Ageing, autoimmunity and arthritis: T cell senescence and contraction of T cell repertoire diversity – catalysts of autoimmunity and chronic inflammation
Full text
Figure
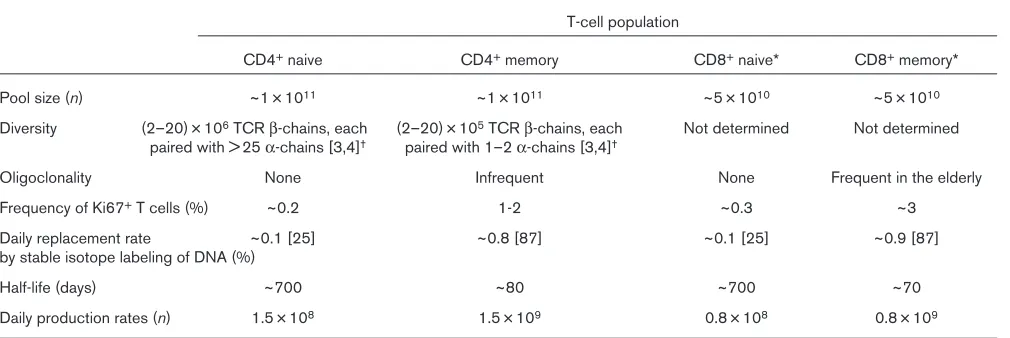
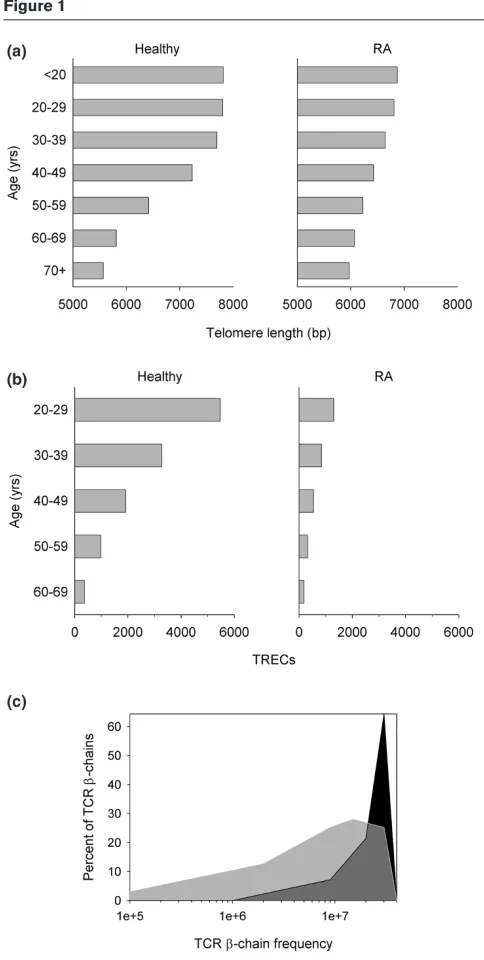
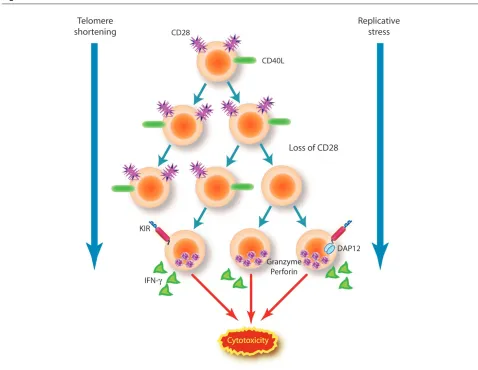

Related documents
In order to obtain experim ental values of the aperture averaging factor, variances from the larger apertures have to be norm alised by those from the smallest,
Figure 2 The number and incidence rates per 100,000 person-years of fracture at ( A ) the hip and ( B ) other sites by 10-year age groups among males and females in Kuwait,
To investigate its immune action in vivo , we selected the murine myeloma cell line 5TGM1, which is resistant to direct tumoricidal effects of lenalidomide in vitro.. and
Among the 19 observed strains that were phenotypically resistant to SLIDs, 4 strains had mutations in the rrs gene, 8 strains had mutations in the eis gene, one had mutations in
In this study, we report that the first-promoter-specific transcript 1 is the major PEMT mRNA species in human breast tissues, and that methylation of the -132 site is a
We carried out a mutational analysis of 3,594 genes coding for cell surface proteins (Surfaceome) in 23 colorectal cancer cell lines, searching for new altered pathways,
They were cultured on Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium. Spores were harvested in 0.1% Tween – 80 solution in double distilled water. Concentration of spores/ml in the
Methods/ Statistical analysis: A control circuit is constituted by utilizing a discharge element with control electrode and a surge voltage is applied to the control circuit