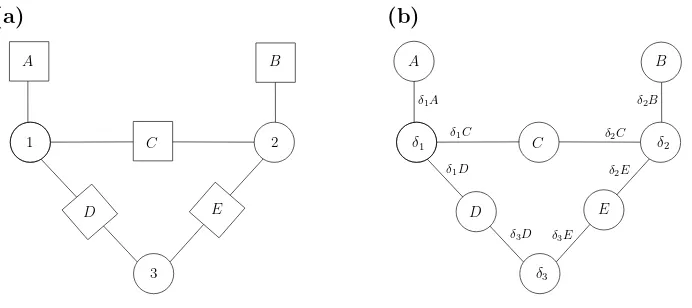
Approximate Inference on Planar Graphs using Loop Calculus and Belief Propagation
Full text
Figure
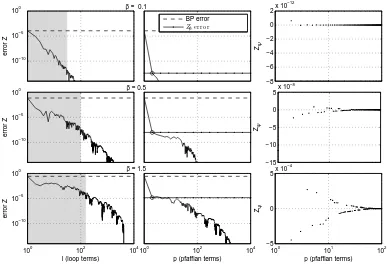
Related documents
Grünbaum on existing of admissible vertex coloring of every planar graph with 5 colors, in which every bichromatic subgraph is acyclic, is proved and some corollaries of this result
Specific protection goals were defined: (1) for off-field NTTPs as key drivers for nutrient cycling, water regulation, food web support, aesthetic values
Non-instructional Support Services Review Template Objective # Objectives (Improvements) Objective Measure (conditions/ criteria) Objective Baseline data Objective Current
Motivated by our recent joint SST-SSH identification of characterization of upper ocean dynamical modes, we here show that a multi- regime model, formally stated as a
Parish Council- Anne Schrishuhn ponzovista@gmail.com Education- Mary
While these studies deal exclusively with farms and not food sector businesses, Zambia provides an interesting contrast to Ethiopia and Ghana, particularly given the larger number
V záv ě ru byla navržená technologie porovnána se stávající technologií výroby pomocí ekonomických ukazatel ů používaných ve firm ě Honeywell Aerospace
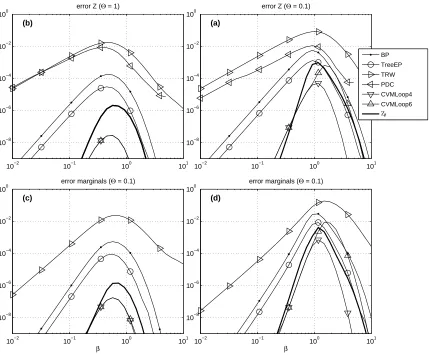
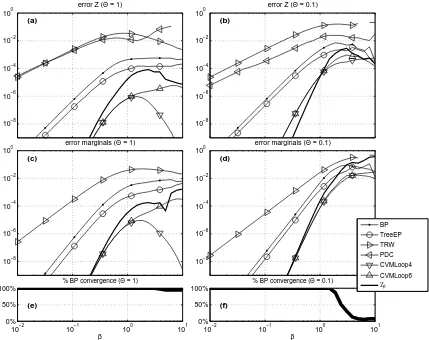
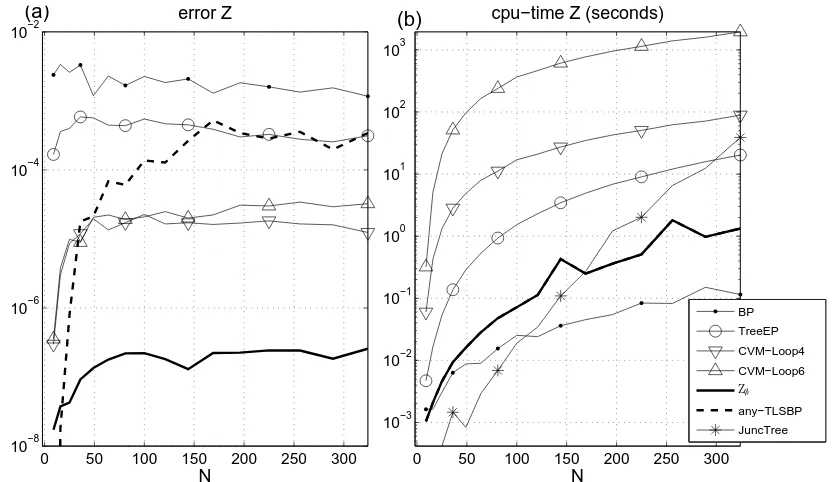
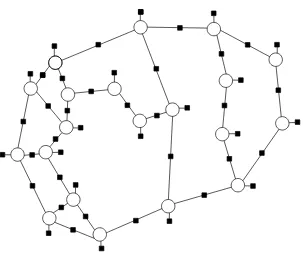
![Figure 8: Two examples of planar graphs used for comparison between methods. We fix the num-ber of concentric polygons to 9 and change the degree d of the central node within therange [3,...,25]](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/9825186.1968501/18.612.128.488.390.623/figure-examples-comparison-methods-concentric-polygons-central-therange.webp)