Job satisfaction of employees of public and private
organizations in Bangladesh
Md. Nazirul Islam Sarker
1, Arifin Sultana
2, AZM Shafiullah Prodhan
3 1School of Public Administration, Sichuan University, China.
2
Department of Psychology, National University, Bangladesh.
3
Department of Horticulture, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University, Gazipur, Bangladesh.
This study examined the level of job satisfaction among the employees ofprivate and public organizations in Bangladesh. Data have been collected randomly from 40employees of Gaibandha District in Bangladesh through a structured questionnairein January to February, 2010. Among the respondents 50% is government employee while 50% is non-government employee. Brayfield and Rothe (1951) method was used to determine the job satisfaction of the employees. Likert scale was used for measuring the attitude of the employees on their job. This research revealed that there was no significant difference between the job satisfaction of government and non-government employees. The study suggests that an effective policy on recruitment, job security, service rules, promotional opportunities, regular payments, retirements’ benefits should be made by the government to improve the job satisfaction and attitude of employees in both government and non-government employees.
Keywords: Job satisfaction, employees, private, public organizations, government, Bangladesh.
INTRODUCTION
Job satisfaction is the key factors for the success of an organization. Most of the organizations usually take initiative to satisfy their employees for makes them committed and developing their effective roles. It is the difference between the level of rewards employees receive and the level they believe they should receive (Robins 1997). Herzberg (1952) identified motivation factors and hygiene factors while investigating satisfaction on the job. He concluded that motivation factors (e.g., achievement recognition, responsibility, advancement, growth and work itself) lead to satisfaction on the job and factors like supervision, policy and administration, relationship with supervisor, relationships with peers, relationships with subordinates, work conditions, salary, status, personal life, security may guide to job dissatisfaction.
An important issue of every organization is job satisfaction among the employees as it is positively
related to its goal achievement. Job satisfaction is a set of favorable or unfavorable feeling and emotions with which employees view their work and the supervisors should concentrate about employees’ job satisfaction level (Newstrom, 2007; Sarker et al., 2015).Locke (1976) defined job satisfaction as anenjoyable or positive emotional state, resulting from the assessment of one’s job experiences. It is described as how people feel about their jobs and its different aspects.
*Corresponding author: Md. Nazirul Islam Sarker, School of Public Administration, Sichuan University, China. Email: sarker.scu@yahoo.com.
Vol. 1(1), pp. 002-008, June, 2017. © www.premierpublishers.org. ISSN: xxxx-xxxx
Research Article
Job satisfaction is collection of feelings that an individual holds toward job (Robbins and Sanghi, 2006; Rahman, 2008). Mobey and Lockey (1970) expressed as a perceived relationship between what one expects and obtains from one’s job and how much importance or value one attributes to it. The Harvard Professional Group (1998) reportedit as a condition that leads to recognition, income, promotion, and the achievement of other goals for fulfillment. Bullock (1952) defined it as an attitude which results from a balancing and exact of likes and dislikesexperienced in connection with the job. One of the major challenges in organizational management is employee job performance which mainly affects the performance of the organization (Lee and Wu 2011; Sarker, 2016). Ogbulafor (2011) suggested that employee performance was instrumental to organizational growth and profitability. The employees are regarded as the major business resources that help the daily activities and operations of an organization (Mudah, RafikiandHarahap2014; Rahmean et al., 2017). Similarly, Oluwafemi (2010) mentioned that organizational effectiveness and efficiency depends on how effective and efficient the employees in the organization are. Employer’s ability to understand employee’s satisfaction as it relates to schedules and daily duties will impact greatly on employee efficiency and performance. Howard (2009) viewed job satisfaction as a blend of likable and unlikable moods or behavior of an individual worker on their work schedule, implying that when an individual is employed such individual might come along with desires, wants and anticipations which define their meaning for being there. Satisfaction on a job symbolizes the enormousness to which optimism are align with real rewards and benefits. Most employees have a high degree of job frustration which create attitudes that are undesirable on the job and deteriorate their performance ability and that their working place as well (Mowday, Porter and Steers 2013; Sarker and Rashid, 2015). The concept of employee performance is preferably stressed lately in the viewpoint of transparency (Hood and Healed, 2006), managerial accountability (Broaddbent and Laughlin, 2003), a performance measurement (Ferreira and Otley, 2005) and managerial control (Berry, Broadbent and Otley, 2005).
Job satisfaction is the positive and negative attitude towards the job of employee. There are some commonfactors like security of their existing job, employee’s autonomy, salary and other facilities, working environment and schedule, career improvement opportunity, performance appraisal process and evaluation etc which always contribute directly and indirectly to theemployees mind as well as performance of the organization. Since organizational performance and service delivery mainly depends on job satisfaction, so it is a critical issue to measure the job satisfaction of
employees of both public and private organizations. The review of literature suggests that no previous study done on this issue in the study area which leads the researchers to select this piece of research. This study explored the level ofjob satisfaction of employees of public and private organization.In line with the objective, the alternative hypothesis was formulated.
H1: There is a positive and significant relationship
between job satisfaction and employee performance in public and private organization.
Rationale of the Study
Job Satisfaction is an important concern in the world of professional commitments.The outcome of the companiesis largelydepends on the employees’ job satisfaction. When an employee get reward and satisfied to his or her job, definitely he or she can contribute better for organization. As a result, a lot of factors bring the job satisfaction and at the same time lack of them are responsible for job dissatisfaction. Employee’s job satisfaction seems very essential concerning about the company’s constant growth.In the first world, this issue has been understood reasonably because they do understand that the job satisfaction of the employees is much more important than other components of the organization. In this respect, Bangladesh has yet to do something trustworthy as the concept is relatively new in Bangladesh (Sarker et al., 2017). So, it has been realized the fact that job satisfaction has to be taken care of practically. What makes a firm best is not just technology, bright ideas, strategy or the use of tools, but also the fact that the best firms are better organized to meet the needs of their people, to attract better people who are more motivated to do a superior job (Waterman, 1994). In thismanner, the management of human resources becomes very crucial. Almost no research has been done on the employees’ job satisfaction in the study area. Thus, this study on employees’ job satisfaction of the employees of public and private organization was taken up.
Objectives of the Study
The main objective of this study was to determine the level of job satisfaction among the public employees and private employees of Bangladesh. The main objectives split into the followings:
a) To explore the relationship of employees’ level of job satisfaction with their socio-economic, demographic, andeducational status.
b) To determine the variation of job satisfaction between the public employees and private employees of Bangladesh.
SURVEY OF RELATED LITERATURE
Some recent research works were included in this section as evidence to the relation between job satisfactions public and private employees with other factors.
Employee performance
Employee job performance has always been an important concern for managers of organizations (Kelidbari, Dizgah, and Yusefi, 2011). Similarly, employee performance is key component of an organization therefore; aspects that place the grounds for high performance must be scrutinized critically by the organizations for them to succeed (Abbas and Yaqoob, 2009). The effect of job satisfaction and service attitude on job performance among high-tech has always been regarded as an important item in organizational management.Job performance is generally considered as workers’ total performance in meeting the anticipated worth and achievement of tasks under the procedure and time requirements of the organization. Similarly Liao et al., (2012) definedjob efficiency as the common for improvements, redundancy, benefits, punitive measures, opinions and wage changes. It also meets the needs for workers to realize themselves. Ahmad and Khurram (2011) also argued that worker performance represents the wide perception of the employees about their actions and efforts towards the accomplishment of the company. Ahmad and Shahzad (2011) mentioned that apparent employee performance embodies the whole belief of the employee about their conduct and contributions to the accomplishment of the organization and compensation practices, performance assessment and promotional practices as a determinant of employee performance. Similarly, Anitha (2013) defined it as an indicator of financial or other outcome of the employee which has a direct relation with the performance of the organizationand its achievement, further reported that working environment, leadership, team and co-worker involvement, training and career development, incentive program, guidelines and procedures and workplacecomfort as well as employee commitment are major factors which determine employee performance. Alagaraja1 and Shuck (2015) argued that employee performance can be enhanced through training and development by organizational configuration and employee engagement in order to understand reasons associated with enhancing individual performance. Furthermore, Thomas and Feldman, (2010) adopted measures of employee performance as core task performance, which includes in-role performance, safety performance, and creativity, followed by citizenship performance, categorized into both targets-specific and general organizational citizenship behaviors and lastly, counterproductive performance that consists of general counterproductive work behaviors, workplace violence, substance use, sluggishness, and malingering.
Therefore, worker efficiency brings about advancement efficiency and firm efficiency as a whole, in such a way that successful effort of satisfied, motivated, and dedicated recruiting produce impressive ideas for new services or products and increase quality efficiency, surgical activities, and customer support directly (Sadikoglu and Cemal, 2010).Globalization has designed a lot of variations and difficulties that impact both the public and private industry around the world which make job industry of Bangladesh not exceptional to such circumstances. Although there are some undeniable justifications about the beneficial and side results about such changes, an effective analysis of worker efficiency therefore becomes absolutely essential (Krishna, 2010).
Measures for employee performance
quality and satisfaction of the clients (Sadikoglu and Cemal, 2010).
Job satisfaction
Job satisfaction is considered not to have a generally decided meaning despite of its importance and wide utilization in the world of commercial mindset and business actions, which make it vital that before clear significance is given, there is the need to put into consideration benefit and characteristics actions of humans all over the world (Aziri, 2011). Hop pock (1935) stated that job satisfaction was seen as any form of blend of psychological environmental as well as physiological circumstances. Another definition given by Vroom (1964) effective alignment of person in regard to their process and plans is what describes job satisfaction; this meaning put much focus on the part performed by a worker in the working place.
The most commonly used significance of job fulfillment is the created by Spector (1997) which declares that job fulfillment facilities mostly on the emotions of people about their whole job, which focuses on the stage to which people like or dislike their tasks. Therefore job fulfillment provides as a standard on how workers either feel adverse or beneficial about their job and that is the primary reason why job fulfillment and discontentment always exist at certain point and scenario (Davis, Nestrom 1985). Aziri (2011) claimed that the quality of job fulfillment was within the range of excessive fulfillment and excessive discontentment. Also, according to Kaliski (2007) job fulfillment can be considered emotions of success and how effective a worker is on his/her job which can have a primary connection to worker efficiency as well as wellness of the staff member. Moreover, Henry and Jackson (2008) recommend that job fulfillment is consisting of values and emotions that people understand about their specific tasks. However, job fulfillment is considered to be multi- perspective and complex, it can be considered in many different ways by different people, usually, it is associated with inspiration even though the opportunity of the text is still not very obvious Aziri (2011).
Factors Determining Job Satisfaction
Rue and Ryaes (2003) recommend that job fulfillment is driven by some look at the office which include financial offers like incomes, possibilities, progression, working circumstances, and workgroup, further the resulting effect of the determinant functions as measuring stick for job fulfillment of discontentment as well as what the results will be as stated by Aziri (2011) that when talking about issues regarding job fulfillment, job discontentment should be considered to ensure balance. Squires et al. (2015) suggested that though, disappointed employees may not stop their tasks, but such feeling of
discontentment could affect them, their co-workers as well as their quality of efficiency and the service they provide in the sense that such disappointed employees have propensities of showing anger on anybody else in the office.
Bos et al. (2009) described that job fulfillment has five factors which involve freedom, expertise attention, support from excellent, chances to further knowledge and connection with co-workers. Statistic of employee’s job fulfillment is one of the significant characteristics when it comes to skills and effectiveness of employees. In functionality, the first-hand decision-making design which types it as essential that employees should be maintained and well thought-out essentially as humans that have their own wishes, needs, and own wishes are a very good range for the popularity of job fulfillment in modern-day companies (Usman and Jamal, 2013). In the process examining job fulfillment, the sagacity that a pleased worker is a pleased worker and a pleased worker is a dynamic worker (Aziri, 2011).
On the opposite Aziri (2011) further suggested that there was no strong nexus between job fulfillment and worker efficiency considering the fact that a meta-analysis of past experiments charges 0.17 best-estimate connections between job fulfillment and worker efficiency. He further stated that a worker with an advanced stage of job fulfillment might not actually have an advanced stage of efficiency. Furthermore, in a research by Increased et al (2011) targeted at monitoring the text job fulfillment and perform efficiency by an example of community service authorities in Malaysia realize that business learning was set up to be favorably similar to business dedication, job fulfillment, and perform efficiency. In the same line of thinking, Raza, Rafique, Ali, Mohsin, and Shah, (2015) also performed a research with the goal of searching the outcomes of job fulfillment and revenue representative’s efficiency with flexible selling actions of companies, the research divulges that that there is a strong organization of salesman efficiency and job fulfillment. Moreover, in the perform of Vermeeren, Kuipers and Steijn (2014) in a research is designed to observe the association concerning community business efficiency and workers control with specific focus on job fulfillment as a reputable mediating varying between business efficiency and HRM, on the effect of a supervisor’s control smartness on the application of human resources (HR) methods. However, their findings direct that job fulfillment is favorably related to worker efficiency.
nature of perform, interaction, job stress, worker character and employment and selection procedures have significant organization with workers job fulfillment. Shaukat et al. (2012) discovered that supply of assistance at performs and higher leader-member return interaction favorably forecasts workers job fulfillment. It shows that when the organization provides assistance to its workers or when manager is helpful and workers have excellent return regards with their manager, they reciprocate it with higher interaction and increase job fulfillment.
Jehanzeb et al., (2012) figured degree of advantages, inspiration and job fulfillment of workers has a strong relationship in the financial industry of Saudi Arabic further it has been found that workers in the financial industry give more importance to economic or dollars. Rahman et al. (2012) figured the female workers overall job fulfillment of private banks is associated with adequate compensation for perform, available chance of promotion, job analyzed advantages, identification for great perform, pleased supply wage rise, pleased supply wage rise, pleased inspiration and advantages, wage increases on performance, motivated to operate pleased available chance, training course regularly, pleased space available, pleased atmosphere. Hoque et al. (2012) indicates that the factors of job fulfillment such as job status, wage edge advantages, job security, promotional opportunities, workplace, job independence, identification for great perform, co-workers, and monitoring have been assigned by both the amount of professionals, junior and top stage as the major factors of their respective job fulfillment. It is also revealed that each of their factors has significant positive relation with the overall job fulfillment of the professionals. Therefore, improve in values/standard of each of these factors would definitely improve the amount of job fulfillment of the selected professionals.
METHODOLOGY
The research data have been collected from both primary and secondary sources. Primary data have been collected through a structured questionnaire from Gaibandha district of Bangladesh in January to February, 2010. The data is collected using a well-designed interview schedule. All the variables were measured using a five point Likert scale ranging from strongly disagrees to strongly agree (Sarker et al., 2007). In addition, different national and international articles and websites were researched for a quality work. Job satisfaction of the public and private employees was measured by the scale developed by Brayfield-Rothe (1951). Reliability of the scales has been assessed by using test-retest reliability approach and validity has been assessed by examining content validity. The secondary
data have been collected through desk study which covered research articles, research monographs, textbooks and various published and unpublished materials on the subject.
Sampling
Sampling from public organizations
Serial no.
Name of the organizations Number of respondent 1 Upazila statistics office 4 2 Upazila livestock office 7 3 Rural development office 3 4 Upazila fisheries office 2 5 Upazila election office 3 6 Upazila food control office 1
Total 20
Sampling from private organizations
Serial no.
Name of the organizations Number of respondent 1 Samaj Kallyan Sangstha 3 2 Unnayan Sohojogy Sangstha 4 3 Association for Social
Advancement (ASA)
7
4 Unnayan Shangha 6
Total 20
Measurement of variables
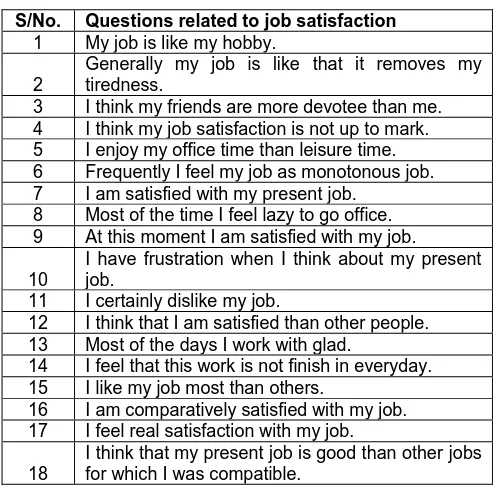
The following questions were asked to the public and private organization employees for determination of the level of job satisfaction (Table 1).
Table 1. Questions related to job satisfaction.
S/No. Questions related to job satisfaction
1 My job is like my hobby.
2
Generally my job is like that it removes my tiredness.
3 I think my friends are more devotee than me. 4 I think my job satisfaction is not up to mark. 5 I enjoy my office time than leisure time. 6 Frequently I feel my job as monotonous job. 7 I am satisfied with my present job.
8 Most of the time I feel lazy to go office. 9 At this moment I am satisfied with my job.
10
I have frustration when I think about my present job.
11 I certainly dislike my job.
12 I think that I am satisfied than other people. 13 Most of the days I work with glad.
14 I feel that this work is not finish in everyday. 15 I like my job most than others.
16 I am comparatively satisfied with my job. 17 I feel real satisfaction with my job.
18
DISCUSSION
The study found out the job satisfaction level of private and public organization employees. It was done in Bangladesh which focused the current trend and future prospects of job satisfaction. The type of issue is relevant to the current situation when people and government increasing their concern about privatization. This study revealed that job satisfaction as a complex matter which depend on various factors like working environment, professional and intellectual realities (Lortie 1975), issues and policies related to job etc. The following results obtained from research work.
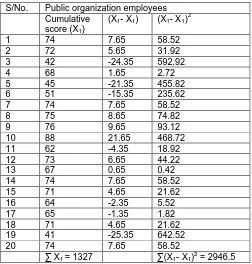
Table 2: The data obtained from public organization employees of the study area.
S/No. Public organization employees Cumulative
score (X1)
(X1- X̅1) (X1- X̅1) 2
1 74 7.65 58.52 2 72 5.65 31.92 3 42 -24.35 592.92 4 68 1.65 2.72 5 45 -21.35 455.82 6 51 -15.35 235.62 7 74 7.65 58.52 8 75 8.65 74.82 9 76 9.65 93.12 10 88 21.65 468.72 11 62 -4.35 18.92 12 73 6.65 44.22 13 67 0.65 0.42 14 74 7.65 58.52 15 71 4.65 21.62 16 64 -2.35 5.52 17 65 -1.35 1.82 18 71 4.65 21.62 19 41 -25.35 642.52 20 74 7.65 58.52
∑ X1 = 1327 ∑(X1- X̅1)2 = 2946.5
Table 3: The data obtained from private organization employees of the study area
Sl no.
Private organizationemployees
Cumulative score (X1)
(X1- X̅1) (X1- X̅1)2
1 73 11.15 124.32 2 58 -3.85 14.82 3 73 11.15 124.32 4 57 -4.85 23.52 5 60 1.85 3.42 6 33 -28.85 832.32 7 67 5.15 26.52 8 43 -18.85 355.32 9 62 0.15 0.02 10 39 -22.85 522.12
11 44 -7.85 61.62 12 74 12.15 147.62 13 83 21.15 447.32 14 77 15.15 229.52 15 60 -1.85 3.42 16 64 2.15 4.62 17 67 5.15 26.52 18 62 0.15 0.02 19 73 11.15 124.32 20 58 -3.85 14.82
∑X1 = 1237 ∑(X1- X̅1) 2
= 3086.5
Table 4: statistical test of job satisfaction of employees.
Sam ple type
Sam ple
Me an
Stand ard deviati on
t-val ue
Degr ee of freed om
Level of freque ncy
Criti cal zone
Publi c
20 66. 35
9.63 1.4 5
38 .05 2.01
Priva te
20 61. 85
10.89
Source: filed survey, 2010
CONCLUSION
Job satisfaction has a wide area of implication like context of job, working environment, policy matters etc. Policy makers in the government and private organization need to be concentrating to make good policy which is really effective considering employees motivation, salary, promotion, working environment etc. This study also revealed that the government officers were reluctant to their duties and responsibilities but private employees were sincere to their assigned duties. Though there was no mentionable difference between job satisfaction of private and public employees but there was attitude differences between them. This study revealed the gap between private and public employees which will help policy makers of both organizations to develop employee friendly policy in the future.
REFERENCES
Abbas Q, Yaqoob S (2009). Effect of leadership development on employee performance in Pakistan. Pakistan Economic and Social Review, 269-292. Ahmad S, Shahzad K (2011). HRM and employee
performance: A case of university teachers of Azad Jammu and Kashmir (AJK) in Pakistan. African Journal of Business Management, 5(13): 5249.
Alagaraja M, Shuck B (2015). Exploring Organizational Alignment-Employee Engagement Linkages and Impact on Individual Performance a Conceptual Model. Human Resource Development Review, P.153.
Anitha J (2014). Determinants of employee engagement and their impact on employee performance. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 63(3): 308-323.
Aziri B (2011). Job satisfaction: A literature review. Management research and practice, 3(4): 77-86. Bhatti MA, Sundram VPK (2015). Business Research,
Pearson Publication. Petaling Jaya, Malaysia.
Bos JT, Donders NC, Bouwman-Brouwer KM, Van der Gulden JW (2009). Work characteristics and determinants of job satisfaction in four age groups: university employees’ point of view. International archives of occupational and environmental health, 82(10):1249-1259.
Brayfield AH, Rothe HF (1951). An index of job satisfaction. Journal of Applied Psychology, 35:307-311. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/h0055617
Bullock RP (1952). Social Factors Related to Job Satisfaction, Research Monograph, No. 70, Ohio State University, Bureau of Business Research, Columbus. Davis K, Newstrom J (1997). Organizational Behavior:
Human Behavior at Work (11th Ed.). NY: McGraw-Hill. Federico V (1996). Relationship between Communication
Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment in Three
Guatemalan Organizations. The Journal of Business Communication, 33(2): 111-140.
George W, Jones I (1976). Work performance. New Delhi: McGraw-Hill.
Greener S (2008). Business research methods. Book Boon.
Herzberg F, Mausner B, Synderman B, (1952). The Motivation to Work, John Willy and Sons, New York. Hoppock R ( 1935). Job Satisfaction. Harper and
brothers, New York, USA
Hoque MJ, Raihan MZ (2012). Assessment of Job Satisfaction in some selected private commercial banks in Bangladesh, pp. 1-12.
Inuwa M (2016). Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance: An Empirical Approach. The Millennium University Journal, 1(1): 90.
Ismail H, Karkoulian S (2013). Interviewers’ Characteristics and Post-Hire Attitudes and Performance. Contemporary Management Research, 9(4): 441-462, doi:10.7903/cmr.10453
Jahufer A (2015). Determinants of Job Satisfaction among Government and Private Bank Employees in Sri Lanka (Case Study: Ampara Region), Int. J. Manag. Bus. Res., 5 (2): 159-168.
Kelidbari HR, Dizgah MR, Yusefi A (2011). The relationship between organization commitment and job performance of employees of Guilan Province social security organization. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 3(6): 555.
Khawaja J, Mazen F, Rasheed A, Aamir A (2012), Impact of rewards and motivation on job
satisfaction in banking sector of Saudi Arabia.
Liao CW, Lu CY, Huang CK, Chiang TL (2012). Work values, work attitude and job performance of green energy industry employees in Taiwan. African Journal of Business Management, 6(15): 5299-5318.
Liao CW, Lu CY, Huang CK, Chiang TL (2012). Work values, work attitude and job performance of green energy industry employees in Taiwan. African Journal of Business Management, 6(15): 5299-5318.
Locke E (1976). The Nature and Causes of Job Satisfaction, In Dunette, M. D. Handbook of Industrial and Organisational Psychology, Chicago: Rand Mcnally.
Mobey, Lockey EA (1970). Job Satisfaction and Performance: A theoretical Analysis, Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, pp. 484-500. Mowday RT, Porter LW, Steers RM (2013).
Employee-organization linkages: The psychology of commitment, absenteeism, and turnover. Academic Press.
Newstrom JW (2007). Organizational Behavior (12th Ed.). New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd.
Niger State. International Journal of Business and Management, 7(14):142.
Rahman M (2008). An Appraisal of Job Satisfaction Levels at Alltex Enterprise- A TQM Approach. Dhaka University Journal of Business Studies, 21(2):131-145. Rahman M, Saha NK, Sarker MNI, Sultana A, Prodhan
AZMS (2017). Problems and Prospects of Electronic Banking in Bangladesh: A Case Study on Dutch-Bangla Bank Limited. American Journal of Operations Management and Information Systems, 2(1): 42-53. doi: 10.11648/j.ajomis.20170201.17
Rahman MM, Gupta AD, Moudud-Ul-Huq S (2012). Job Satisfaction of Female Employees in Financial Institutions of Bangladesh: A Study on Selected Private Commercial Banks in Chittagong. Global Journal of Management and Business Research, 12(14): 232-240. Robbins SP, Sanghi S (2006). Organizational Behavior
(11th Ed.). Dellhi: Dorling Kindersley (India) Pvt. Ltd. Robins, Stephen P, (1997). Organizational Behavior.
Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Rose RC, Kumar N, Pak OG (2011). The effect of organizational learning on organizational commitment, job satisfaction and work performance. Journal of Applied Business Research (JABR), 25(6).
Rue L, Byars L (2003). Management: Skills and Application. McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
Sadikoglu E, Zehir C (2010). Investigating the effects of innovation and employee performance on the relationship between total quality management practices and firm performance: An empirical study of Turkish firms. International Journal of Production Economics, 127(1): 13-26.
Salem S, Majeed S, Aziz T, Usman M (2013). Determinants of Job Satisfaction among Employees of Banking Industry at Bahawalpur, JEIEFB, 1 (2): 150-159.
Sarker MNI (2016). Poverty of Island Char Dwellers in Bangladesh, Hamburg, Diplomica Publishing
GmbH,Germany. http://www.anchor-publishing.com/e-
book/318628/poverty-of-island-char-dwellers-inbangladesh.
Sarker MNI (2016). Role of Banks on Agricultural Development in Bangladesh. International Journal of Ecology and Development Research, 1(1): 010-015. Sarker MNI, Bingxin Y, Sultana A, Prodhan AZMS
(2017). Problems and challenges of public administration in Bangladesh: pathway to sustainable development. International Journal of Public Administration and Policy Research, 2(1): 008-015. Sarker MNI, Islam MS, Rahman MM (2015). Effects of
electronic banking on performance of banks in Bangladesh. International Journal of Applied Research, 1(1):28-34.
Sarker MNI, Rashid MHO (2015). An Impact of Banking Activities of Private Commercial Islamic Bank to Economic Development in Bangladesh: A Case Study
on First Security Islami Bank Limited (FSIBL), Journal of Investment and Management, 4(5): 264-272. doi:10.11648/j.jim.20150405.28
Shaukat MZ, Senin AA, Ahmed I (2012). An exchange perspective of job satisfaction: A study of banking sector of Pakistan. Business Management Dynamics, 1(12): 59-65.
Spector PE (1997). Job satisfaction: application, assessment, cause, and consequences. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Squires JE, Hoben M, Linklater S, Carleton HL, Graham N, Estabrooks CA (2015). Job Satisfaction among Care Aides in Residential Long-Term Care: A Systematic Review of Contributing Factors, both Individual and Organizational. Nursing Research and Practice.
Talukder MS, Talukder MFH, Alam MJ (2014). Job dissatisfaction and turnover: Bangladesh perspective. European Journal of Contemporary Economics and Management, December 2014 Edition, 1(2):183. Vermeeren B, Kuipers B, Steijn B (2014). Does
leadership style make a difference? Linking HRM, job satisfaction, and organizational performance. Review of Public Personnel Administration, 34(2): 174-195. Vroom VH (1964). Work and Motivation. John Wiley, New
York, USA
Waterman RH (1994), What America does right: Learning from companies that put people first. New York: Norton. Wu MY, Lee YR (2011). The effects of internal marketing, job satisfaction and service attitude on job performance among high-tech firm. African Journal of Business Management, 5(32): 12551-12556.
Accepted 19 May, 2017.
Citation: Sarker MNI, Sultana A, Prodhan AZMS (2017). Job satisfaction of employees of public and private organizations in Bangladesh. Journal of Political Science, Public and International Affairs, 1(1): 002-008.