Predictive Model for Serious Bacterial Infections Among Infants Younger Than 3 Months of Age
Full text
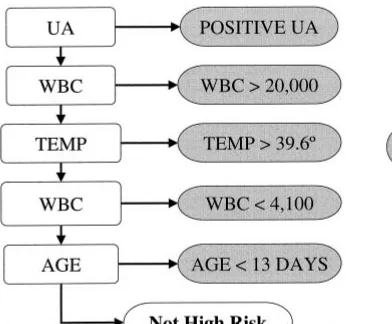
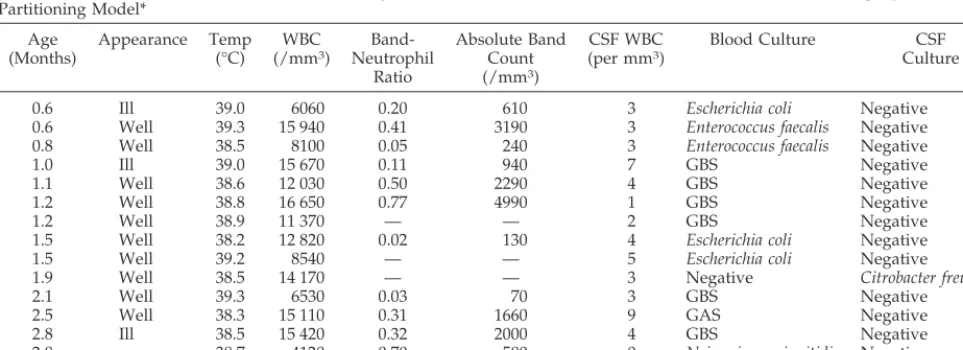
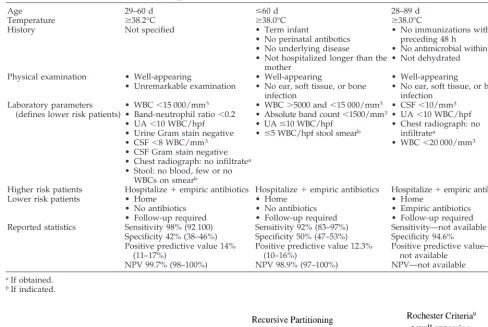
Figure

Related documents
Despite the fact that pre-committal proceedings involve interpreters in many more cases, that last for many more days and present a lot more challenges, the
In summary, from cluster formation to relay capacity es- timation and rate allocation, passing through D2D resource allocation and interference coordination, TOMRAN permits to
In conclusion, this study showed that in a patient group with mainly moderate and severe COPD experience a loss of peripheral muscle strength and endurance, exercise capacity
the hyperthyroid mother has produced goi- ter in the newborn.3 The precise functional status of the goiter presumably reflects the interplay between the dosage and duration
disorders should include explicitly theoretical elements. Does delusion have to be about external reality? Consider delusions that concern the subject’s own body — such
In the present study anatomical and chemical properties of Dendrocalamus memberceus Munro species results are shows that number of vascular bundle frequency and
Passed time until complete analysis result was obtained with regard to 4 separate isolation and identification methods which are discussed under this study is as
The following variables were included in the analysis: sex, age, body weight, body mass index (BMI), serum creatinine, CD4+ cell count, HIV-RNA, concomitant medications,