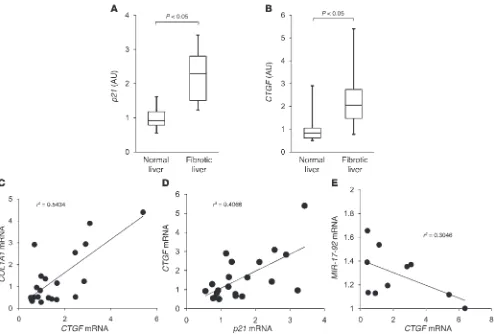
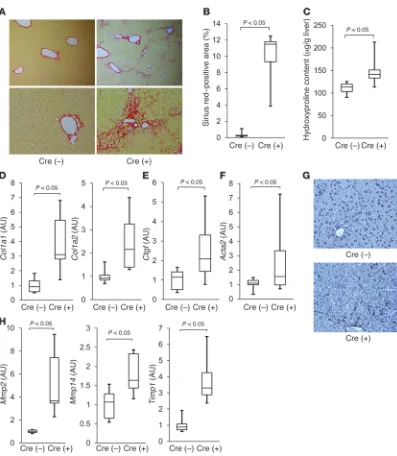
Increases in p53 expression induce CTGF synthesis by mouse and human hepatocytes and result in liver fibrosis in mice
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Considering the importance of religion and spirituality in psychological health, the present study was conducted to examine the role of religious coping styles in predict -
Barth syndrome should be suspected in the case of a male child with dilated cardiomyopathy with or without fi broe- lastosis, LVHT, or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, together
associated methods as it improves its knowledge: there is something like positive feedback between them (which helps account for the explosive growth in scientific knowledge).
Impact of non sustainable forest management to other sectors (agriculture, energy production, tourism etc)..
5.2.5 The mediating effects of job burnout on the relationship between work environment (dimensions) and intention to quit and also between organizational
ABSTRACT : This paper examines that Financial barrier, Technical barrier; Time barrier, Psychological barrier, Social barrier, Legal barrier, organizational barrier and Change
, which means that that a perfect reconstruction of a band-limited function from its nonuniform samples in is possible [17]. Efficient numerical methods for performing
247, 297, 320 (1999) (discussing the limitations of breach of fiduciary duty claims and concluding that those limitations have rendered the cause of action “almost nonexistent”). See


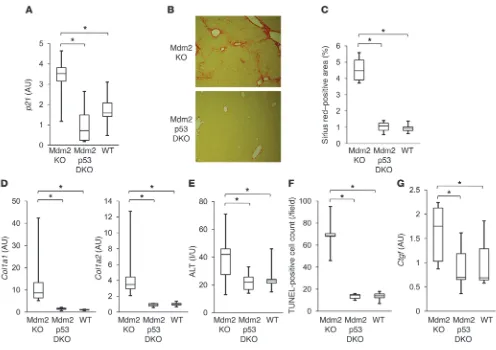
![Figure 7p53 regulates CTGF synthesis in hepatocytes. (A) Hepatocytes and NPCs were isolated from Mdm2fl/fl [Cre(–)] mice and Mdm2fl/flalb-cre [Cre(+)] mice by collagenase-pronase perfusion of the liver](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/8164530.806813/9.585.51.538.77.502/figure-regulates-synthesis-hepatocytes-hepatocytes-isolated-collagenase-perfusion.webp)