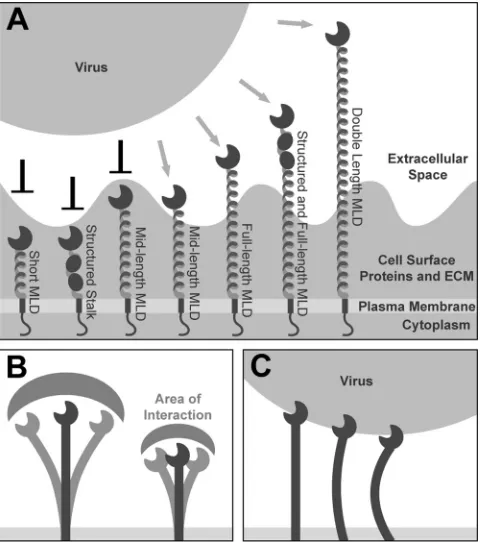
Characterizing Functional Domains for TIM-Mediated Enveloped Virus Entry
Full text
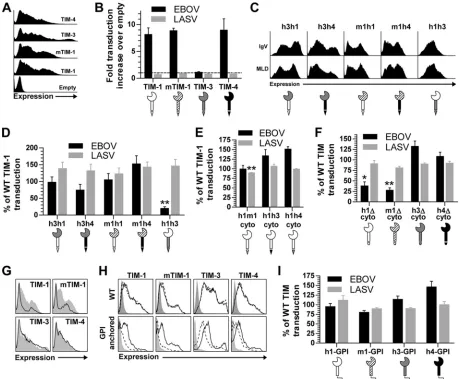
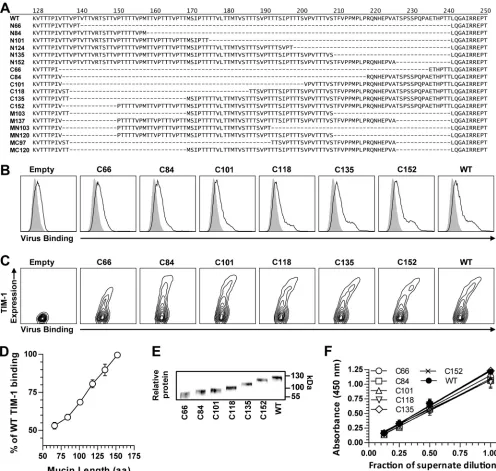
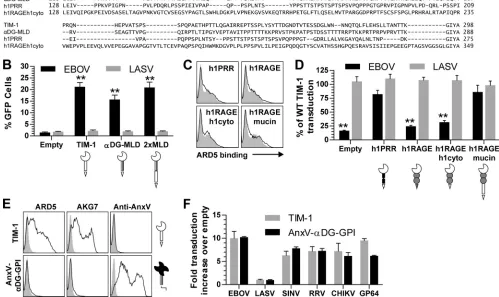
Figure
Related documents
Because of the nonlinearity behavior of the left-handed region of composite right/left-handed transmission line, the proposed antenna has compact size compared to conventional
We focus on three environmental impacts particularly influenced by population age- structure — carbon emissions from transport and residential energy and electricity.. consumption —
Comité Consultatff, afin d'assurer la permanence de cet or· gane communautaire (cf. S'il est vrai que le Traité confère à la Commission des fonctions
In this study, LRT splicing pat- terns in TG of infected calves were compared to those of productively infected bovine cells or COS-7 cells transfected with a plasmid that expresses
Stages Types Normoglycemia Hyperglycemia Normal Glucose regulation Impaired Glucose Tolerance or Impaired Fasting Glucose Diabetes Mellitus Non Insulin requiring Insulin
To identify the level of uric acid in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.. To identify whether any association exist between age,
Characterization of hepatitis C virus envelope protein complexes expressed using recombinant vaccinia viruses, abstr. HCV,