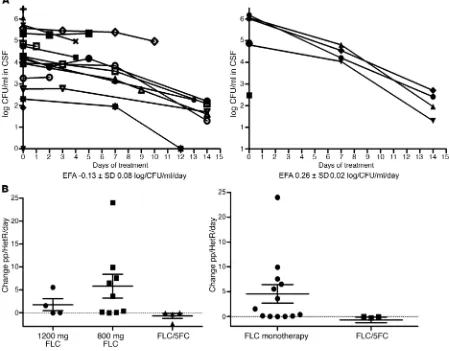
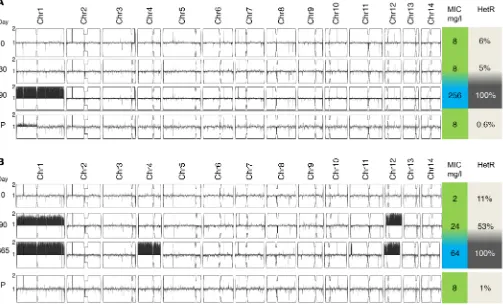
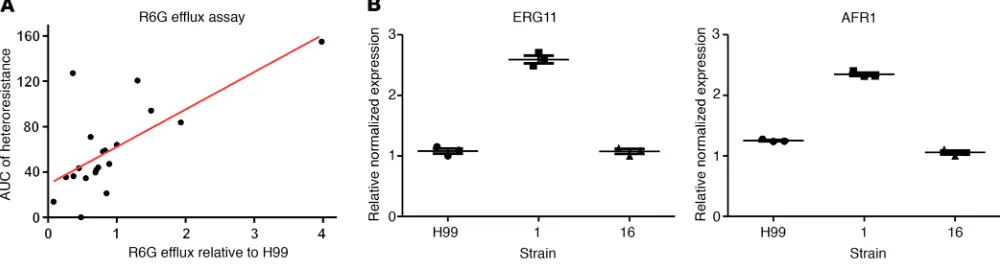
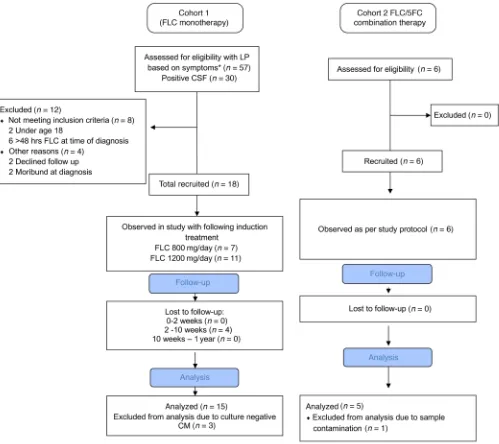
Dynamic ploidy changes drive fluconazole resistance in human cryptococcal meningitis
Full text
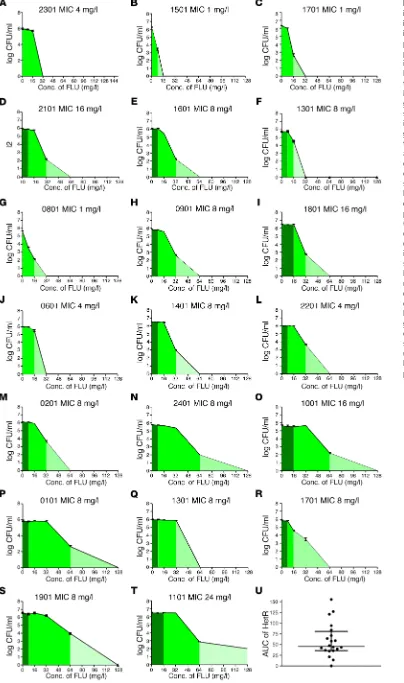
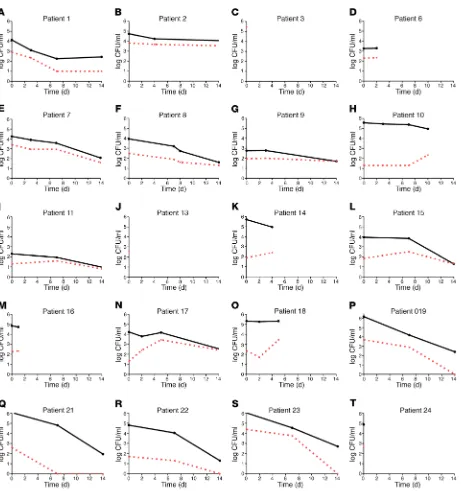
Figure

Related documents
After the fifth player reported an infection, the staff athletic trainers, team physicians, and a consultant infectious disease physician met to discuss infection control
In bold type : university site 20,000 5,000 less than 300 1,000 50,000 Loudéac Quessoy Tréguier Châteaulin Carhaix- Plouguer Auray Locminé Lamballe Questembert St-Jacut-
Safe childbirth in rural communities depends on good risk assessment and decision making as to whether and when the transfer of a woman in labour to an obstetric led unit is
Recently, we reported that the activity of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) is de- creased in the frontal cortex of subjects with regres- sive autism
Dow does not routinely analyze for additional materials that are not listed in the MSDS or Sales Specification.. Specifically, while we have not analyzed for Bisphenol A, it is
It can only be stated that, for the Hamilton (CMA) the compact urban form leads to congestion and nitrogen oxide levels which are significantly lower than the magnitudes of
Community hospitals provide a wide range of services, covering the whole spectrum of care provision, from pre- ventative [20, 21] and primary care [22, 23], through to
This paper has proposed a new method to extend pricing rules in both incomplete and imperfect markets by using general risk functions, with special focus on Expectation Bounded Risk