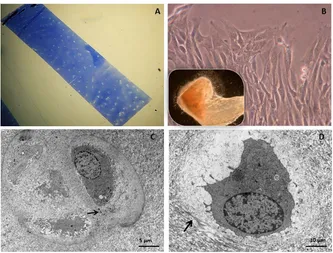
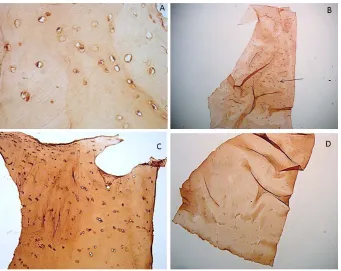
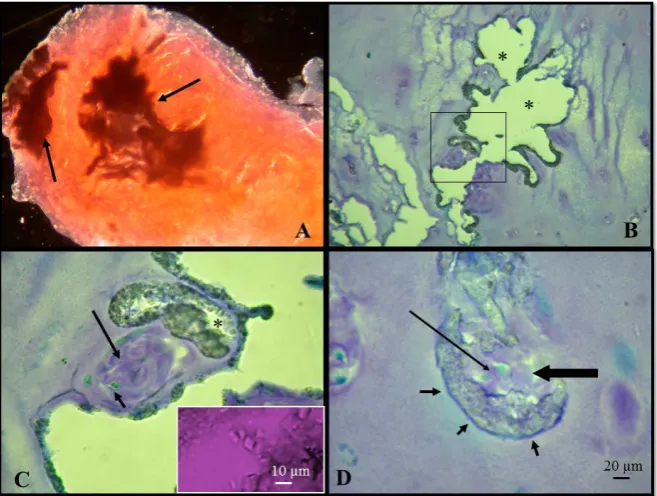
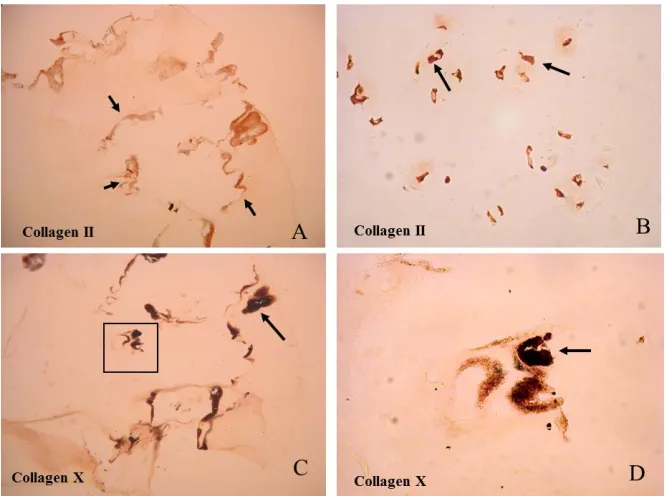
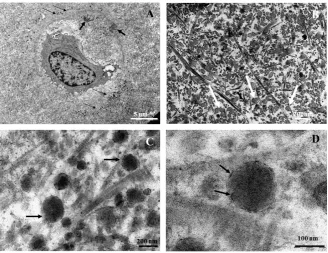
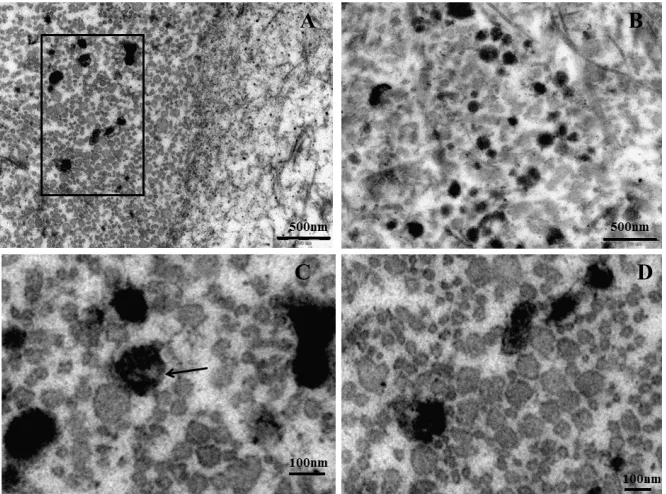
Intra Articular Cartilage Calcification Associated with Type II Pro Collagen Accumulation in Chondrocytes and Abnormal Fibrils in the Extra Cellular Matrix (ECM): Case Report
Full text
Figure
Related documents
A total of 399 of these interviews, conducted with parents or guardians, collected information on the bicycle and helmet use patterns of children younger than 15 years of age..
(a) Results of the transfer function output shows the performance of the weighted-average model with inverse and classical deshrink- ing (WAinv, WAcla), weighted-average partial
Abbreviations: A anterior, CMB cartilage of the mushroom body, D dorsal, DV duct of the vomeronasal organ, L lateral, LDL lateral diverticulum of the lacrimal duct, LDV lateral
adolescent CD patient who presented with severe anorexia and thinness, mimicking the restricting type of anorexia nervosa (AN)..
Almost all of the women in the study expressed a personal desire to help their peers, and many of them said that they would be happy to per- sonally be more actively engaged
The focus of the paper, however, is a computational account of random generation which critically involves the control processes of memory updating and monitoring,
Facility Layout Problems (FLPs) are known to be NP-hard problems; various optimization approaches for small problems and heuristic approaches for the larger problems