Studying the History of Ideas Using Topic Models
Full text
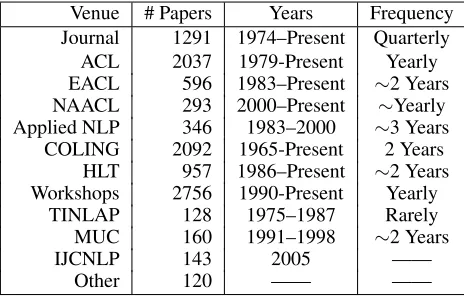
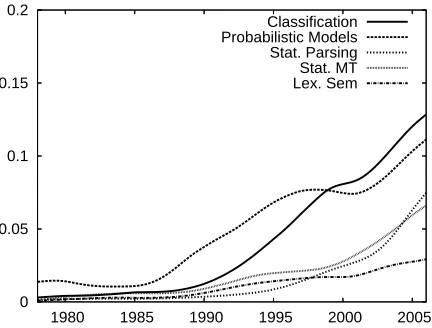
Figure


Related documents
More specifically, LCTM models each topic as a distribution over the latent con- cepts , where each latent concept is a local- ized Gaussian distribution over the word embedding
We propose three models which are suitable for different situations: Model I requires knowledge of the prior distribution over senses and directly maximizes the conditional
This method fits a probability distribution over the data and applies a statistical test to detect anomalous elements.. In the corpus error detec- tion problem,
Topic Models + Word Alignment = A Flexible Framework for Extracting Bilingual Dictionary from Comparable Corpus.. Xiaodong Liu, Kevin Duh and Yuji Matsumoto Graduate School
3 Sub-word n-gram language models Sub-word based search vocabularies and language models can reduce the OOV rate of a speech recognition system by decomposing whole words
In the isAccessible operation of the OrganizeParty attack step, we encounter a proba- bilistic distribution. The success probability of this particular attack step has been defined
Probabilistic generative models provide a general framework for learning representations: a model is specified by a joint probability distribution both over the data and over
User Persona Model (UPM) tries to model each question based on its content sim- ilar to other probabilistic topic models and then use these learned topics to represent


