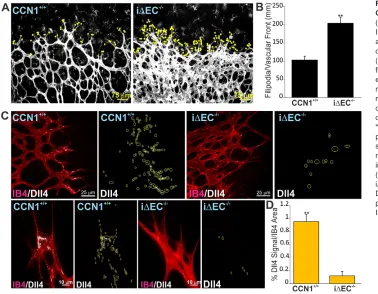
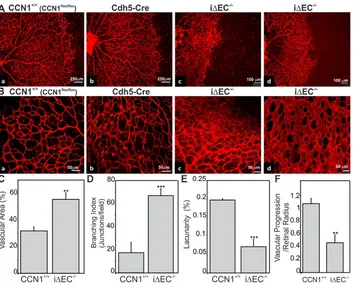
The matricellular protein CCN1 controls retinal angiogenesis by targeting VEGF, Src homology 2 domain phosphatase 1 and Notch signaling
Full text
Figure



Related documents
Preble Street funds a program called Logan Place, the goal of which is to provide permanent housing for the homeless population in Portland, which has been steadily increasing for
Herein, we describe a practical procedure for the acylation of various amines and sulfonamides with acetic anhydride at room temperature and without a solvent using
The microparticles were subjected to accelerated stability testing and it was found that there was no significant decrease in drug content or particle size of VEML and
It is noticed that place of resident, marital status, diabetes symptoms: nausea, diabetes symptoms: frequent urination, previous generation and treatment Gap
Therefore, considering the deployment of GNAs in the practical WiNoC, it is crucial to investigate the effects of various propagation environment parameters inside a chip package on
We investigated the effect of Cu applications (up to 1000 mg kg j1 ) to a Xeric Haplocalcid (Declo series) and a Typic Calciaquoll (Logan series) on corn ( Zea mays L.) growth and