EFFECT OF DIFFERENT CONCENTRATIONS OF POWER LAW NON- NEWTONIAN LIQUIDS ON THEIR CRITICAL TURBIDITY AND RHEOLOGY Ahmed H. Hadi*, Hussein Y. Mahmood
Full text
Figure
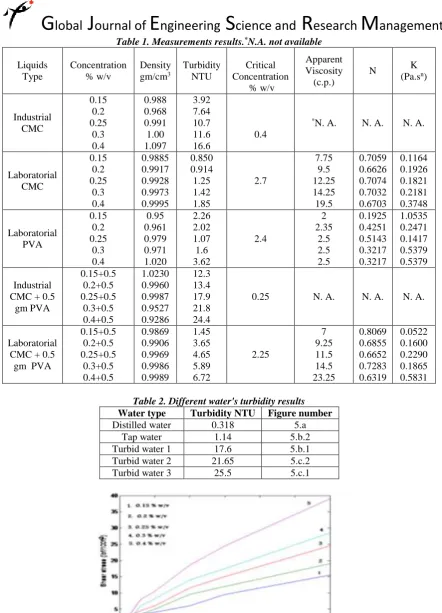
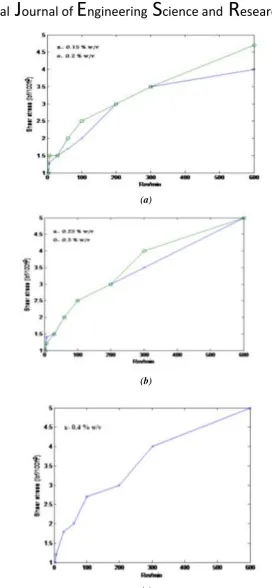
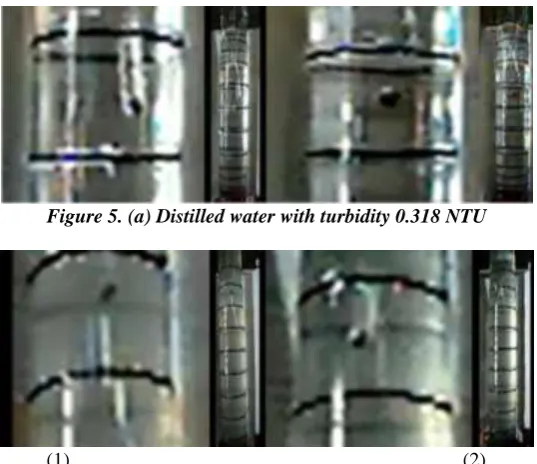

Related documents
We investigate how Cougaar components may be composed into a General Cougaar Application Model (GCAM) and used to develop a General Domain Application Model (GDAM) for specifying
The operational definition is the model you can test for reliability and validity using the tools of science.. Once validated at some level, the operational definition could then
In the present study an attempt is made with 10 red soils for various geotechnical characteristics to relate the collapsibility of these soils by considering
Results: In line with Goal 3 of SDGs: "ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages", the conference discussed various aspects of Universal
Biofilm production by selected strains of bacteria (a) and yeasts (b) in the presence of Textus bioactiv, Textus multi dressings, and culture broth without dressing.. The figures
Results: We observed significant inhibition of b -hexosaminidase release in RBL-2H3 cells and suppressed mRNA expression and protein secretion of IL-4 and IL-5 induced by
Another study with diabetic patients and the West Nile virus had observed that these patients were at greater risk of developing encephalitis and other severe forms of the disease
The pathogen–host interaction database (PHI-base) is a web-accessible database that catalogues experimentally verified pathogenicity, virulence and effector genes from bacterial,