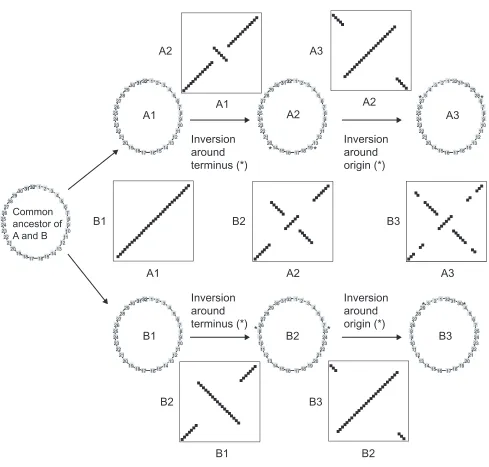
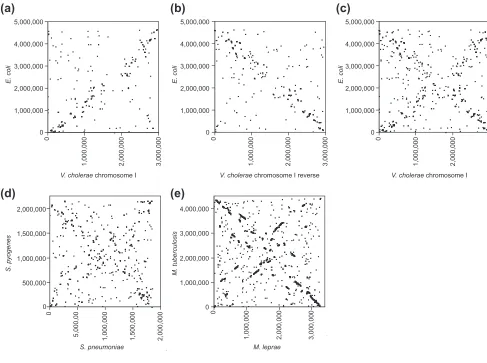
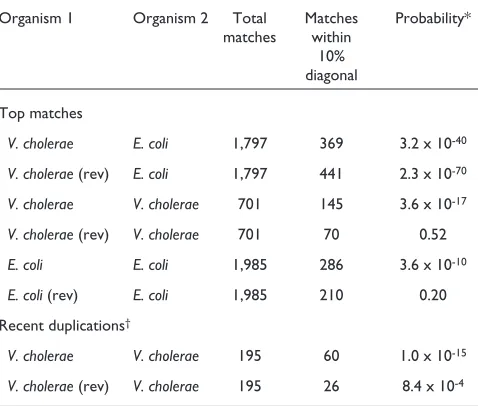
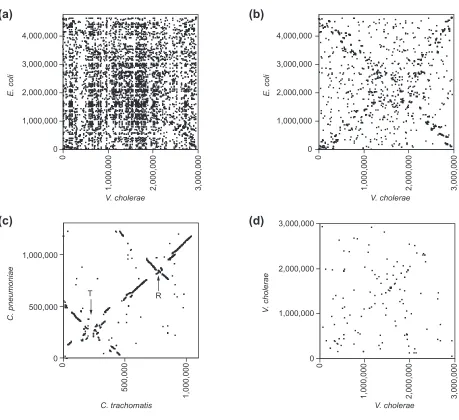
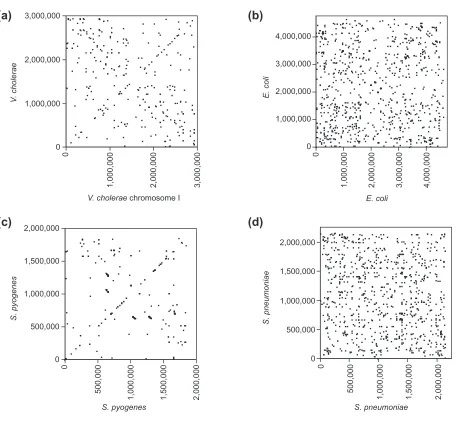
Evidence for symmetric chromosomal inversions around the replication origin in bacteria
Full text
Figure
Related documents
Two groups of students identified the negative and positive characteristics of the neighborhood, mapping community assets in the City of Springfield and the Laura Street
The results of the present study indi- cate that the 6-week dynamic neuromuscular training programme reduced the angle of ankle joint plantar flexion upon initial contact during
A customised approach for teaching and learning is proposed, incorporating the previous findings: the skills required by modern industry; Bloom‟s learning domains for
In this report, we discuss the use of stimulated Raman histology as a means to identify tissue boundaries during the resection of an extensive, recurrent, atypical
The cytosolic tail, transmembrane domain, and stem re- gion of GlcNAc6ST-1 were fused to the catalytic domain of GlcNAc6ST-2 bearing C-terminal EYFP, and the substrate preference of
Cloud or on premise Financial planning and analysis Treasury and financial risk Enterprise risk and compliance Accounting and financial close Collaborative finance
Мөн БЗДүүргийн нохойн уушгины жижиг гуурсанцрын хучуур эсийн болон гөлгөр булчингийн ширхгийн гиперплази (4-р зураг), Чингэлтэй дүүргийн нохойн уушгинд том
Progression of tau pathology in cholinergic Basal forebrain neurons in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) and