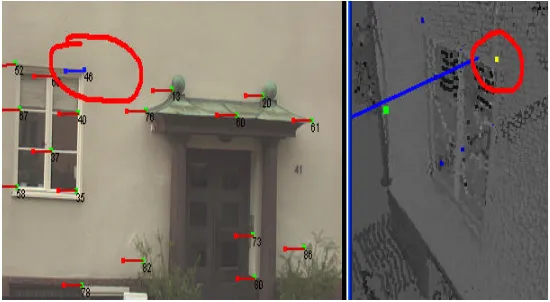
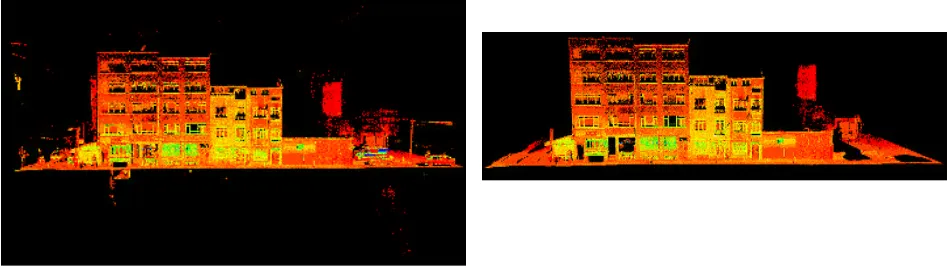
3D geospatial database from terrestrial /laser scanning (TLS) data
Full text
Figure




Related documents
This paper presents the process of implementation of an efficient framework for precast concrete using terrestrial laser scanning that enables contractors to acquire accurate data
So the parameters of the laser will depend on the main area using 3D scanner.For example, for mapping glaciers or the mining industry is an important distance scanning
KEY WORDS: Photogrammetry, Laser Scanning, Heritage Documentation, Data Integration, 2.5D
validation for a mobile laser scanning data based automated road edge extraction algorithm. Automated road markings extraction from
ANALYSING AND MODELLING TERRAIN SURFACE CHANGES USING AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING DATA.. Ana-Maria Loghin* 1 , Valeria Ersilia Oniga 2 and Martin
This paper reviews ground based 3D laser scanning technologies and it discusses the use and integration of 3D scanned building data with city scaled spatial data to build wide scale
Classification and segmentation of terrestrial laser scanner point clouds using local variance information. A comparison between photogrammetry and laser
LFM Server enables users to access and work with pre- registered 3D laser scan data from any scanner vendor, to clash detect a proposed design against as-built data, and to