A STUDY OF INFORMATION
COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
EFFECTIVENESS IN SELECT
GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATION AT
JHARKHAND STATE
TANUSHREE BHATNAGAR
Assistant Librarian, Birla Institute of Technology, Deemed University, Mesra, Ranchi, Jharkhand, tanushreebhatnagar@gmail.com
A.N. JHA
Professor & I/C BIT Extension Centre Lalpur, Ranchi, Jharkhand
H.K SINGH
Xavier Institute of Social Sciences(XISS) Ranchi, Jharkhand, hkxiss@rediffmail.com
Abstract :
This article describes the role of Information communication Technology in electronic governance in Jharkhand State. Importance of e-governance in current scenario, Influences of ICT in governance process & Implementation of e-governance in Jharkhand are also discussed. The success of e-governance depends on the use of ICT in mobilization of government resources with an aim to provide better services to citizens.The main purpose of this study is to find out the effectiveness of ICT in e-Governance in the departments of Jharkhand States
Keywords: ICT; e-Governance; e-governance in Jharkhand
1. Introduction
e-Governance is used as a synonym to describe an IT driven system of Governance that works better, costs less and is capable of servicing the needs of the citizens and businesses as never before. Its goal is to create a more responsive, productive and effective administration. E-Governance is also referred to as SMART Governance because it aims at using IT to the processes of Government functioning to bring about Simple, Moral, Accountable, Responsive and Transparent Governance. The Citizens to Government (C2G) and Government to Citizen (G2C) are the core pillars of not only e-governance but electronic commerce (e-commerce) as well
2. IT Policies of Jharkhand
The new State Jharkhand formerly a part of Bihar state, was formed on November 15th, 2000 with Ranchi as its capital. Jharkhand is the 28th state of the Indian Union. Jharkhand.
Jharkhand was formed as a separate state on November 15th, 2000 with Ranchi as its capital. Government of Jharkhand took conscious decision to make greater use of IT in governance. Thus in 2002 process of e-governance started.
2.1.1 Vision
“To ensure large scale socio-economic development, sustained growth, transparency in government policies & decisions, and enhanced service delivery by effective use of Information Technology.”
2.2.2 Objectives
IT policy of the State of Jharkhand will provide guidance to all agencies involved in the goal of overall development of the state using IT as the enabler. Agencies in the state who are likely to use the IT policy are Citizens, various ministries, legislative, IT entrepreneurs, business & professional associations and other stakeholders.
Initiatives for “Improved Communications & Infrastructure”
• JharNet State wide High Speed, Reliable & Scalable Communication links will be set up by the state government.
• Internet connectivity across the state
• Seamless connectivity among various govt. organizations • Internet connectivity across the state
3. Genesis of e-Governance in Jharkhand at a glance
Following table enlists the important events in the genesis of e-governance initiative in the state of Jharkhand which we have taken as the target state for our research.
Table 1.Genesis of e-Governance in Jharkhand
Source: Bhatnagar, Tanushree et. al. “Use of Information Communication Technologies(ICT) in E-governance: A review” IJ-ETA-ETS July 2010ISSN : 0974-3588
During the past few year’s with the active support of various agencies, following are the some of the Year Mile-stones for
E-governance
Goal
2000 Origin in Jharkhand Decision to make greater use of IT in governance
2000 Setting up of NIC To provide Intranet and Internet connectivity to the State Administration through NICNET.
2002 New Computer Policy Process of e-governance started
2002 Setting up of JharNet State wide High Speed, Reliable & Scalable Communication links will be set up by the state government.
2003 Passport Control and Issuance System
Online passport System
2005 Treasury Computerization computerize the functioning of all the treasuries departments.
2007 CSC plans to set-up 4562 Common Service Centres (CSC) through out all the panchayats in the State in first phase a
2007 E-Nagrik Seva to provide good governance to the common citizens through the usage of ICT, for providing G2C services from the Kendra
2008 Jharkhand Agency for Promotion of Information Technology (JAP-IT)
GOJ designated JAP-IT- as the nodal agency for the implementation of Common Service
• Land Records Information System • Election Support System
• Prison Management System
• Video Conferencing based Public Justice in jails of Jharkhand • City Civil Court Computerization.
• High Court Computerization
• Computerization Support to the Raj Bhawan and CM Secretariat • Training Support
• Public Grievances Monitoring System
• Human Resource Management System (e-Personnel) • DM’s Court Monitoring System
• Online Project Monitoring • Online Passport
• Other District Activities • E-Nagrik Seva
• Pragya Kendra
Govt of India , NCAER made a survey in 2003 about the development and penetration of IT in the state economics. In this survey states have been rated on Five parameters viz. network access, Network Learning, Network society, network Economy and E-Governance. Further states have been slotted into 6 categories these are: Leaders, Aspiring Leaders, Expectants, Average Achievers, Under achievers and Laggards. According to this survey Jharkhand is a Laggards in the Information Technology in India. First time in 2006 Government of Jharkhand won the award for its achievement in E-governance.
According to Datquest IDC Survey in 2008 Jharkhand comes in a last position. Jharkhand is a worst State in Satisfaction level of Business with governance services and also the satisfaction level of citizens with e-governance services in the Agriculture, Healthcare, Transport Services, Employment Exchange& Land Property Department.
4. Methodology
The data has been collected from the Government of Jharkhand three departments ie Land Record, Treasury and Transport Department. There are three set of questionnaire for three different types of respondents ie. Top management, IT management and Users of the system. Out of total 85 questionnaire only 68 respondents have responded fairly. Data is collected from Ranchi and Jamshedpur districts of the Jharkhand State. The frequency tables along with charts are prepared as per the requirement of the study using statistical package for Social Science (SPSS).
5. Descriptive Statistical Analysis
This part covers the analysis of data using descriptive statistics. The objective of descriptive statistics was to provide summary measures of data contained in all the elements of the sample. In doing so we use frequency tables, mean, percentage of data scored by the elements/variables and standard error. The relevant tables were generated for the variables under study i.e IT use, User satisfaction , IT management and Top management.
5.1. ICT Use
Table 5.1 ICT Use
Q.No Contents Frequent
(%)
Infrequent (%) 1.
M:
How often do you use current System in the organization.
75% 25%
Heavy Light
2. M:
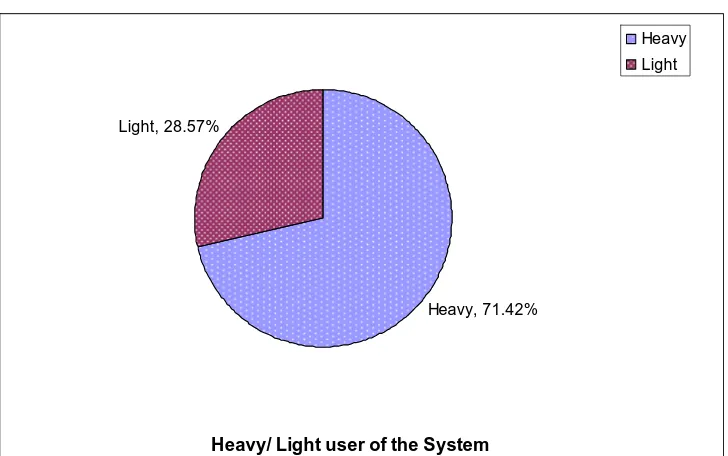
Do you intend to be Heavy/Light user of the System.
71.42% 28.57%
Frequently/Infrequently using the system
Frequent , 75% Infrequent, 25%
Frequent
Infrequent
Figure 5.1.1 Frequently/Infrequently using the System
Heavy, 71.42% Light, 28.57%
Heavy
5.2. User Satisfaction
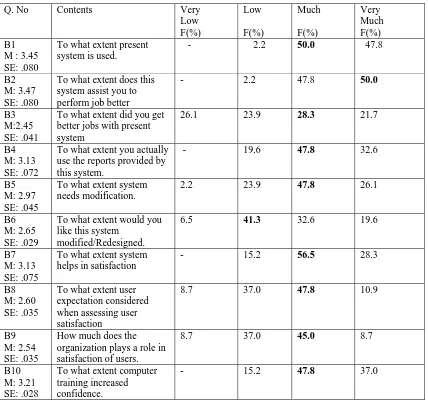
This mainly focuses on the ICT use and satisfaction of users with the system. The result shows that the system use is high in comparison to the original system. As felt by 50% respondents (refer B1Table 5.2) and also 50 % respondents feel that the system assisted them in performing their job better.
The analysis indicates that the respondent got better jobs after implementation of the system.
The 47.8% of users are using the reports provided by the system (refer B4, Table 5.2). And about 47.8% (refer B5) feels that the system require little modifications and about 41.3% (refer B6 Table 5.2) respondents feels that system should be redesign. 56.5% of respondents were highly satisfied with the system (refer B7, table 5.2) and about 40.6% users were of the view that there expectations should be considered while assessing user satisfaction. According to 45% of responded said that organization plays their role in satisfaction of the user. 47.8% of users are of the opinion that the computer training and ICT use increase the confidence among the users to a very high extent (refer B10 Table 5.2.).
As per the users of the system It can be concluded that although the system assists the users in performing their job better. It is not adequate if the proper computer training on a periodic basis is not provided to the users. During interaction with the users, It was found that there was a need for training on ICT applications on a periodical basis for better use of the system.
Table 5.2 User Satisfaction
Q. No Contents Very
Low F(%) Low F(%) Much F(%) Very Much F(%) B1
M : 3.45 SE: .080
To what extent present system is used.
- 2.2 50.0 47.8
B2 M: 3.47 SE: .080
To what extent does this system assist you to perform job better
- 2.2 47.8 50.0
B3 M:2.45 SE: .041
To what extent did you get better jobs with present system
26.1 23.9 28.3 21.7
B4 M: 3.13 SE: .072
To what extent you actually use the reports provided by this system.
- 19.6 47.8 32.6
B5 M: 2.97 SE: .045
To what extent system needs modification.
2.2 23.9 47.8 26.1
B6 M: 2.65 SE: .029
To what extent would you like this system
modified/Redesigned.
6.5 41.3 32.6 19.6
B7 M: 3.13 SE: .075
To what extent system helps in satisfaction
- 15.2 56.5 28.3
B8 M: 2.60 SE: .035
To what extent user expectation considered when assessing user satisfaction
8.7 37.0 47.8 10.9
B9 M: 2.54 SE: .035
How much does the organization plays a role in satisfaction of users.
8.7 37.0 45.0 8.7
B10 M: 3.21 SE: .028
To what extent computer training increased confidence.
5.3. ICT management
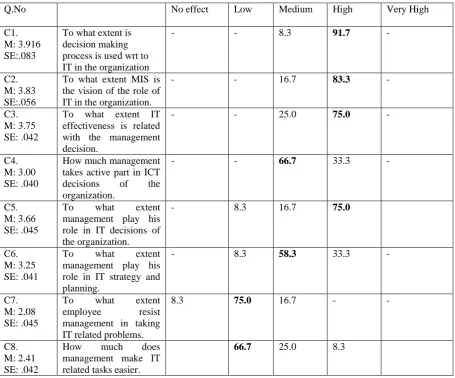
This part focuses the role of IT management or System analyst of the organization who were involved in the implementation of information system in the organization. The contribution of IT management should improve the effectiveness on ICT in the organization.As result shows about 91.7% felt that decision making process is used with respect to IT in the department which is very high (refer C1, Table 5.3) .According to 83.3% (refer C2,Table 5.3)respondents felt that MIS is the vision of the role of IT in the organization which clearly shows that the organization is affected by the ICT effectiveness.
About 75% (refer C3,Table 5.3) users found that ICT effectiveness is related with the management decision. The 66.7%(refer C4,Table 5.3) respondents takes active part in taking IT related decisions which is very important for any organization to increase the ICT effectiveness. Abot 75%(refer C5,Table 5.3) respondent said that management play his role effectively and highly in IT related decisions of the organization. According to 58.3%(refer C6,Table 5.3) respondents said in ICT strategy and planning there contribution is medium. From the result it clearly shows that employee of the organization does not resist management in taking ICT related decisions as they know it will only increase the efficiency and productivity of the organization (75%). Management makes ICT related tasks easier is very low felt by (66.7%) respondents (refer C8,Table5.3)
This concludes that IT management plays very important role in ICT decision making, in ICT strategy and Planning and also we found MIS is the vision of the role of IT in the organization.
Table 5.3 ICT management
Q.No No effect Low Medium High Very High
C1. M: 3.916 SE:.083
To what extent is decision making process is used wrt to IT in the organization
- - 8.3 91.7 -
C2. M: 3.83 SE:.056
To what extent MIS is the vision of the role of IT in the organization.
- - 16.7 83.3 -
C3. M: 3.75 SE: .042
To what extent IT effectiveness is related with the management decision.
- - 25.0 75.0 -
C4. M: 3.00 SE: .040
How much management takes active part in ICT decisions of the organization.
- - 66.7 33.3 -
C5. M: 3.66 SE: .045
To what extent management play his role in IT decisions of the organization.
- 8.3 16.7 75.0
C6. M: 3.25 SE: .041
To what extent management play his role in IT strategy and planning.
- 8.3 58.3 33.3 -
C7. M: 2.08 SE: .045
To what extent employee resist management in taking IT related problems.
8.3 75.0 16.7 - -
C8. M: 2.41 SE: .042
How much does management make IT related tasks easier.
5.4 Top Management
Top Management is very crucial for the success of IT projects. The role of Top Managent on ICT related decisions are explained in (Table 5.4). In the Jharkhand Government , the trend is improving of involvement of Top management in ICT related decisions. 90% (refer D1,table 5.4)respondent felt that the top management is Highly involved in ICT usage in the organization. 50%(refer D2,Table 5.4)respondent said that there are many training programs from top management with respect to ICT in the organization. Similarly top management motivates and promotes ICT initiatives in the organization according to 66.7%(refer D3,Table 5.4) respondents. The inter-departmental communication flow is high (50%) refer d5,table 5.4) ).in the organization and management is highly clear about the role of ICT in the organization (66.7%) (refer D5,Table 5.4).According to 66.7% felt that top management involves in budget allocation of the organization(refer D6,Table 5.4). From the table we found that 83.3% (refer D7, Table 5.4)respondents relies on external help in ICT related decisions. The Top management is proactive in ICT related decisions (50%) and also they are facing competitive pressure (50%) .
In the view of above we found that top management gives due regard to ICT personnel in the organization and allocates quantum of budget for ICT. The top management involvement in IT projects was found to be high, but also they are highly relies on external consultant. The training given to the users were adequate but it should be more frequently. The top management is clear about their role and also role of ICT in the organization and also their role was proactive in Information Communication Technology related decisions in the organization.
Table 5.4 Top Management
Q. No. Contents Low
(%) Medium (%) High (%) Very High (%) 1. M: 3.90 SE: .042
To what extent is personal involvement of Top Management in ICT usage
- - 10 90
2. M: 3.50 SE: .043
Are there any training program from Top Management wrt ICT in the Organization.
- - 50 50
3. M: 3.66 SE: .040
To what extent the Top Management motivates and promotes ICT initiatives in the Organization.
- - 33.3 66.7
4. M: 3.16 SE: .044
What is the extent of Inter-departmental management communication Flow.
- 16.7 50.0 33.3
5. M: 3.33 SE: ..040
How much is the Top management is clear about the role of ICT in the orzanization.
- - 66.7 33.3
6. M: 3.33 SE: .044
How much is the Top management is involves in Budget allocation.
- - 66.7 33.3
7. M: 3.83 SE: .042
To what extent top management relies on external help in ICT decisions.
- - 16.7 83.3
8. M:3.50 SE: .043
How far is Top Management is proactive in ICT related decisions.
- - 50 50
9. M:3.50 SE: .045
To what extent top management is facing competitive pressure.
- - 50 50
10. M:3.50 SE: .042
How much was the quantum of investment in ICT wrt the total budget allocation.
6. Conclusion of the Study : The result shows that the system was frequently and highly used in the government of Jharkhand departments and system provides report as per the users. The analysis indicates that the respondent got better jobs after implementation of the system. The system helps user to perform their job better and also they are highly used the reports provided by the system. It is found from the result that computer training will increases the confidence among users, organization plays an important role in the satisfaction of users and the system actually assists the user in their jobs. ICT effectiveness has been related with the management role in IT decisions of the organization. Top management emphasizes on training program wrt ICT in the Organization and also Top Management motivates and promotes ICT initiatives in the Organization. The management allocates budget for Information Communication Technology investment, motivates and promotes ICT initiatives in the organization, conducts training program related to Information Communication Technology. This concludes that Information Communication Technology effectiveness would be increased with the initiatives providing by the top management and IT management. Although there are so many training programs conducted by NIC for all the departments but it felt there should be more training programme wrt to ICT to increase confidence among the users. We can say that the emergence of web based delivery system has increased the relevance of these tools in the collection collation and sharing of information at low cost. Hence, it is important to maximize the use of ICT tools and application for successful transformation of government delivery systems with minimized cost and maximized speed.
For coming years State has to computerize all major departments and ensure that information and services are delivered through electronic media to achieve speedy, transparent and accountable governance.
Reference
[1] Bhatnagar, Tanushree, Jha, A.N , and Singh, H.K “Use of Information Communication Technologies(ICT) in E-governance: A review”IJ-ETA-ETS July 2010ISSN : 0974-3588
[2] Bhatnagar Tanushree, Singh H.K. “Role of ICT in E-Governance with special reference to Jharkhand State” National Conference on Recent Advance in Information Technology (RAIT)ISM Dhanbad, 6-7 Feb 2009.
[3] http://210.212.20.85/New_Depts/infor/itpolicy.pdf, accessed on 16th April 2011
[4] http://www.jharkhand.gov.in/New_depts/infor/infor_policy.html, accessed on 16th April 2011