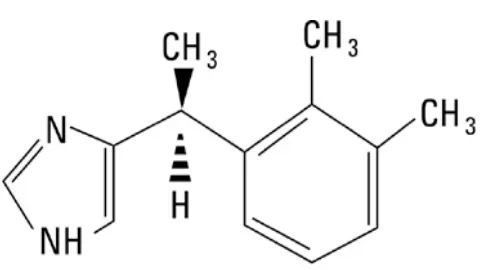
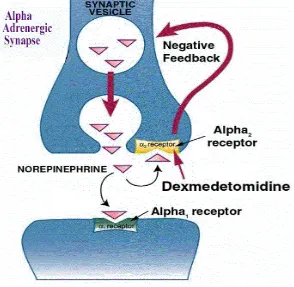
A study on the anaesthetic and analgesic effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine as premedication for spinal anaesthesia
Full text
Figure
Related documents
In a case report, prolonged motor and sensory block after low-dose spinal hyperbaric bupivacaine administration was attributed to low CSF volume.. The authors reported that
In our study when 10 mg of 0.5% Bupivacaine is added with 5µg of Dexmedetomidine it significantly prolongs the duration of sensory blockade, motor blockade and duration of
Conclusions: Using dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to bupivacaine for spinal anesthesia in lower limb surgeries has longer duration of sensory and motor block and longer
request, duration of analgesia, opioid consumption, and sensory and motor block times; and different types of pro- cedures such as orthopedic and abdominal surgery and labor
MAGNESIUM ON ANALGESIC REQUIREMENTS OF PATIENTS UNDERGOING LOWER LIMB..
[9] conducted study on dexmedetomidine and clonidine as an adjuvant to Ropivacaine for epidural anaesthesia in lower abdominal and lower limb surgeries- concluded that
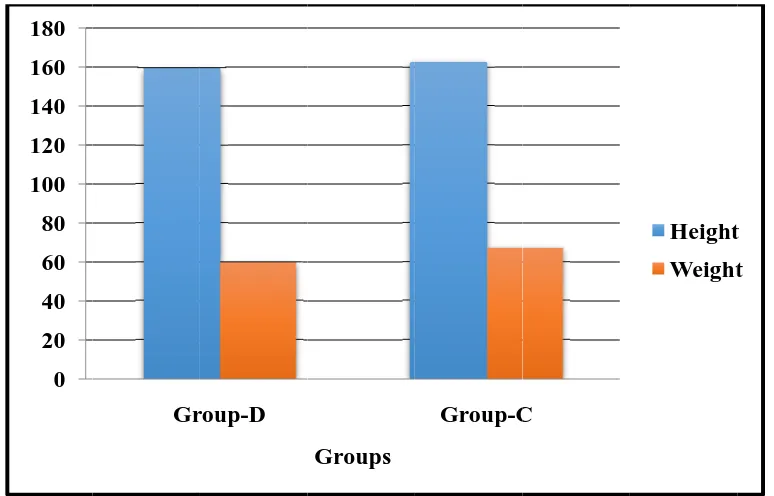
hyperbaric bupivacaine 15 mg + 0.5ml of normal saline. Group “B” 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine 15 mg+5 µg Dexmedetomidine. Group “C” 0.5%hyperbaric
Conclusion: As an adjuvant to hyperbaric bupivacaine, clonidine (30 mcg) showed longer duration of sensory block and longer post operative analgesia when compared to