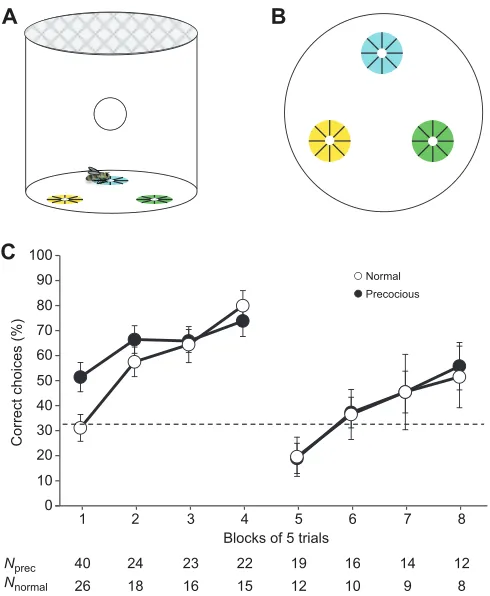
Accelerated behavioural development changes fine scale search behaviour and spatial memory in honey bees (Apis mellifera L )
Full text
Figure


Related documents
This clinical case report describes a case of full mouth rehabilitation of a severely worn out dentition managed by the twin-stage procedure to produce definite esthetic and
Cloud storage is provided storage services, storage services through the network data stored in local storage service provider to provide online storage
ELEKTROCHEMICKÝ PROCES SPRACOVANIA POZLÁTENÝCH KONTAKTOV Z výsledkov hydrometalurgických skúšok získavania zlata z pozlátených kontaktov je zrejmé, že použitie
also says that to lowest order, the component of the magnetic moment along the local magnetic field direc- tion is a constant which we can call m i.. We consider the case shown
They provide specific criteria for diagnoses contained in the "Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines" (CDDG) that have been produced for general clinical
Recovery under section 324A may be the only available means of re- covering from the HCIS vendor whose product causes injury. Compensa- tion for personal injury resulting from
Most of the imaging examples above compared patients with schizophrenia to healthy controls, however a more clinically useful test would be used to determine the diagnosis of a
The information extracted from the selected studies included: study author(s), study sponsors, date of publication, study period, study location, study design, sample size,