Analysis of Implantable Ultrasonic Coupling Wireless Power Transmission System
Full text
Figure



Related documents
Wireless power transmission using microwaves and high voltage direct current transmission is efficient way of transmitting electrical energy with less loss. The SPS will be
Qiao, “Simultaneous energy and data wireless transfer attenuation in biological channel of deep implantable medical devices: Characteristic analysis and modeling,” Progress
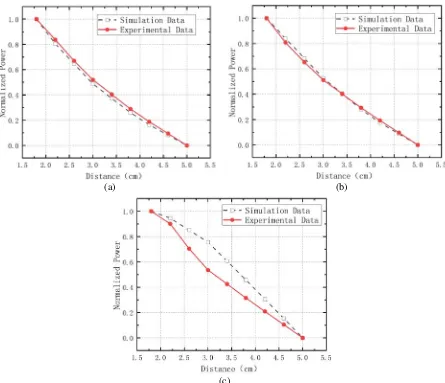
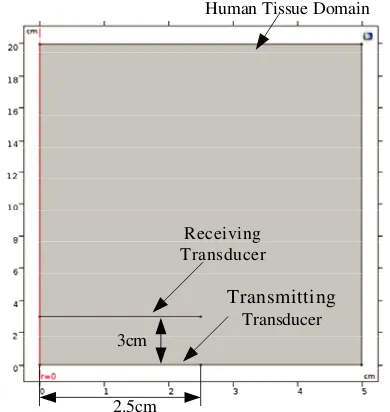
10(c), the transmission property (S 21 ) and transmission efficiency of the wireless energy transmission resonator having circular transmitting and receiving coils with coupling
Keywords: biomedical implants, wireless power transfer, inductive coupling, resonance– based power delivery, power harvesting, coil misalignment, mutual inductance, finite
The Primary components of Wireless Power Transmission are Microwave Generator, Transmitting antenna and Receiving antenna (Rectenna).. The components are described
However If long distance, high efficiency wireless power transmission is possible than night time off peak load is available, it also make possible that half
The transmitting antenna is continuously fed power and this power is transferred to the receiving antenna via a wireless magnetic resonance coupling.. Typical
Wireless power transfer system is used to transfer the power one device to another device through the air medium or intervening space by inductive coupling or capacitive coupling,