Laboratory evaluation of bleeding diathesis in medical ICU patients.
Full text
Figure




Related documents
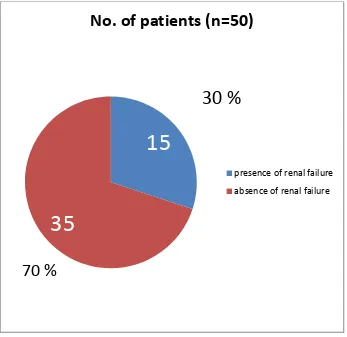
The results of the correlation between haemostatic parameters (Platelet counts, PT, APTT, D-dimers, fibrinogen, Factor VIII levels) and phase of the disease and status
To determine whether the release of IL-6 was required for the PM-induced prothrombotic tendency, we measured bleeding time, PT, aPTT, platelet count, factor VIII activity, and
2 : in the 53 patients with confirmed dengue virus infection and thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100 x 10 9 /L), conventional coagulation tests (PT, TT, INR and aPTT),
When the results from the screening tests in an emergency situation suggest a risk of bleeding in patients without bleed- ing complications (eg, marked prolongations of the PT and
dose: 50unit/kg X 1, NO additional blood product or rFVIIa given4. PT, aPTT, TT, ECT were used as surrogate markers, ie NOT
Standard coagulation testing (APTT, PT and TT) and where available specific drug levels should be per- formed to assess the contribution of excess drug to the bleeding event and
The aim of the study is to identify platelets in the unstained peripheral blood smear, to compare the platelet count in unstained smears with that of stained smear and to
Changes in (A) hematocrit, (B) platelet count, (C) prothrombin time, (D) activated partial thromboplastin time, (E) fibrinogen level, and (F) D-dimer level over time in