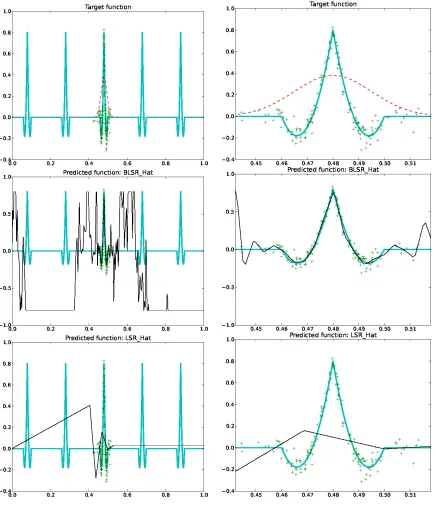
Linear Regression With Random Projections
Full text
Figure
Related documents
In conjunction with in vitro studies, a primary cell culture model will be developed to examine the separate functions of uterine smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts at term
These can be broadly grouped into the technological, the ideological and the ethical (or moral order). 1) Technologically, the developments in genetics early this century in
The objective of the present work is to establish a HSI simulator known as the Cranfield Hyperspectral Image Modelling and Evaluation System (CHIMES), which features an
In this study, satellite-based data with relatively high resolution are used as input data for empirical modeling with machine learning approaches in order to resolve the
In model 3, the lagged variable of total contributions is included to ensure the results are not driven by the function of the previous year’s values. The key results that show
VALUE $360M EXPERTISE Design + Construct TIMELINE 2011 - 2015 Wheatstone LNG Project BESIX, in a joint venture with Thiess, delivered a Material Offloading Facility (MOF) for
This study aimed to identify the impact of the information used in the internal control to improve internal control of accounting quality in Jordan Insurance companies IT
Finally, following all previous observations, we encode a constraint if at least one of two conditions holds: (i) the number of different explanations is more than half the number