Exploiting Constituent Dependencies for Tree Kernel Based Semantic Relation Extraction
Full text
Figure



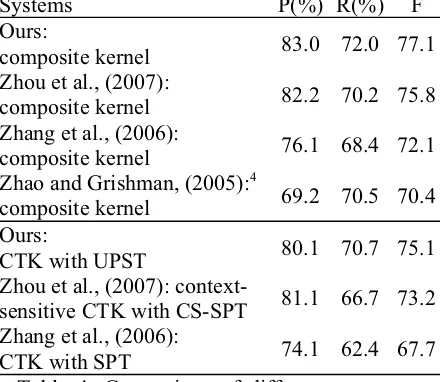
Related documents
Background: Little is known about the course of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome 1 and potential factors influencing the course of this disorder over time. The goal of this study is
In the present study, we determined stem cell specific marker gene expression of SP cells in bovine synovial membrane, and constructed a culture system for efficient collection and
Damages of the tibial post in constrained total knee prostheses in the early postoperative course – a scanning electron microscopic study of polyethylene inlays.. Adrian Skwara* 1
Methods: The measurements were performed on CT sagittal plane, including the thickness of cancellous bone (L1), the theoretical optimal angle of the tibial tunnel (TOA, which
Subjects in Arm 4 receive a true physical therapy intervention consisting of manual therapy (MT) and supervised strengthening exercise once a week and complete the protocolized
ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; ANOVA: Analysis of variance; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; BMD: Bone mineral density; BMI: Body mass index; CI:
Proteomics has now published a series of Dataset Briefs on the EyeOme from the HUPO Human Proteome Project with high-quality analyses of the proteomes of these compartments of
Hence, we also performed a sub- group analysis by ethnicity and the outcomes indicated no association of COL9A3 trp3 polymorphism with IDD risk in any of ethnicity subgroup.. Based