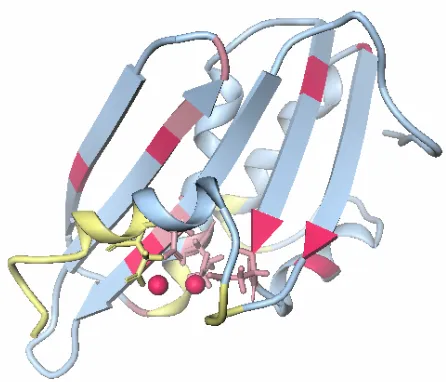
Targeting Divalent Metal Ions at the Active Site of the HIV 1 RNase H Domain: NMR Studies on the Interactions of Divalent Metal Ions with RNase H and Its Inhibitors
Full text
Figure




Related documents
[r]
The study revealed that most teachers in both private and public pre-primary schools used school homework as a method of teaching-learning. It is therefore
Reconstructed interference phase and corresponded temperature field measured on Twymann - Green type of interferometer.. There is also higher energy loss on the divider
Briefly, at the end of the study, the body weights in the conjugated (P0.05) and pure QC groups significantly (P0.01) increased compared to the diabetic rats,
As we conclude that by using varying the various heights and widths of actuator then founda new shape microgripper which is called as bottleneck shape microgripper.The simulation
The ultrasonic features and the clinical manifestations of the two groups were retrospectively analyzed, with an emphasis on the following parameters: onset age, gender
Unfortunately, this type of archival information was not available for Austria and Norway (the case study areas used in Sect. 3) or for other regions with winter air tem- peratures
To test this, we modeled residence time distributions of both pressure (hydraulic connectivity) and tracer (chemical connectivity) in an array of shallow monitoring wells in a