Structured Learning for Taxonomy Induction with Belief Propagation
Full text
Figure
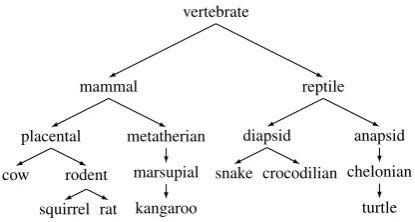



Related documents
concentrations of soluble heavy metals, pesticides, and pathogenic microorganisms); combined sewage overflows (poor water quality with high pathogenic microorganism concentrations
Effect of whole quinoa flour on chemical composition of bread, mineral 525. dietary reference intake contribution and mineral
Additionally, user acceptance of biometrics devices and authentication processes was used as key factors to determine the success of the biometric system (Pons and Polak,
It further explores how evidence-based practice can be used by occupational therapists to inform decision-making related to the development of community-based rehabilitation
Women and men in Sweden Statistics Sweden National coordination of gender equality work.. The Minister for Gender Equality coordinates the policies of
Combining the two studies, three main trends emerged: (1) religious commitment contributes positively to a belief in special creation and negatively to acceptance of evolution,
Since the last eradication of Mediterranean fruit flies (Medflies) in Florida, which was declared in October 1998, sterile Medflies have been released on a preventive basis in
While numerous studies have investigated the determinants of the going public decision (e.g. Beatty and Ritter, 1986 ; Brav, Geczy, and Gompers, 2000 ; Espenlaub and Tonks,