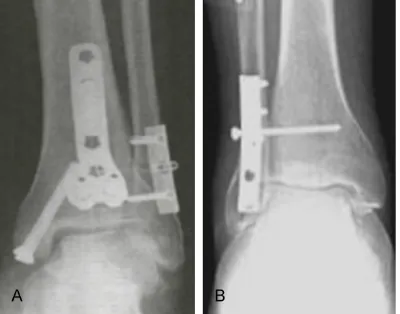
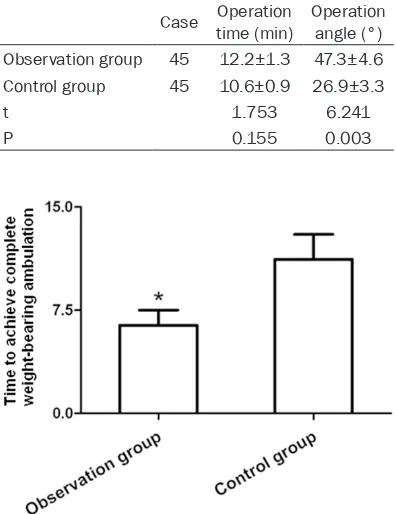
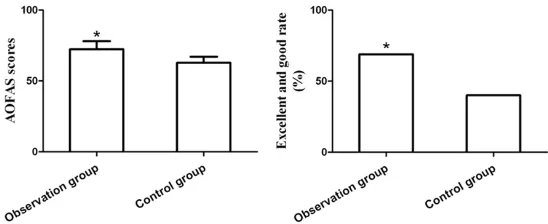
Original Article Surgical effects and prognosis of non-rigid internal fixation for ankle fractures combined with tibiofibular syndesmotic injuries
Full text
Figure
Related documents
In this study, score of a clinical test of physical mobility identified by Timed up and go (TUG) testing also effect of a cognitive task on TUG performance were compared between
The antimalarial therapy recommended for use by the WHO is the Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) in uncomplicated malaria infection, but the tablets
The films were evaluated for various properties such as weight variation, thickness, tensile strength, folding endurance, disintegration time, drug content.. The
In general, we show that price elasticity, total travel demand, costs, service quality, and airline competition play significant roles in the airline’s optimal corporate discount-
Controlling for the risk classification of the insurance company, we find the following aspects of driving behavior to be significantly linked to contract choice and/or a
There was no significant diet effect on digesta retention time, but assimilation efficiency for radiolabeled starch tended to be higher ( P = 0.054) in nestlings raised
Origin of the legal divers fishing at industrial levels spiny lobsters and queen conch in the San Andres Archipelago.. Colombian divers are being asked to have a legal residence in
In this Northern California population of term and late preterm infants, elevated bilirubin levels were not associated with an increased risk of sensorineural hearing loss unless