Multi Task Transfer Learning for Weakly Supervised Relation Extraction
Full text
Figure

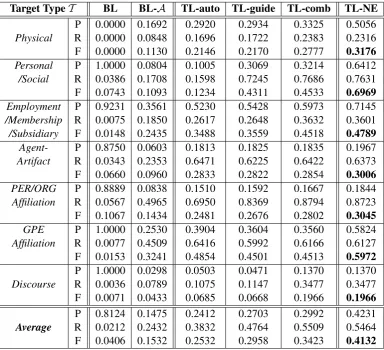


Related documents
Therefore, for the distantly labeled data the relation between the annotation quality and the information gain, given the seed set which is used for selecting instances is
Transfer Learning aim to improve the performance of low-resource domain task by exploiting the anno- tated data form high-resource domain, thus the Disparity between different tasks
This paper proposes a novel context-aware joint entity and word-level relation extraction ap- proach through semantic composition of words, introducing a Table Filling
multitask learning in which performances on a given task are improved using information con- tained in the training signals of auxiliary related tasks ( Caruana , 1997 ) from
To address this issue, we propose Relational Siamese Networks (RSNs) to learn similar- ity metrics of relations from labeled data of pre-defined relations, and then transfer
multitask learning in which performances on a given task are improved using information con- tained in the training signals of auxiliary related tasks ( Caruana , 1997 ) from
This paper describes the first task on seman- tic relation extraction and classification in sci- entific paper abstracts at SemEval 2018. The challenge focuses on domain-specific
In this work, we incorporate selectional pref- erences , i.e., relations enforce constraints on the allowed entity types for the candidate en- tities, to multi-hop relation