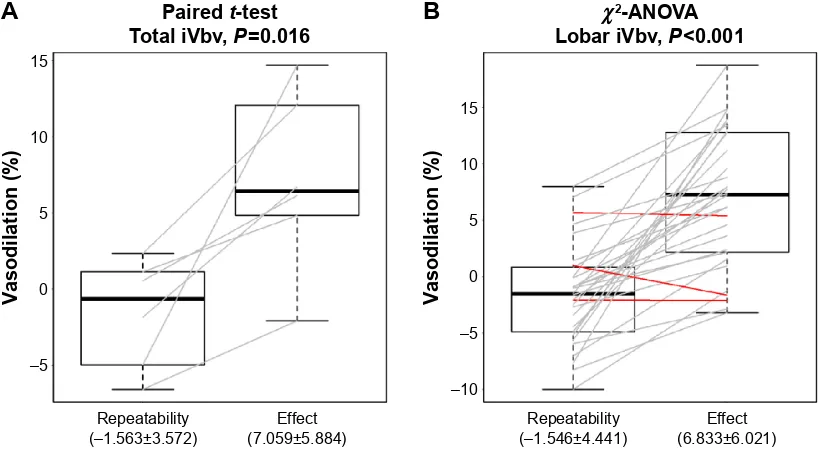
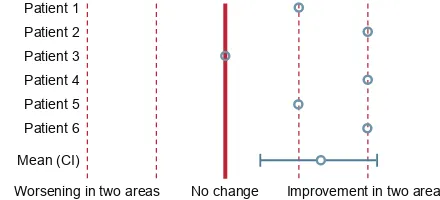
Pulmonary vascular effects of pulsed inhaled nitric oxide in COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension
Full text
Figure




Related documents
Combined effect of different levels of salt stress and calcium nitrate showed significant differences on dry matter content in fruit (Table 2).. Yield
Since biosensor networks require a low data rate, increasing the spreading factor by compromising data rates can justify application as an ideal modulation scheme for
The present study was thus designed to investigate the variations in body composition, maximal oxygen uptake (VO 2max ), and gas exchange threshold values of cross-country
Effectiveness of simulation technique in teaching learning process of CPR among nursing students at PSG College of Nursing, Coimbatore..
the independent variables (ie capital base, demand deposit, investment, loan and advances, liquidity ratio, bank size and inflation rate. This indicates a good fit of
Objective: This study aimed to show the changes in oxidative stress and clinical condition from either chest physical therapy (CPT) or CPT with aerosol treatment in infant
TABLE 2 Incidence of Any Wheeze or Asthma and HRs Comparing Children Partially and Fully Vaccinated Against Pertussis With Children Nonvaccinated for the Whole Time Period and