DNA Repair Mechanisms and the Bypass of DNA Damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Full text
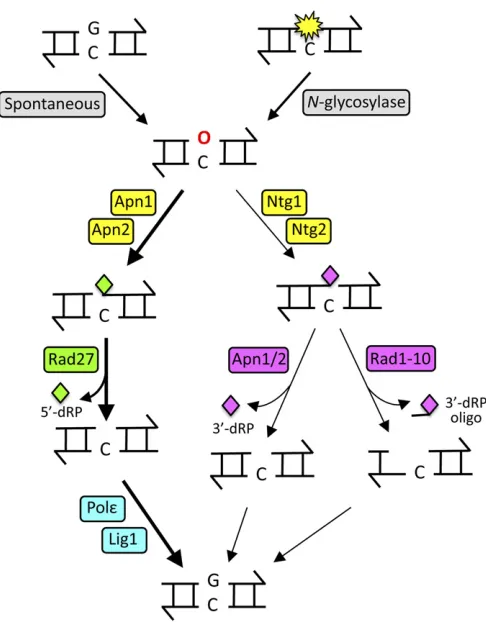
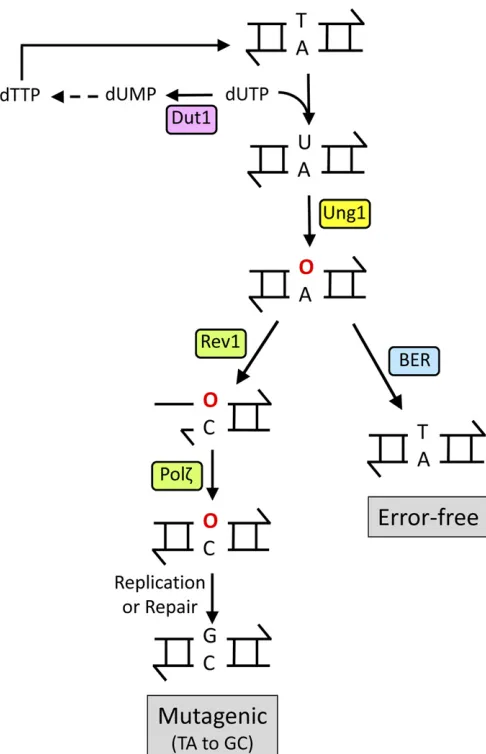
Figure


Related documents
sensitivity to attentional load as demonstrated by larger visual N1 to picture onset for high- than low-complexity images, (2) reduced emotional processing of unpleasant compared
Contributions of the non-alpha subunit residues (loop D) to agonist binding and channel gating in the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.. In vivo incorporation of
One major problem stems from the fact that before digital controls can be applied to a given process, formulas must be developed relating operating variables to
Archive: George Eastman Museum [USR] , Library of Congress [USW] , Museum of Modern Art [USM] , BFI National Archive [GBB] , EYE Filmmuseum [NLA] , UCLA Film and
One analysis by the Industry Commission finds that the estimate for Australia is that a 1 per cent fall in demand for scrap metal results in a fall in domestic scrap metal prices
1) Inadequate Growth: The current reality is that most organizations have spent the last decade investing in existing or mature products that are not providing
The Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats are more insulin resistant, less obese, and quickly development to diabetes due to lack of adequate insulin secretion.. The serum
Followed by James A.F Stoner (1996: 34) in his book "Administration" classifies management functions, namely a) Planning (Planning), b) Organizing




