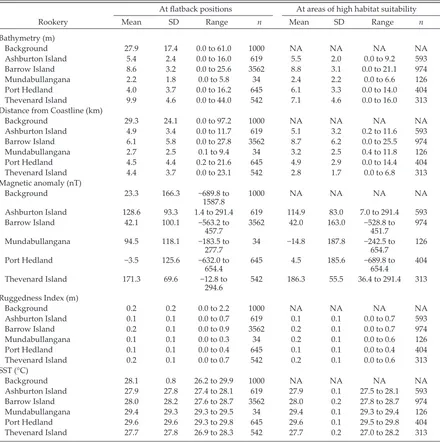
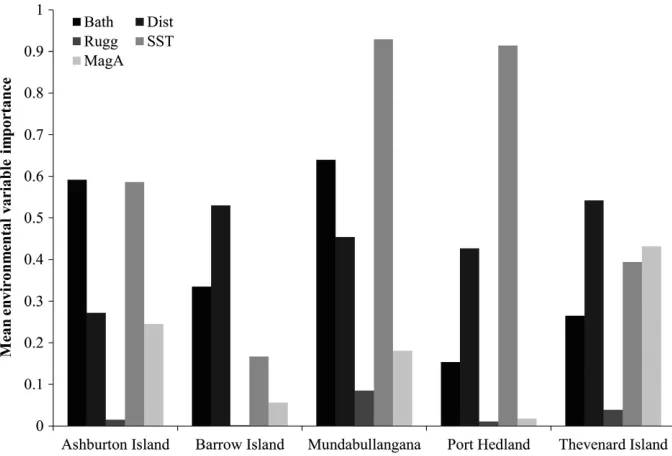
Using habitat suitability models in an industrial setting: the case for internesting flatback turtles
Full text
Figure




Related documents
a) As a prerequisite, all applicants are expected to have completed an approved Research Methods Course at the Graduate Level. Where this is not the case, they would need to
infected HeLa cells , fused in a minimal reaction resulting in binucleated or trinucleated syncytia. Nor- mal heteroploid cells adsorbed with para-infiuenza
Field experiments were conducted at Ebonyi State University Research Farm during 2009 and 2010 farming seasons to evaluate the effect of intercropping maize with
Primary: To test the effect of a face-to-face structured patient-specific smoking cessation program delivered by trained ambulatory pharmacists on smoking cessation rates in
Because of the recommended procedure for evaluating reliability (and validity) is to have bilingual participants fill out the questionnaire in both languages and assess the
There are infinitely many principles of justice (conclusion). 24 “These, Socrates, said Parmenides, are a few, and only a few of the difficulties in which we are involved if
3 Simulation results for additive and interaction models using grammatical evolution Bayesian Network (GEBN), grammatical evolution neural network (GENN), logistic regression,
In this present study, in agreement with previous findings (Clifford et al 1980) the improved functional capacity and walking ability in both exercise training groups was