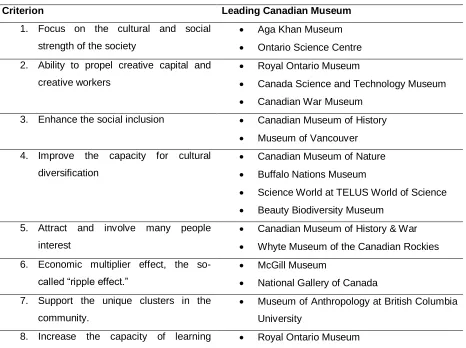
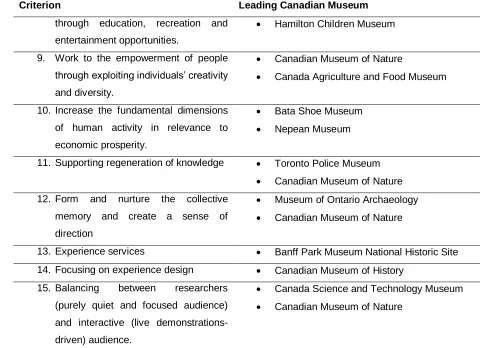
MUSEUMS AND THEIR ROLE IN RESILIENT CREATIVE ECONOMY – THE CANADIAN EXPERIENCE
Full text
Figure


Related documents
The paper is discussed for various techniques for sensor localization and various interpolation methods for variety of prediction methods used by various applications
In Step 2 we will look more closely at the links between thoughts, feelings and behaviours, particularly when we feel Anxious, Depressed and Angry. We will also start to learn
Results of the survey are categorized into the following four areas: primary method used to conduct student evaluations, Internet collection of student evaluation data,
Since Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is developed to get the maximum possible power from one or more solar panels, several algorithms and techniques have been proposed for
After 1970, “modern” (publicly available and issuer-paid) ratings were of particular interest for foreign corporate bond issuers increasingly entering the American bond
In this article, we devise a LSTM-Gauss-NBayes method for outlier detection in IIoT. The LSTM-NN [17] is a variation of the RNN that can address the issue of gradient vanishing
With hollow fibre membranes, water vapour interacts with air in membrane pores; these pores allow water vapour transfer but are too small (0.1 P m) to allow microbial
Of course, in a real experiment, the atomic energy levels are influenced by external fields (see section 1.1) and other effects, such as collisional, gravita- tional, or rotational