The Metabolic Cost of Swimming in Ducks
Full text
Figure


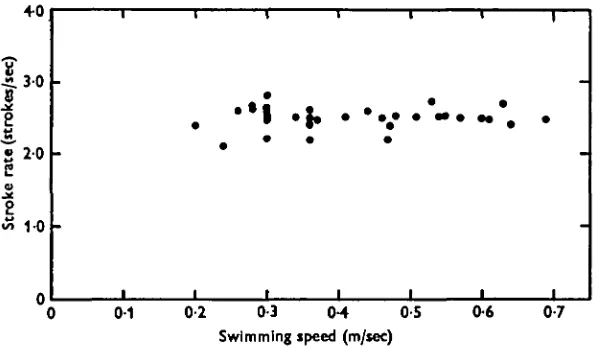
Related documents
For a small subset of these ( Illex illecebrosus , Loligo opalescens and Lolliguncula brevis ), relationships between oxygen consumption and swimming speed allowed extrapolation
Our objectives were: (1) to establish the link between active metabolic rate and maximum swimming speed, (2) to model the controlling effect of temperature on the cost of swimming
To determine the energetic costs of rigid-body, median or paired-fin (MPF) swimming versus undulatory, body- caudal fin (BCF) swimming, we measured oxygen consumption as a function
In the present study, the kinematics and critical swimming speed (maximum aerobically sustainable swimming speed, U crit) of juvenile scalloped hammerhead sharks Sphyrna lewini
Relationship between oxygen consumption rate and swimming speed for Atlantic salmon (mean total length, 58.3cm) ( d ) and Atlantic mackerel (mean total length, 34.7cm) ( m )
By using a new video activity monitoring processor (Kaufmann, 1983) in conjunction with a large respirometer, we have measured swimming activity, oxygen consumption and
The critical swimming speed for the non-loaded control group was 1-73 body length/sec, and fell in groups 1-4 as the magnitude of the extra drag loads increased.. The critical
This experiment was done to determine the effect of swimming deprivation on drinking behaviour, feather pecking behavior, feed consumption, weight gain, feed conversion ratio, live