Functional electrical stimulation and ankle foot orthoses provide equivalent therapeutic effects on foot drop : a meta analysis providing direction for future research
Full text
Figure

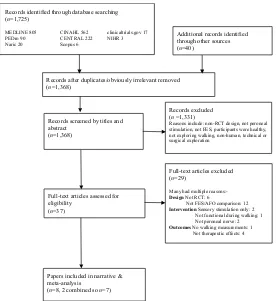


Related documents
The research study investigated if the test scores used in the mathematics placement process at UNF effectively predict students’ success in their first mathematics course in the
To evaluate the potential of the invasive alien weed; Parthenium hysterophorus L., as a source of nutrients for growth of maize and sorghum, experiments were conducted in
Higher tuber yield in summer could be attributed to longer crop duration, higher harvest index, leaf area index and net assimilation rate.. The physiological age of
6 7 In October of 1995, due to its illegal business, inferior asset quality and undisciplined management, the Shanghai Branch of Zhongyin Trust and Investment
Having avoided the issue of individual standing to assert treaty provisions in Cadena, Cortes and Conroy, the Fifth Circuit has ef- fectively closed the door on
The following configuration was used to test the study variables: model 1 (sociodemographic variables only); model 2 (all significant variables from model 1 plus variables related
As we are unable to account for effects triggered by long-term culture, secondary miRNA targets and the kinetics of each endogenous protein expression and stability, the difference in
The present study suggested that LIMKs promote prostate smooth muscle contraction by phosphorylating cofilin and subsequent causing actin organization, which could be