Iterative Looping for Impulsive Noise Channels in QAM- OFDM Based Systems
Full text
Figure
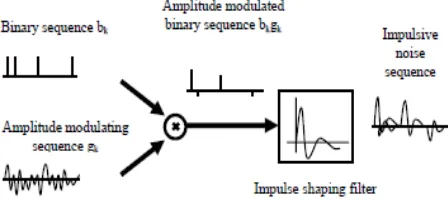
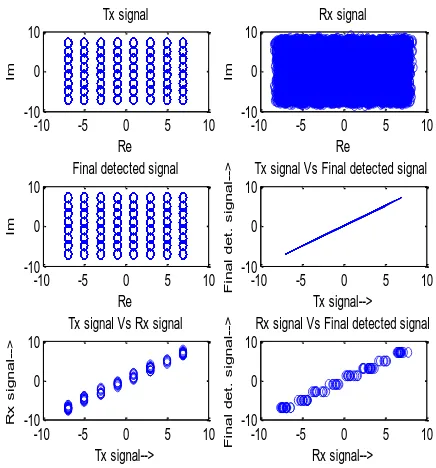
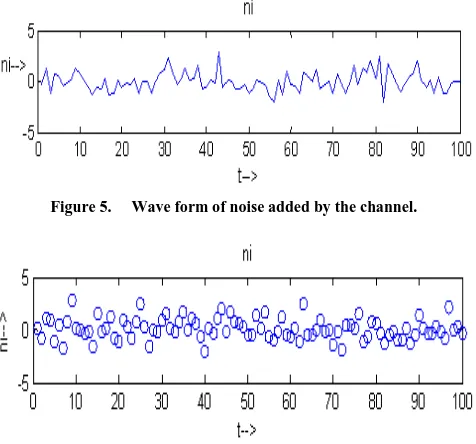
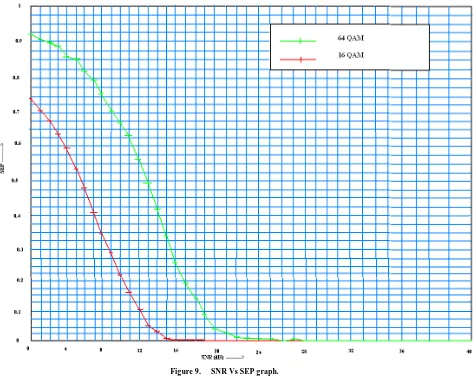
Related documents
Because they had been found to be associated with measures of clinical severity, YKL-40 and IL-6 were further examined for association with CSF tau and NFL levels, each of which
Species and diameter at breast height are required on each tree record, and optional data includes tree count, diameter growth, height, height growth, crown ratio, and various
Figure 4.2 The mean number of trials, errors, trials correct first time and blocks until criterion was reached on the trial-and-error learning version of the visual
For the performance evaluation of the LPM support, we use a traffic generator tool Network Function Performance Analyzer (NFPA) that al- lows generating different types of
An increase in risk lowers the certainty-equivalent rate of return, which then increases or decreases consumption depending upon whether relative risk aversion γ , is less than
Table I reports the magnitude of the reduction in steady state capital that occurs when financial innovation moves an economy from a golden eggs financial technology to a new
The main point of equation (16) is that Self 0 is willing to pay some- thing to make the nonsmoking agreement go through if Self 2’s income is insufficient. The very complexity of
While ratings, accounting, and reporting used to be only used for financial purposes, these classification systems are now used to enable sustaina- ble financial markets by