STRESS AND COPING STRATEGIES AMONG NURSING STUDENTS
Sheuli Sen
Professor, Amity College of Nursing, Amity University, Gurgaon
ABSTRACT
Students are subjected to different kinds of stressors, such as the pressure of academics with an
obligation to succeed, an uncertain future and difficulties of integrating into the system. A
descriptive study was conducted in a private nursing institute of Bangalore affiliated with The
Rajiv Gandhi University of Health sciences, Bangalore to assess stress level and coping
strategies among nursing students. Total of 180 students participated in the study. Perceived
Stress Scale -14 (PSS-14) was used to assess stress level and ACOPE was used to identify the
coping strategies. Results revealed that 34% students were having moderate stress and 33%
each were having mild and severe stress. Class of the students and their courses were found to
be significantly associated with the stress level of nursing students. Majority of subjects tend to
use more of healthy coping strategies as compared to negative or un-healthy ones. "Seeking
diversion" is the most common and "Seeking professional support" is the least common coping
strategy identified in nursing students.
Key words: Stress, Coping Strategy, Nursing Students
INTRODUCTION
Students are subjected to different kinds of stressors, such as the pressure ofacademics with an
obligation to succeed, an uncertain future and difficulties of integrating into the system1.
Moreover the transition between the middle childhood and adolescence represents a confluence
International Research Journal of Human Resources and Social Sciences
ISSN(O): (2349-4085) ISSN(P): (2394-4218) Impact Factor- 5.414, Volume 4, Issue 7, July 2017
Website- www.aarf.asia, Email : editor@aarf.asia , editoraarf@gmail.com
of social, academic, cognitive, physiological and physical changes. Pubertal maturation brings
morphological changes heralding reproductive maturity as well as increase in gonadal hormones
which influence central and peripheral stress response systems throughout the body and brain2.
Thus, stress among young brings socioemotional changes. Earlier studies have classified
stressors into three main categories: academic pressures, social issues and financial pressures3.
Academic stress among college students has been a topic of interest for many years. College
students, especially freshmen, are particularly prone to stress due to transitional nature of college
life, for e.g. many college students move away from home for first time, which can necessitate
leaving all previously learned support system such as parents, siblings and high school friends.
Students may need to develop entirely new social contacts and are expected to take responsibility
for their own needs. They may have difficulty in adjusting to more rigorous academic
expectations and the need to learn to deal with individuals of different culture and belief. Thus,
stress may result from being separated from home for the first time, the transition from personal
to impersonal academics and the vary structure of academic experience at the college level. In
nursing, students experience increased tension prior to their clinical rotation and written
examination especially their finals. Dhar R et al reported 48.83% mild stress and 11.62%
moderate stress among nursing students4. Clinical sources of stress include working with dying
patient, interpersonal conflict with other nurses, insecurity about clinical competence and fear of
failure and interpersonal relations with patients, work overload and are concerned about nursing
care given to the patient. Other potential sources of stress are assignment submission, excessive
homework, assessment deadlines, unclear assignments, uncomfortable classrooms and relations
with faculty members. Stress can have a significant effect on adolescent's long term physical and
mental well-being. The adolescents may become irritable, show lack of concentration, decreased
academic performance, poor interpersonal relations, insomnia and absenteeism5. Previous
studied have shown fairly high level of distress such as symptoms of depression and even
suicidal thoughts among medical undergraduates6, 7, 8. Learning to cope with a stress is a useful
skill for nursing career and a life ahead. By setting priorities, planning ahead by organizing self,
one can minimize the impact of stress. Lazarus and Folkman used the term coping to describe the
"cognitive and behavioral efforts", a person employ to manage stress, generally categorized as
emotional- focused and problem- focused coping9. Various coping strategies used by students
include ventilation, diversion, relaxation, self- reliance, social peer group support, avoidance,
found that least number of research databases is available to assess stress level among nursing
students due to their transitional age and academic pressure. Thus, the current study is taken up
to assess the "stress level" and "coping strategies" used by nursing students
METHODOLOGY
A Descriptive Survey study was conducted on nursing students in one of the private nursing
college situated in Bangalore and affiliated to The Rajiv GandhiUniversity of Health Sciences,
Bangalore. The college runs various nursing programs such as General Nursing & Midwifery
(GNM), B.Sc. Nursing, B.Sc. (Post-Basic) Nursing and M.Sc. Nursing. It has total covered area
of12.35 acre with all the basic amenities available within the campus. There are approximately
100 students residing in the hostel. The institution organizes various co curricular activities
regularly. There is provision of spor ts ground and sports equipments for all the students. The
institute organizes various religious activities from time to time. Target population for the study
involved all the nursing students enrolled during 2008- 2010. Total enumeration technique was
adopted and 180 nursing students were included in the study. The tools used for data collection
were Socio-demographic profile sheet, Perceived Stress Scale-14 (PSS-14) 11 and Adolescent
Coping Orientation for Problem Experiences (ACOPE).12,13 Socio demographic profile sheet
contained items such as age, sex, course, class, parent's education and occupation, family
income, distance from college, residential status etc.PSS-14 developed by Dr. Cohen was used
to assess the stress level among nursing students based on their feelings and thoughts in a last
one month. It is a 5-point liker t scale varying from 0=Never, 1=Almost Never, 2=Sometimes,
3=Fairly Often to 4=Very Often with a total of 14 items. The score range from 0-56. The
reliability of the scale was 0.85. ACOPE developed by Patterson & Mc-Cubbin (1987) was used
to assess the coping strategies used by nursing students to overcome stress. It is a 5-point liker t
scale varying from 0=Never, 1=Hardly, 2=Sometimes, 3=Often to 4=Most of the time. It
contains total 54 items under 12 domains. The reliability of the scale was 0.85.Pretesting of the
tool was done to check its clarity, feasibility and practicality. It took around 20-30 minutes to fill
the questionnaire and it was found clear and feasible. The permission for data collection was
obtained from the competent authority of the college. An informed verbal consent was taken
from the students. After filling the demographic profile sheet, the standardized PSS-14 and
ACOPE were administered to the subjects during their free period time. Anonymity and
full autonomy to withdraw from the study at any time. The final data was then transferred
to SPSS 15.0 evaluation version and analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics.
RESULTS
A study found that 58.3 % of nursing students were 19-25 yrs age whereas 41.7 % were below
18 yrs. Majority of the nursing students were females (87.2 %), from 1st year (41.6%), from B.
Sc. Nursing 4 years programme (72.3 %) and belonged to nuclear family (72.8 %). Fur ther data
indicated that only 28.3% and 16.1% nursing student's father and mother respectively had their
education up to graduation. Around 35.6% student's fathers were farmers and 75.6% student's
mothers were house wife. About 50.6 % of the subjects belong to families having monthly
income more than Rs.10, 000/-. Study indicates that 40.6 % of the students resided in the college
campus. Stress Level among Nursing Students The nursing student's stress was measured using
Perceived Stress Scale (PSS-14). The average score of each student's score on PSS-14 was
calculated. The total scores of the all the subjects were further averaged and categorized using
interquartile range into three categories: Low (25%), Moderate (50%) and Severe (75%) stress.
Findings revealed that out of 180 nursing students 62 (34.4%) had moderate stress whereas 59
(32.8%) and 59 (32.8%) fall in the category of low and high stress
respectively (Fig.1)
Fig 1: Stress Level Among Nursing Students
Student's mean PSS-14 score was 43.33 ± 6.22. Majority of the students reported that sometimes
during the last month, they remain upset (56.7%), unable to control important things of life 59.33%
59.33% 62.34%
Low Stress
High Stress
(49.4%), felt nervous or stressed (48.9%), could not cope up with the things (43.3%), exhibit
anger (45.6%) and thought about the accomplished things (42.2%). It was further found that the
students reported that sometimes during the last month, they use coping strategies to overcome
stress (44.4%), control irritation (46.7%), feel that thing are going their way (44.4%) and they
were on the top of the thing (48.9%) and able to control the way they spent their time (41.7%)
(Table1). Table 2 depicts the relationship of stress level of nursing students to the demographic
characteristics. It shows that stress level of nursing students is found to be significantly
associated with their class (p=0.000) and the type of course (p=0.000) i.e. significantly higher
percentage of 1st year students reported moderate and higher level of stress as compared to other
classes and the students undergoing post- graduation experienced high level of stress in higher
percentage followed by B.Sc nursing 4years programme, BSc Nursing Post basic and GNM in
descending order. The other demographic variables did not show any association with the stress
level of the study subjects. However it was observed that students between 19-25 years of age,
female students, and students from nuclear families were having high level of stress in higher
[image:5.612.55.568.411.689.2]percentage as compared to their counterparts.
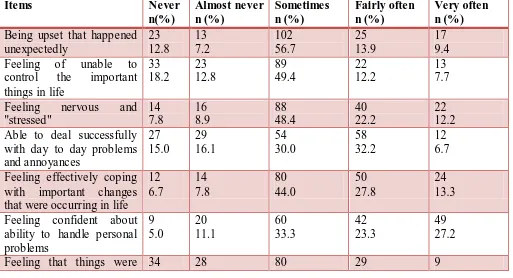
Table 1: Frequency of Perceived stress during the last one month by nursing stude nts as measured on Pe rceived Stress Scale (PSS-14) (N=180)
Items Never
n(%) Almost never n (%) Sometimes n (%) Fairly often n (%) Very often n (%) Being upset that happened
unexpectedly 23 12.8 13 7.2 102 56.7 25 13.9 17 9.4 Feeling of unable to
control the important things in life
33 18.2 23 12.8 89 49.4 22 12.2 13 7.7
Feeling nervous and
"stressed" 14 7.8 16 8.9 88 48.4 40 22.2 22 12.2 Able to deal successfully
with day to day problems and annoyances 27 15.0 29 16.1 54 30.0 58 32.2 12 6.7
Feeling effectively coping with important changes that were occurring in life
12 6.7 14 7.8 80 44.0 50 27.8 24 13.3
Feeling confident about ability to handle personal problems 9 5.0 20 11.1 60 33.3 42 23.3 49 27.2
going according to own way
18.9 15.6 44.4 16.1 5.0
Feeling unable to could not cope with all things that should be do
15 8.3 34 18.9 78 43.3 35 19.41 18 10.0
Able to control irritation in life 13 7.2 21 11.7 84 46.7 39 21.7 23 12.8 Feeling on top of things 31
7.2 29 16.1 88 48.9 20 11.1 12 6.7 Being angered because
things were happening outside of control
14 7.8 12 6.7 82 45.6 40 22.2 32 17.8
Thinking about the things that to be accomplished
15 8.3 20 11.1 76 42.2 39 21.7 30 16.7 Able to control the way of
spending time 13 7.2 31 17.2 75 41.7 43 23.9 18 10.0 Feeling that difficulties
were piling up so high that
they could not be
[image:6.612.55.566.35.325.2] [image:6.612.68.559.406.692.2]overcome 9 6.1 31 17.2 60 33.3 30 20.0 24 (13.1)
Table 2: Stress Level Based on Socio Demographic Changes n=180
Socio Demographic characteristics
Low n(%)
Level of Stress Moderate n (%)
High n (%) Chiq-Square p-value Age(yrs) <18 19-25 28(37.33) 31(29.52) 26(34.67) 36(34.29) 21(28.00) 38(36.19) p= 0.425 Sex Male Female 07(30.44) 52(33.12) 12(52.17) 50(31.85) 04(17.39) 55(35.03)
p= 0.113
Class Fresher Senior 28(33.74) 31(31.97) 27(32.53) 35(36.06) 28(33.73) 31(31.97) p= 0.000* Course GNM B.Sc
B.Sc (Post Basic) M.Sc 28(59.58) 26(23.42) 05(26.32) 00(0.00) 11(23.40) 43(38.74) 08(42.10) 00(0.00) 08(17.02) 42(37.84) 06(31.58) 03(100.00) p= 0.000*
Joint Nuclear
39(29.32) 46(34.59) 48936.09)
Education of father Upto 10th
More than 10th
25(37.31) 34(30.08)
34(35.82) 38(33.64)
18(26.87) 41(36.28)
p= 0.395
Education of mother
Upto 10th More than 10th
41(37.96) 18(25.00)
35(32.41) 27(37.50)
32(29.63) 27(37.50)
p=0.185
Occupation of father
Govt. Employee Non-Govt. Employee
14(25.00) 45(36.29)
21(37.50) 41(33.06)
21(37.50) 38(30.65)
p=0.318
Occupation. of mother
Housewife Working
44(32.35) 15(34.09)
51(37.50) 11(25.00)
41(30.15) 18(40.91)
p=0.257
Monthly income Below Rs 10,000 Above 10000
36(40.45) 23(25.27)
25(28.09) 37(40.66)
28(31.46) 31(34.07)
p=0.069
Distance
Within the campus Between 1- 30 km Above 30 km
22(30.14) 29(43.94) 08(19.51)
28(38.35) 16(24.24) 18(43.90)
23(31.51) 21(31.82) 15(36.59)
p=0.075
Type of residence Living in Hostel Living with Parents Others
27(32.92) 25(31.25) 07(38.89)
31(37.81) 25(31.25) 06(33.33)
24(29.27) 30(37.50) 05(27.78)
p=0.776
p*<0.05, significant
Coping strategies
The coping strategies used by nursing students to overcome stress were measured by using
ACOPE. It contains total 54 items under 12 domains. The mean score of coping strategies used
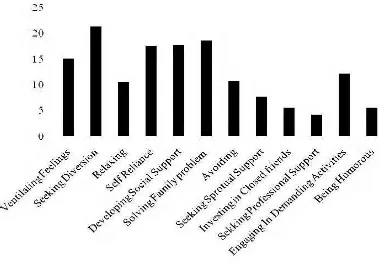
by nursing students under 12 domains of ACOPE showed that from the most commonly used to
least commonly used coping strategies are in the following order seeking diversion (21.3±4.86),
solving family problems (18.6±4.85), developing social support (17.7±3.61), self-reliance
(17.5±4.19), ventilating feelings (15.03±4.23), engaging in demanding activit ies (12.2±2.86),
humorous (5.6 ±2.02), investing in close friends (5.52±2.04), seeking professional support
[image:8.612.88.472.82.348.2](4.14±2.19) (Fig.2).
Fig.2 Coping strategies used by nursing Students
Table 3 shows that most commonly used strategy by the students for ventilating feelings was
complaining to their friends (36.7%) and crying (22.8%). Further, it has been seen that most of
the times, the students
listen to music, stereo or radio (36.7%), engaged in day-dreaming (23.3%) or hobby (14.1%) or
eat food (13.9%) to divert their mind and to relax themselves during the periods of stress. In the
area of self-reliance, students reported that most of the times, the y try to think of or see good
things (26.7%), try to organize their life (19.4%) and try to make their own decisions (18.3%).
Around 32% of the students tried to cope with the stress by helping other people in solving their
problems or by blaming others for their problems respectively. ACOPE showed that most of the
times, nursing students try to reason with parents (21.1%), talk with mother (30%), brother or
sister (21.7%) about their problems and feelings or go along with parents request (22.2%).
of stress. More than 30% of the students try to cope with the stressful situations by figuring out
the way to solve their problems while improving their work performance. Around 25% of the
nursing students reported that the stress was relieved to some extent by being close to someone
who cares or loves (Table 4). It has been further shown that the least common strategies used by
nursing students to cope with stress were smoking (76%), using drugs (73.3%), liquor, wine or
beer (71.7%), drugs prescribed by the doctor (71.7%), talking to minister, priest or rabbi
(58.9%), getting professional help (58.9%),being with the boyfriend or girlfriend (57.8%) and
[image:9.612.68.564.242.690.2]riding around in the car (53.9%) (Table 3 & 4).
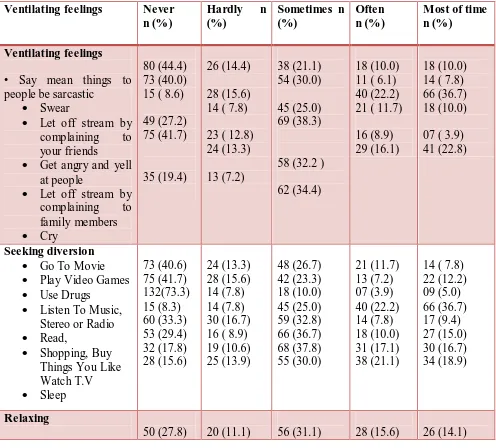
Table 3: Coping strategies used by nursing students
Ventilating feelings Never n (%)
Hardly n (%)
Sometimes n (%)
Often n (%)
Most of time n (%)
Ventilating feelings • Say mean things to people be sarcastic
Swear
Let off stream by complaining to your friends
Get angry and yell at people
Let off stream by complaining to family members
Cry
80 (44.4) 73 (40.0) 15 ( 8.6)
49 (27.2) 75 (41.7) 35 (19.4) 26 (14.4) 28 (15.6) 14 ( 7.8)
23 ( 12.8) 24 (13.3) 13 (7.2) 38 (21.1) 54 (30.0) 45 (25.0) 69 (38.3)
58 (32.2 )
62 (34.4)
18 (10.0) 11 ( 6.1) 40 (22.2) 21 ( 11.7)
16 (8.9) 29 (16.1)
18 (10.0) 14 ( 7.8) 66 (36.7) 18 (10.0)
07 ( 3.9) 41 (22.8)
Seeking diversion
Go To Movie
Play Video Games
Use Drugs
Listen To Music, Stereo or Radio
Read,
Shopping, Buy Things You Like Watch T.V Sleep 73 (40.6) 75 (41.7) 132(73.3) 15 (8.3) 60 (33.3) 53 (29.4) 32 (17.8) 28 (15.6) 24 (13.3) 28 (15.6) 14 (7.8) 14 (7.8) 30 (16.7) 16 ( 8.9) 19 (10.6) 25 (13.9) 48 (26.7) 42 (23.3) 18 (10.0) 45 (25.0) 59 (32.8) 66 (36.7) 68 (37.8) 55 (30.0) 21 (11.7) 13 (7.2) 07 (3.9) 40 (22.2) 14 (7.8) 18 (10.0) 31 (17.1) 38 (21.1)
14 ( 7.8) 22 (12.2) 09 (5.0) 66 (36.7) 17 (9.4) 27 (15.0) 30 (16.7) 34 (18.9) Relaxing
• Work on a hobby
Eat food
Day dream
Ride around in the car 67 (32.2) 39 (21.7) 97 (53.9) 33 (18.3) 12 (6.7) 18 (10.0) 38 (21.1) 52 (28.9) 26 (14.4) 17 (9.4) 42 (23.3) 23 (12.8) 25 (13.9) 42 (23.3) 16 (8.9) Self-reliance
• Get a job or a work harder
Try to think of good things
Try to make your own decisions
Organize your life that what you have to do
Get more involved in activities in school
Tell yourself that problem(s) is not important 67 (32.2) 21 (11.7) 23 (12.8) 46 (25.6) 60 (33.3) 27 (15.0) 30 (16.7) 18 (10.0) 13 (7.2) 08 (66) 29 (16.1) 29 (16.1) 37 (20.6) 51 (28.3) 69 (38.3) 66 (36.7) 66 (36.7) 71 (39.4) 25 (13.9) 42 (23.3) 42 (23.3) 25 (13.9) 14 (7.8) 31 (17.2) 21 (11.7) 48 (26.7) 33 (18.3) 35 (19.4) 11 (6.1) 22 (12.2) Developing social support
• Blame others for what's going on
Apologize to
people
Try to help other people solve their problems
Try to keep up friendships or make new friends
Say nice things to others
Table 4: Coping strategies used by nursing students Coping strategies
Solving family problems
Talk to your
father about what bothers you
Try to reason with parents and talk
things out,
compromise
Go along with parents request
Do things with your family
Talk to a brother or sister about how you feel
Talk to your
mother about
what bothers you
57 (31.7) 27 (15.0) 23 (12.8) 37 (20.6) 41 (22.8) 21 (11.7) 18 (10.0) 13 (7.2) 20 (11.1) 14 (7.8) 24 (13.3) 25 (13.9) 66 (36.7) 69 (38.3) 68 (37.8) 61 (33.9) 46 (25.6) 55 (30.6) 13 (7.2) 33 (18.3) 29 (16.1) 33 (18.3) 30 (16.7) 25 (13.9) 26 (14.4) 38 (21.1) 40 (22.2) 35 (19.4) 39 (21.7) 54 (30.0) Avoiding • Smoke
Use drugs
prescribe by
doctors
Try to stay away from home as much as possible
Try to see the good things
Drink beer ,wine , liquor 137 (76.1) 129 (71.7) 81 (45.0) 21 (11.7) 129 (71.7) 8 (4.4) 20 (11.1) 20 (11.1) 18 (10.0) 09 (5.0) 15 (8.3) 13 (7.2) 39 (21.7) 51 (28.3) 16 (8.9) 09 (5.0) 05 (2.8) 21 (11.7) 42 (23.3) 11 (6.1) 11 (6.1) 13 (7.2) 19 (10.6) 48 (26.7) 15 (8.3) Seeking spiritual support
• Talk to minister, priest or rabbi
Go to church
Pray 106 (58.9) 88 (48.9) 21 (11.7) 22 (12.2) 21 (11.7) 13 (7.2) 31 (17.2) 38 (21.1) 45 (25.0) 14 (7.8) 12 (6.7) 37 (20.6) 07 (3.9) 21 (11.7) 64 (35.6)
Investing in close friends
Be close with someone you care about
Be with a boy
friend or girl friend
Seeking professional support
• Get professional counseling
Talk to counselor at school about what bothers you
106 (58.9) 83 (46.1)
19 (10.6) 24 (13.3)
34 (18.9) 37 (20.6)
11 (6.1) 16 (8.9)
10 (5.6) 20(11.1)
Engaging in de manding activities
• Do a strenuous physical activity ( jogging, biking etc)
Try, on your own, to figure out how to deal with your problems and tensions
Try to improve yourself (get body in shape, get better grades, etc.)
Work hard on school work or school projects
86 (47.8)
08 (4.4)
14 (7.8)
46 (25.6)
21 (11.7)
17 (9.4)
19 (10.6)
30 (16.7)
50 (27.8)
58 (32.2)
48 (26.7)
50 (27.8)
11 (6.1)
42 (23.3)
40 (22.2)
26 (14.4)
12 (6.7)
55 (30.6)
59 (32.8)
28 (15.6)
Being humorous • Joke and keep a sense of humor
Try to be funny and make it light of it all
54 (30.0) 38 (21.1)
23 (12.8) 14 (7.6)
6.5 (36.1) 72 (40.0)
19 (10.6) 22 (12.2)
19 (10.6) 34 (18.9)
DISCUSSION
Stress in nursing students is an area of growing concern and it may result in psychological
distress, physical complaints, behavior problem and poor academic performance. The present
The Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore to assess the stress level and coping
strategies used by nursing students.
Findings revealed that out of 180 nursing students 34.4% had moderate stress whereas 32.8%
and 32.8% fall in the category of low and high stress respectively which was slightly consistent
with the study conducted among undergraduates students of CMH Lahore medical college,
Pakistan on 200 students which reported 30.84 overall mean perceived stress14. However, stress
level of first year and third year B.Sc. Nursing students is found to be significantly high than
other classes (p=0.000, p=0.000 respectively). The findings were consistent with the findings of
an Iranian study conducted by Seyedfatemi et al10 among nursing students. This may be because
the students face more of stressors when they come to college during first year of their training
because of being placed in an unfamiliar environment, separation from the parents and the
demand of making new social groups apart from academic pressures and clinical training.
However, the nursing students were constantly facing demands and challenges of the curriculum
which had being a source of stress during their total training program.
Coping strategies refer to the specific efforts, both behavioral and psychological, that people
employ to master, reduce tolerate or minimize stressful events. Coping with stress for a student
nurse is a dynamic and ongoing process, aimed at survival, growth and maintenance of the
individual integrity. She tries to restore the imbalance and disequilibrium within her by
attempted adjustment through the use of various coping strategies which can be healthy or
unhealthy. WHO/EHA guidelines have stated that there are no standard for coping strategies;
rather they were depending on socio-economic factors. In the present study, majority of subjects
tend to use more of healthy coping strategies as compared to negative or unhealthy ones.
"Seeking diversion" is the most common and "Seeking professional support" is the least common
coping strategy identified in nursing students which are consistent with the findings of a similar
study among nursing students at Chiang Mai University which revealed that the most frequently
used coping strategies were seeking social support (62.25%), painful problem solving (23.73%)
and accepting responsibility (8.47%)15. Another study at the NINE, PGIMER, Chandigarh
reported the five most frequently used coping strategies were positive thinking, listening to the
music/radio, indulging in creative activities, talk to parents and pray more4. However, the study
findings was inconsistent with the findings of the study done on Iranian students which reported
solving family problems and being humorous as the most common and least common used
Stress has become a chronic and pervasive condition in the world today. Every person
experience different forms of stress throughout their life, therefore a student nurse is no
exception as she has to adjust to an entirely new environment on joining a tra ining course in
nursing. It has been concluded that the nursing students perceived different levels of stress due to
academic, clinical and other psychosocial factors. Further, they use a mix of coping strategies to
overcome stress so as to maintain a balance on a wellness-illness continuum. Coping with stress
for a student nurse is a dynamic and ongoing process, aimed at survival, growth and maintenance
of the individual integrity. She tries to restore the imbalance and disequilibrium within her by
attempted adjustment through the use of various coping strategies which can be healthy or
unhealthy. It is important for nurse educator to find out the sources of stress and coping
strategies used by the students so that they can be helped to cope well with upcoming problems
and situations.
REFERENCES
1. Chrousos GP, Torphy DJ, Gold PW. Interaction between the hypothalamic –pituitaryadrenal
axis and the female reproductive system: clinical implications. Annals Intern Med 1998; 129(3):
229-40
2. Spear LP. The adolescent brain age - related behavioral review 2000; 24(4):417-63
3. Fisch, Niles MA. Health students in college environment. Public Health Nursing 1996
;13:104- 11
4. Dhar R., Walia I, Das K. A descriptive study to assess the causes of stress and coping
strategies used by the newly admitted basic B.Sc nursing students. Nursing and midwifery
research journal 2009; 5(1):31-37
5. Dahlin M, Joneborg N, Runeson B. Stress and depression among medical students: a cross
sectional study . Med educ 2005; 39:594-604.
6. Zocolillo M, Murphy GE, Wetzel RD: Depression among medical students. J affect disord
1986;11:91-96.
7. Pheukphan AP. Stress and coping strategies among AU (Australian) nursing students 2009
Available at url: www.nurse.au.edu/. Accessed on 23.03.2011
8. Papazisis G, Ulasidis I. Depression and anxiety among students in Greece 2008 Available at
url: www.annals-general-psychiatry.com/ content/7/s1/s209. Accessed on 23.03.2011
10. Seyedfatemi N. Experienced stressors and coping strategies among Iranian nursing students,
BMC nursing 2007, 6(1). Available at url: http:/www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6955/6/
11. Accessed on 25.03.2011 11. Copeland EP, Hess RS. Differences in young adolescents'
coping strategies based on gender and ethnicity. Journal of Early Adolescence 1995; 15:203-19.
12. Patterson JM, McCubbin HI. Adolescent coping style and behaviors – conceptualization and
measurement. Journal of Adolescence 1985; 10(2):163-186.
13. Dr. Cohen's Scale [online] Available from url: http://www.psy.cmu.edu/~scohen/
Perceived%20Stress%20Scale%20(PSS)%2014- item.doc
14. Shah M, Hasan S, Malik S, Seeramareddy CT. Perceived stress, sources and severity of stress
among medical undergraduates in Pakistani medical school. BMC medical education [online]
2010, 10(2). Available at url: http://www.biomedcentral.com/ 1472-6920/10/2.
15. Hsiao YC, Chier LY, Wu Lt, Chiang CM, Huang ST et al. Spiritual health, clinical practice
stress, depressive tendency and health promoting behaviors among nursing students, Journal of