metal-organic papers
m566
Reza Kiaet al. [Re(C2F3O2)(C20H24N2)(CO)3] doi:10.1107/S1600536805005003 Acta Cryst.(2005). E61, m566–m567
Acta Crystallographica Section E
Structure Reports
Online
ISSN 1600-5368
[
N
,
N
000-Bis(2,4-dimethylbenzene)-2,3-dimethyl-1,4-diazabuta-1,3-diene]-
fac
-tricarbonyl-(trifluoroacetato)rhenium(I)
Reza Kia,aValiollah Mirkhani,a* Andrea Dea´kb* and
Alajos Ka´lma´nb
aDepartment of Chemistry, University of Isfahan,
Isfahan 81746-73441, Iran, and Institute of Structural Chemistry, Chemical Research Center, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, PO Box 17, H-1525 Budapest, Hungary
Correspondence e-mail: mirkhani@sci.ui.ac.ir, deak@chemres.hu
Key indicators
Single-crystal X-ray study
T= 293 K
Mean(C–C) = 0.013 A˚ Disorder in main residue
Rfactor = 0.042
wRfactor = 0.087
Data-to-parameter ratio = 16.0
For details of how these key indicators were automatically derived from the article, see http://journals.iucr.org/e.
#2005 International Union of Crystallography Printed in Great Britain – all rights reserved
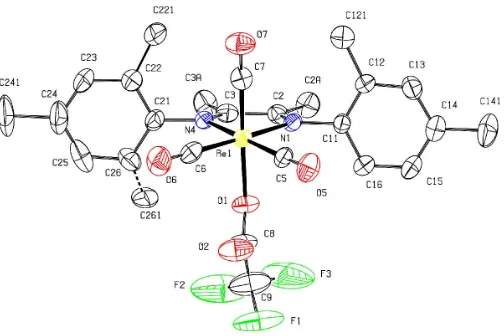
In the title compound, [Re(CF3COO)(C20H24N2)(CO)3], the Re atom has a distorted octahedral configuration. The 1,4-diazabutadiene part of the donor ligand and two carbonyl groups occupy the equatorial plane of the complex, with the third carbonyl ligand and the trifluoroacetate group in the axial positions. The equatorial diimine ligand is bound to the Re center in anN,N0-bidentate chelating fashion, leading to a five-membered ReN2C2chelate ring with an N—Re—N bite angle of 73.4 (2).
Comment
We report here the results of an X-ray structure investigation of the title complex, (I). The Re atom has a distorted octa-hedral configuration (Fig. 1) and is coordinated by two carbonyl groups [Re—C = 1.900 (9) and 1.901 (9) A˚ ] and the diimine group of the organic ligand [Re—N = 2.156 (5) and 1.157 (5) A˚ ] in the equatorial plane. Octahedral coordination is completed at the axial positions by another carbonyl ligand [Re—C = 1.912 (8) A˚ ] and a carboxyl O atom of the tri-fluoroacetate anion [Re—O = 2.157 (4) A˚ ]. The orientation of the coordinated trifluoroacetate anion can be defined by the O2—C8—C9—F1 torsion angle of 16 (2). The equatorial arrangement, defined by the Re and donor atoms (N1/N4/C5/ C6) of the corresponding diimine and carbonyl ligands is essentially planar; the deviation of the Re atom from the N1/ N4/C5/C6 plane is 0.068 (3) A˚ .
The equatorial diimine ligand is bound to the Re center in a
N,N0-bidentate chelating fashion, leading to a five-membered
ReN2C2 chelate ring with an N1—Re1—N4 bite angle of 73.4 (2). The other cis-equatorial angles at Re1 are C5—
Re1—C6 of 88.3 (3), N1—Re1—C5 of 98.9 (3) and N4—
Re1—C6 of 97.0 (2). The axial C7—Re1—O1 angle is
177.4 (3). The aromatic rings are oriented essentially at right
angles to the chelate ring plane [dihedral angle between C11– C16 and Re1/N1/C2 is 84.9 (2) and between C21–C26 and Re1/N4/C3 is 87.4 (3)]; this orientation leads to C121 O7
and C221 O7 intramolecular separations of 3.737 (11) and 3.738 (18) A˚ , respectively. The CF3 group has high thermal motion consistent with some unresolved rotational disorder, as is often found in other trifluoroacetate compounds (Rodrigueset al., 2000, 2001).
Experimental
Compound (I) was synthesized as described in the literature (Kleinet al., 1996). Dark red block-shaped crystals of (I) suitable for X-ray structure analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution in dichloromethane/n-hexane at room temperature.
Crystal data
[Re(C2F3O2)(C20H24N2)(CO)3]
Mr= 675.66 Monoclinic,P21=c a= 12.818 (3) A˚ b= 13.026 (3) A˚ c= 16.554 (4) A˚
= 106.07 (2)
V= 2655.9 (11) A˚3 Z= 4
Dx= 1.690 Mg m
3
MoKradiation Cell parameters from 25
reflections
= 14.0–15.9 = 4.63 mm1 T= 293 (2) K Block, dark red 0.550.300.30 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
!–2scans
Absorption correction: scan (DATCOR; Reibenspies, 1989) Tmin= 0.137,Tmax= 0.250
5775 measured reflections 5369 independent reflections 2977 reflections withI> 2(I)
Rint= 0.015 max= 26.3
h= 0!15 k= 0!16 l=20!19 3 standard reflections
frequency: 60 min intensity decay: 3%
Refinement
Refinement onF2
R[F2> 2(F2)] = 0.042 wR(F2) = 0.087
S= 0.92 5369 reflections 335 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained w= 1/[2
(Fo2) + (0.0422P)2] whereP= (Fo2+ 2Fc2)/3 (/)max= 0.004
max= 0.76 e A˚ 3
min=0.63 e A˚ 3
One of them-xylol rings of the diimine ligand has orientational disorder and the refined site-occupancy factors of the disordered parts (methyl groups C221/C226 and associated H atoms) are 0.651 (15) and 0.349 (15). None of the the H atoms of the methyl groups was clearly resolved in difference maps and they were
subsequently included as six half-occupancy H atoms on each group. Other H atoms were located in difference maps and were subse-quently repositioned geometrically and refined as riding, with C—H distances of 0.93 (aromatic) and 0.96 A˚ (methyl), and withUiso(H) = 1.2 (aromatic) or 1.5 (methyl) timesUeq(C).
Data collection: CAD-4 EXPRESS (Enraf–Nonius, 1992); cell refinement: CAD-4 EXPRESS; data reduction: XCAD4 (Harms, 1996); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997); program(s) used to refine structure:SHELXL97(Sheldrick, 1997); molecular graphics:PLATON(Spek, 2003); software used to prepare material for publication:SHELXL97.
References
Enraf–Nonius (1992).CAD-4 EXPRESS. Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Nether-lands.
Harms, K. (1996).XCAD4. University of Marburg, Germany. Klein, A., Conny, V. & Kaim, W. (1996).Organometallics,15, 236–244. Reibenspies, J. (1989).DATCOR. Texas A&M University, USA.
Rodrigues, V. H., Paixa˜o, J. A., Costa, M. M. R. R. & Matos Beja, A. (2000). Acta Cryst.C56, 1053–1055.
Rodrigues, V. H., Paixa˜o, J. A., Costa, M. M. R. R. & Matos Beja, A. (2001). Acta Cryst.C57, 417–420.
Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97. University of Go¨ttingen, Germany.
[image:2.610.315.567.69.237.2]Spek, A. L. (2003).J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Figure 1
supporting information
sup-1
Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m566–m567
supporting information
Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m566–m567 [https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536805005003]
[
N
,
N
′
-Bis(2,4-dimethylbenzene)-2,3-dimethyl-1,4-diazabuta-1,3-diene]-
fac
-tri-carbonyl(trifluoroacetato)rhenium(I)
Reza Kia, Valiollah Mirkhani, Andrea De
á
k and Alajos K
á
lm
á
n
[N,N′-Bis(2,4-dimethylbenzene)-2,3-dimethyl-1,4-diazabuta-1,3-diene]- fac
-tricarbonyl(trifluoroacetato)rhenium(I)
Crystal data
[Re(C2F3O2)(C20H24N2)(CO)3]
Mr = 675.66 Monoclinic, P21/c
Hall symbol: -P 2ybc a = 12.818 (3) Å b = 13.026 (3) Å c = 16.554 (4) Å β = 106.07 (2)° V = 2655.9 (11) Å3
Z = 4
F(000) = 1320 Dx = 1.690 Mg m−3
Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å Cell parameters from 25 reflections θ = 14.0–15.9°
µ = 4.63 mm−1
T = 293 K Block, dark red 0.55 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm
Data collection Enraf–Nonius CAD-4
diffractometer
Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-ray tube Graphite monochromator
ω–2θ scans
Absorption correction: ψ scan (DATCOR; Reibenspies, 1989) Tmin = 0.137, Tmax = 0.250
5775 measured reflections
5369 independent reflections 2977 reflections with I > 2σ(I) Rint = 0.015
θmax = 26.3°, θmin = 2.6°
h = 0→15 k = 0→16 l = −20→19
3 standard reflections every 60 min intensity decay: 3%
Refinement Refinement on F2
Least-squares matrix: full R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042
wR(F2) = 0.087
S = 0.92 5369 reflections 335 parameters 0 restraints
Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods
Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map
Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites
H-atom parameters constrained w = 1/[σ2(F
o2) + (0.0422P)2]
where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3
(Δ/σ)max = 0.004
Δρmax = 0.76 e Å−3
Special details
Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes.
Least-squares planes (x,y,z in crystal coordinates) and deviations from them (* indicates atom used to define plane) - 1.6263 (0.0298) x + 9.3049 (0.0251) y + 11.5288 (0.0329) z = 4.1307 (0.0086)
* 0.0101 (0.0041) N1 * 0.0068 (0.0057) C2 * 0.0060 (0.0060) C3 * -0.0168 (0.0041) N4 * -0.0149 (0.0039) C2A * 0.0088 (0.0039) C3A 0.1421 (0.0074) Re1
Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0113
- 0.9022 (0.0308) x + 10.3125 (0.0171) y + 9.9760 (0.0277) z = 4.3039 (0.0065) Angle to previous plane (with approximate e.s.d.) = 7.20 (0.34)
* -0.0149 (0.0031) N1 * 0.0150 (0.0031) N4 * 0.0143 (0.0029) C5 * -0.0144 (0.0030) C6 - 0.0684 (0.0033) Re1 0.1363 (0.0087) C2 0.1688 (0.0091) C3
Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0146
2.5347 (0.0379) x + 9.5766 (0.0308) y - 11.2199 (0.0425) z = 1.3603 (0.0146) Angle to previous plane (with approximate e.s.d.) = 79.94 (0.17)
* -0.0008 (0.0053) C11 * 0.0055 (0.0052) C12 * -0.0083 (0.0057) C13 * 0.0060 (0.0061) C14 * -0.0012 (0.0065) C15 * -0.0013 (0.0059) C16
Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0048
- 2.2442 (0.1026) x + 9.6505 (0.0276) y + 11.1169 (0.0404) z = 4.0982 (0.0185) Angle to previous plane (with approximate e.s.d.) = 84.86 (0.22)
* 0.0000 (0.0000) Re1 * 0.0000 (0.0000) N1 * 0.0000 (0.0000) C2 Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0000
5.2381 (0.0431) x + 7.9671 (0.0443) y - 12.6485 (0.0461) z = 1.4195 (0.0299) Angle to previous plane (with approximate e.s.d.) = 86.69 (0.29)
* 0.0102 (0.0063) C21_a * 0.0044 (0.0078) C22_a * -0.0027 (0.0089) C23_a * -0.0148 (0.0084) C24_a * 0.0299 (0.0076) C25_a * -0.0270 (0.0063) C26_a
Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0182
- 0.4186 (0.0861) x + 9.3460 (0.0519) y + 11.2180 (0.0424) z = 4.4705 (0.0189) Angle to previous plane (with approximate e.s.d.) = 87.37 (0.30)
* 0.0000 (0.0000) Re1 * 0.0000 (0.0000) N4 * 0.0000 (0.0000) C3 Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0000
Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2,
conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used
only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2
are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
x y z Uiso*/Ueq Occ. (<1)
supporting information
sup-3
Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m566–m567
C2 0.1806 (6) 0.3401 (5) 0.1099 (4) 0.0566 (19) C2A 0.1294 (6) 0.4136 (6) 0.0415 (5) 0.082 (2)
H2A1 0.0520 0.4121 0.0316 0.123* 0.50 H2A2 0.1474 0.3944 −0.0090 0.123* 0.50 H2A3 0.1558 0.4816 0.0577 0.123* 0.50 H2A4 0.1848 0.4466 0.0219 0.123* 0.50 H2A5 0.0894 0.4644 0.0626 0.123* 0.50 H2A6 0.0810 0.3771 −0.0042 0.123* 0.50 C3 0.3004 (6) 0.3280 (6) 0.1365 (4) 0.062 (2)
C3A 0.3703 (6) 0.3911 (7) 0.0956 (5) 0.089 (3)
H3A1 0.4453 0.3741 0.1201 0.133* 0.50 H3A2 0.3593 0.4628 0.1042 0.133* 0.50 H3A3 0.3509 0.3768 0.0364 0.133* 0.50 H3A4 0.3250 0.4350 0.0537 0.133* 0.50 H3A5 0.4110 0.3463 0.0696 0.133* 0.50 H3A6 0.4194 0.4323 0.1374 0.133* 0.50 C5 0.1065 (6) 0.1436 (6) 0.2940 (5) 0.0614 (19)
C6 0.3228 (7) 0.1175 (6) 0.3377 (5) 0.070 (2) C7 0.2063 (6) 0.0640 (6) 0.1878 (5) 0.064 (2) C8 0.2346 (7) 0.3425 (7) 0.3917 (6) 0.080 (3) C9 0.2362 (16) 0.4553 (10) 0.4178 (8) 0.140 (5) C11 0.0109 (5) 0.2880 (5) 0.1271 (4) 0.0520 (18) C12 −0.0506 (6) 0.2293 (5) 0.0626 (4) 0.0612 (19) C13 −0.1619 (6) 0.2381 (6) 0.0462 (5) 0.076 (2) H13 −0.2052 0.1977 0.0036 0.091* C14 −0.2120 (7) 0.3026 (7) 0.0887 (6) 0.082 (2) C15 −0.1486 (7) 0.3594 (7) 0.1521 (6) 0.093 (3) H15 −0.1808 0.4032 0.1826 0.111* C16 −0.0357 (6) 0.3531 (6) 0.1722 (5) 0.081 (2) H16 0.0074 0.3925 0.2156 0.097* C121 −0.0026 (8) 0.1595 (7) 0.0109 (6) 0.117 (3)
H12A −0.0598 0.1263 −0.0309 0.175* 0.50 H12B 0.0415 0.1087 0.0465 0.175* 0.50 H12C 0.0414 0.1988 −0.0163 0.175* 0.50 H12D 0.0752 0.1629 0.0304 0.175* 0.50 H12E −0.0261 0.1805 −0.0470 0.175* 0.50 H12F −0.0260 0.0904 0.0159 0.175* 0.50 C141 −0.3354 (7) 0.3117 (7) 0.0654 (7) 0.123 (4)
H14A −0.3671 0.2651 0.0204 0.185* 0.50 H14B −0.3564 0.3807 0.0479 0.185* 0.50 H14C −0.3603 0.2949 0.1134 0.185* 0.50 H14D −0.3554 0.3620 0.1008 0.185* 0.50 H14E −0.3661 0.2465 0.0732 0.185* 0.50 H14F −0.3622 0.3322 0.0077 0.185* 0.50 C21 0.4503 (6) 0.2414 (6) 0.2254 (4) 0.065 (2)
C22 0.4939 (7) 0.1602 (9) 0.1929 (6) 0.114 (4)
H22A 0.4792 0.0580 0.0973 0.293* 0.325 (8) H22B 0.4264 0.1646 0.0661 0.293* 0.325 (8) H22C 0.3670 0.0877 0.1112 0.293* 0.325 (8) H22D 0.3692 0.1488 0.0858 0.293* 0.325 (8) H22E 0.4220 0.0422 0.1170 0.293* 0.325 (8) H22F 0.4815 0.1191 0.0718 0.293* 0.325 (8) C23 0.6041 (9) 0.1384 (10) 0.2253 (7) 0.142 (5)
H23 0.6333 0.0837 0.2026 0.170* C24 0.6686 (7) 0.1917 (12) 0.2866 (7) 0.114 (4) C241 0.7906 (7) 0.1702 (10) 0.3168 (7) 0.172 (6)
H24A 0.8236 0.2147 0.3630 0.258* 0.5 H24B 0.8226 0.1823 0.2716 0.258* 0.5 H24C 0.8023 0.1000 0.3346 0.258* 0.5 H24D 0.8087 0.1166 0.2831 0.258* 0.5 H24E 0.8097 0.1490 0.3746 0.258* 0.5 H24F 0.8300 0.2314 0.3115 0.258* 0.5 C25 0.6258 (9) 0.2732 (10) 0.3166 (7) 0.111 (4)
H25 0.6720 0.3150 0.3564 0.134* C26 0.5154 (7) 0.2974 (6) 0.2907 (5) 0.079 (2)
H26 0.4869 0.3495 0.3165 0.095* 0.651 (15) C261 0.493 (2) 0.3883 (17) 0.3185 (15) 0.098 (10) 0.349 (15) H26A 0.5523 0.4102 0.3643 0.148* 0.175 (8) H26B 0.4285 0.3825 0.3375 0.148* 0.175 (8) H26C 0.4804 0.4377 0.2738 0.148* 0.175 (8) H26D 0.4218 0.4100 0.2861 0.148* 0.175 (8) H26E 0.5456 0.4377 0.3130 0.148* 0.175 (8) H26F 0.4937 0.3825 0.3766 0.148* 0.175 (8)
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
U11 U22 U33 U12 U13 U23
supporting information
sup-5
Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m566–m567
C7 0.067 (5) 0.060 (5) 0.068 (5) −0.008 (4) 0.022 (4) 0.012 (4) C8 0.110 (7) 0.077 (7) 0.072 (6) −0.024 (5) 0.054 (5) −0.028 (5) C9 0.245 (16) 0.112 (11) 0.103 (9) −0.012 (11) 0.113 (11) −0.004 (8) C11 0.042 (4) 0.056 (5) 0.058 (4) 0.004 (3) 0.014 (3) 0.000 (3) C12 0.058 (5) 0.061 (5) 0.066 (5) 0.007 (4) 0.019 (4) −0.013 (4) C13 0.060 (5) 0.074 (5) 0.083 (6) −0.001 (4) 0.003 (4) −0.004 (5) C14 0.060 (5) 0.091 (7) 0.097 (6) 0.013 (5) 0.024 (5) 0.006 (6) C15 0.066 (6) 0.121 (8) 0.096 (7) 0.028 (6) 0.031 (5) −0.015 (6) C16 0.066 (5) 0.092 (6) 0.085 (6) 0.013 (5) 0.021 (5) −0.028 (5) C121 0.086 (6) 0.135 (9) 0.117 (7) 0.015 (6) 0.009 (6) −0.050 (6) C141 0.057 (5) 0.143 (9) 0.174 (10) 0.010 (6) 0.039 (6) 0.006 (8) C21 0.054 (5) 0.089 (6) 0.059 (5) 0.010 (4) 0.025 (4) 0.001 (4) C22 0.061 (6) 0.186 (11) 0.093 (7) 0.011 (7) 0.018 (5) −0.056 (7) C221 0.078 (11) 0.25 (2) 0.23 (2) 0.040 (13) −0.007 (12) −0.177 (19) C23 0.068 (7) 0.245 (14) 0.114 (8) 0.047 (8) 0.026 (6) −0.063 (9) C24 0.047 (5) 0.194 (13) 0.103 (8) 0.011 (8) 0.023 (5) 0.034 (9) C241 0.035 (5) 0.327 (18) 0.144 (9) 0.018 (8) 0.009 (5) 0.050 (11) C25 0.069 (7) 0.140 (10) 0.101 (8) −0.029 (7) −0.016 (6) 0.021 (7) C26 0.076 (6) 0.073 (7) 0.075 (5) −0.010 (5) −0.001 (4) −0.008 (5) C21A 0.054 (5) 0.089 (6) 0.059 (5) 0.010 (4) 0.025 (4) 0.001 (4) C22A 0.061 (6) 0.186 (11) 0.093 (7) 0.011 (7) 0.018 (5) −0.056 (7) C23A 0.068 (7) 0.245 (14) 0.114 (8) 0.047 (8) 0.026 (6) −0.063 (9) C24A 0.047 (5) 0.194 (13) 0.103 (8) 0.011 (8) 0.023 (5) 0.034 (9) C242 0.035 (5) 0.327 (18) 0.144 (9) 0.018 (8) 0.009 (5) 0.050 (11) C25A 0.069 (7) 0.140 (10) 0.101 (8) −0.029 (7) −0.016 (6) 0.021 (7) C26A 0.076 (6) 0.073 (7) 0.075 (5) −0.010 (5) −0.001 (4) −0.008 (5) C261 0.11 (2) 0.055 (17) 0.11 (2) 0.007 (14) 0.009 (16) −0.038 (15)
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
C2—C3 1.484 (10) C221—H22A 0.96 C2—C2A 1.490 (9) C221—H22B 0.96 C2A—H2A1 0.96 C221—H22C 0.96 C2A—H2A2 0.96 C221—H22D 0.96 C2A—H2A3 0.96 C221—H22E 0.96 C2A—H2A4 0.96 C221—H22F 0.96 C2A—H2A5 0.96 C23—C24 1.316 (14) C2A—H2A6 0.96 C23—H23 0.93 C3—C3A 1.508 (9) C24—C25 1.351 (13) C3A—H3A1 0.96 C24—C241 1.530 (12) C3A—H3A2 0.96 C241—H24A 0.96 C3A—H3A3 0.96 C241—H24B 0.96 C3A—H3A4 0.96 C241—H24C 0.96 C3A—H3A5 0.96 C241—H24D 0.96 C3A—H3A6 0.96 C241—H24E 0.96 C8—C9 1.530 (14) C241—H24F 0.96 C11—C12 1.371 (9) C25—C26 1.396 (13) C11—C16 1.372 (9) C25—H25 0.93 C12—C13 1.380 (9) C26—H26 0.93 C12—C121 1.493 (10) C261—H26A 0.96 C13—C14 1.366 (10) C261—H26B 0.96 C13—H13 0.93 C261—H26C 0.96 C14—C15 1.356 (11) C261—H26D 0.96 C14—C141 1.525 (11) C261—H26E 0.96 C15—C16 1.395 (10) C261—H26F 0.96
supporting information
sup-7
Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m566–m567
C14—C13—C12 123.8 (8) C25—C26—H26 121.2 C14—C13—H13 118.1 H26A—C261—H26B 109.5 C12—C13—H13 118.1 H26A—C261—H26C 109.5 C15—C14—C13 117.9 (8) H26B—C261—H26C 109.5 C15—C14—C141 120.7 (8) H26D—C261—H26E 109.5 C13—C14—C141 121.4 (9) H26D—C261—H26F 109.5 C14—C15—C16 120.8 (8) H26E—C261—H26F 109.5