Decision Trees for Lexical Smoothing in Statistical Machine Translation
Full text
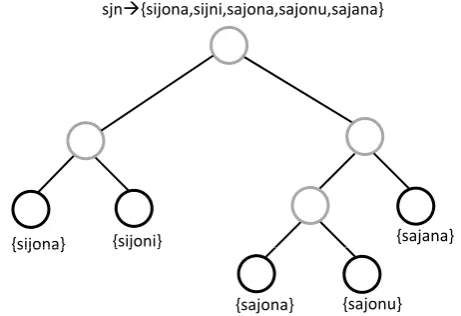
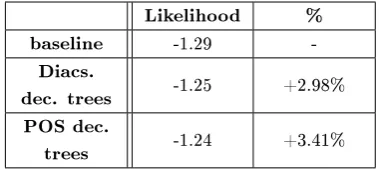
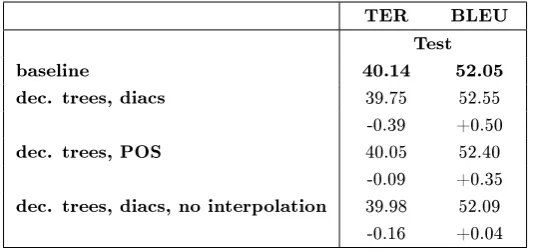
Figure

Related documents
Context Aware Smoothing for Neural Machine Translation Proceedings of the The 8th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, pages 11?20, Taipei, Taiwan, November 27
Meta level Statistical Machine Translation International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, pages 1151?1157, Nagoya, Japan, 14 18 October 2013 Meta level Statistical
In this paper, we investigate three issues of term translation in the context of document- informed SMT and propose three cor- responding models: (a) a term trans- lation
Although the focus of research in machine transla- tion has firmly moved onto neural machine trans- lation, we still built traditional phrase-based statis- tical machine
In order to provide points of comparison with the 2009 Workshop on Statistical Machine Trans- lation shared translation task participants, table 4 lists automatic metric scores for
Statistical machine translation facilitates us to automatically build machine translation systems using statistical models capable by text data. The statistical models comprise
For instance, in statistical machine trans- lation (SMT), [12, 13] showed how the output of a trans- lation model can be used iteratively to improve results in a task like
Sharing source and target side vocabularies and word embed- dings has been a popular practice in neural machine trans- lation (briefly, NMT) for similar languages (e.g., English