The ER Glycoprotein Quality Control System
Full text
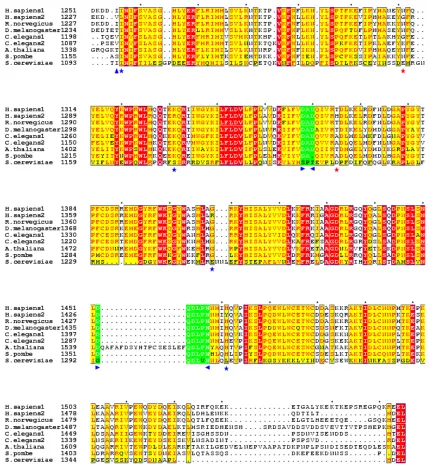
Figure


Related documents
This study aims to test whether the liquidity proxied by Current Ratio (CR) has an effect on the dividend policy of manufacturing sector of consumer goods sector
The objective of this paper is to describe the design of a multicenter, randomized, non-inferiority study to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of 40-h
Defects in microtubule polymerization, spindle pole body duplication, microtubule motors, and kinetochore components all activate the MAD-dependent checkpoint.. In contrast, the
This study demonstrated that the educational intervention consisting of academic detailing and information leaflet is a feasible approach to alter the antibiotic prescribing pattern
In addition to showing resistance to TMP/SMX and CAZ, the latter patient CF6 isolate was resistant to ciprofloxacin (MIC of ⱖ 32 g/ml; Table S3), a fluoroquinolone antibiotic
privilege. See TEXAS DISCIPLINARY RULES OF PROF. The court importantly noted that Orsak's effort to prevent exactly what happened fully complied with the provisions
AIRWAYS ICPs: integrated care pathways for airway diseases; ARIA: Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DG: Directorate General;
It was decided that with the presence of such significant red flag signs that she should undergo advanced imaging, in this case an MRI, that revealed an underlying malignancy, which