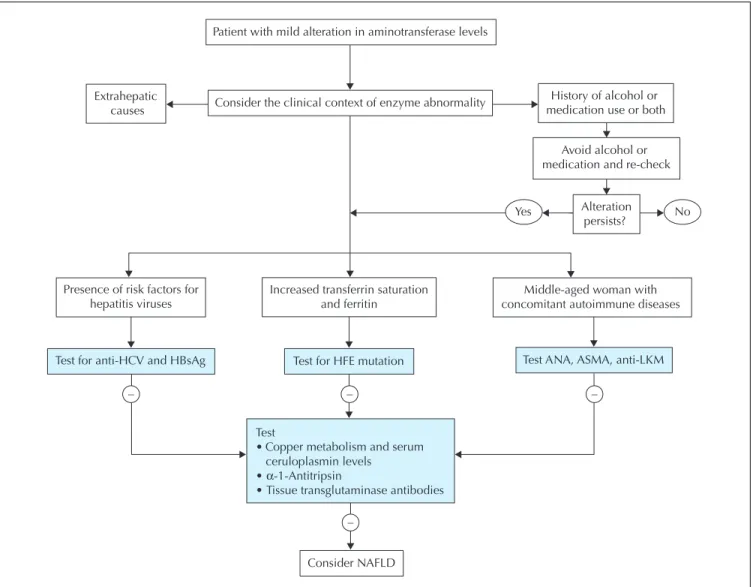
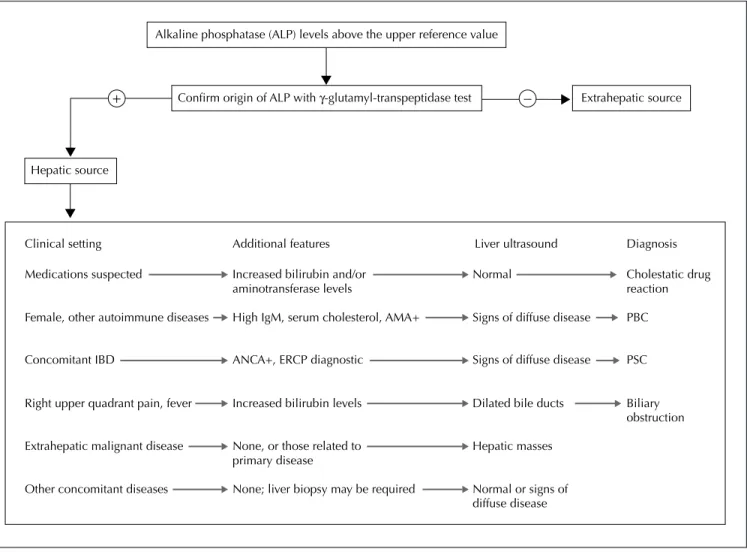
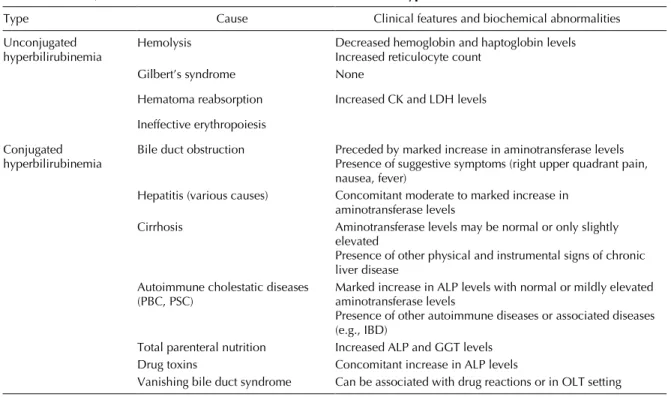
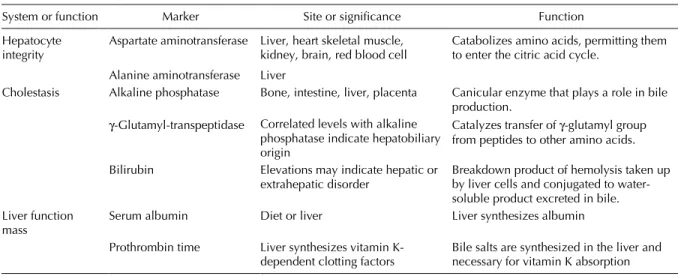
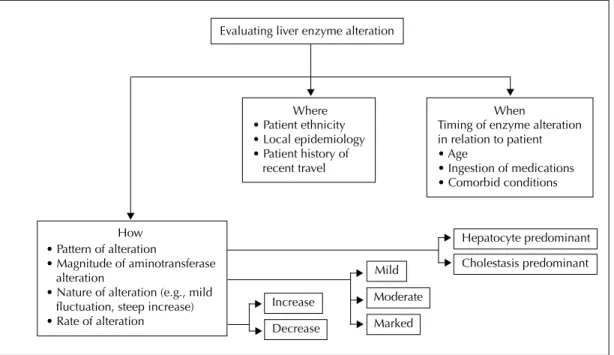
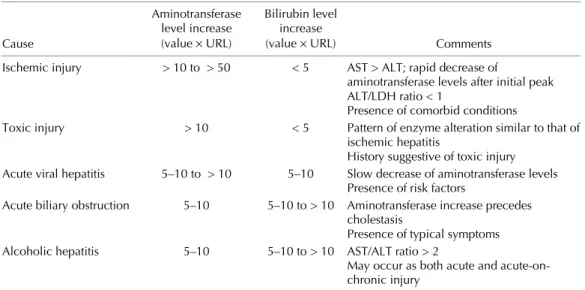
Abnormal liver enzyme levels may signal liver damage
Full text
Figure

Related documents
Liver cirrhosis represents the advanced stage of hepatocellular injury caused by chronic liver diseases such as infectious causes like hepatitis, alcoholic
secondary to cirrhosis, severe alcoholic hepatitis, acute liver failure, or less commonly, a.. metastatic
Abstract: Background: Cognitive dysfunction has been observed in a range of liver diseases including chronic hepatitis C virus , alcoholic liver disease, primary biliary cirrhosis
Keywords: Liver cirrhosis, etiology, alcoholic liver disease, mortality, portal hypertension, esophageal varices, variceal bleeding, hepatitis C, hepatocellular cancer,
Fatty liver with no evidence of liver cell necrosis (ballooning) or fibrosis (bridging): Low risk for cirrhosis or liver failure – Non-alcoholic fatty liver
In the USA, the most common causes of cirrhosis are alcoholic liver disease and chronic viral hepatitis, although there are other causes, include drug related, autoimmune
Thus, alcoholic fatty liver (AFL) is analogous to simple steatosis (NAFL), alcoholic hepatitis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and.. alcoholic cirrhosis to the cirrhotic
Alcohol is another cause of liver disease, and alcohol-related liver disease can range from fatty liver to alcoholic hepatitis with or without cirrhosis.. Along with nonalcoholic